
a.
Fill the missing values.
a.
Answer to Problem 93SE
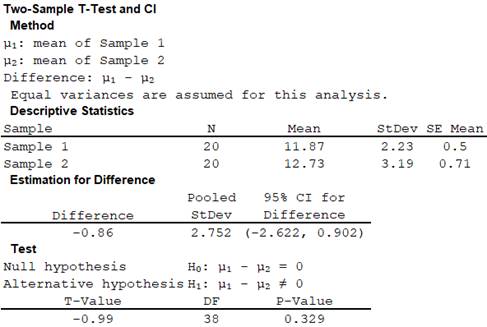
The missing values are as follows,
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
A computer output is provided for two sample T-test.
Calculation:
Test statistic:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step software procedure to obtain the test statistic and P-value using MINITAB software is as follows,
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > 2-Sample t.
- Select Summarized data.
- In Sample 1, enter
Sample size as 20, SampleMean as 11.87 and standard deviation as 2.23. - In Sample 2, enter Sample size as 20, Sample Mean as 12.73 and standard deviation as 3.19.
- Choose Options.
- In Confidence level, enter 95.
- In Alternative, select not equal.
- Select Assume equal variances.
- Click OK in all the dialogue boxes
Thus, the test statistic is –0.99 and the P-value is 0.329.
b.
Check whether it is a two-sided test or one-sided test.
b.
Answer to Problem 93SE
The test is two-sided test.
Explanation of Solution
Justification:
From the MINTAB output in part (a), it is observed that the alternative hypothesis is,
Thus, this is a two-sided test.
c.
Explain the conclusion when
c.
Answer to Problem 93SE
The null hypothesis is not rejected in both the cases.
Explanation of Solution
Justification:
For
Conclusion:
From the MINITAB output in part (a), the P-value 0.329 is greater than the significance level 0.05.
That is,
Hence the null hypothesis is not rejected.
For
Software procedure:
Step-by-step software procedure to obtain the test statistic and P-value using MINITAB software is as follows,
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > 2-Sample t.
- Select Summarized data.
- In Sample 1, enter Sample size as 20, Sample Mean as 11.87 and standard deviation as 2.23.
- In Sample 2, enter Sample size as 20, Sample Mean as 12.73 and standard deviation as 3.19.
- Choose Options.
- In Confidence level, enter 90.
- In Alternative, select not equal.
- Select Assume equal variances.
- Click OK in all the dialogue boxes
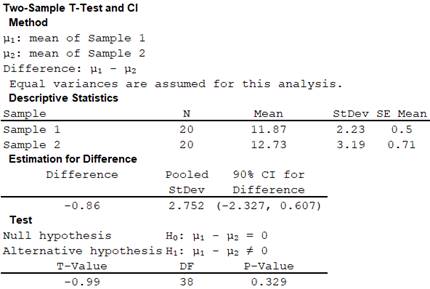
Output using the MINITAB software is as follows,
Conclusion:
Here the P-value 0.329 is greater than the significance level 0.10.
That is,
Hence the null hypothesis is not rejected
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Applied Statistics and Probability for Engineers
- The number of initial public offerings of stock issued in a 10-year period and the total proceeds of these offerings (in millions) are shown in the table. The equation of the regression line is y = 47.109x+18,628.54. Complete parts a and b. 455 679 499 496 378 68 157 58 200 17,942|29,215 43,338 30,221 67,266 67,461 22,066 11,190 30,707| 27,569 Issues, x Proceeds, 421 y (a) Find the coefficient of determination and interpret the result. (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardQuestions An insurance company's cumulative incurred claims for the last 5 accident years are given in the following table: Development Year Accident Year 0 2018 1 2 3 4 245 267 274 289 292 2019 255 276 288 294 2020 265 283 292 2021 263 278 2022 271 It can be assumed that claims are fully run off after 4 years. The premiums received for each year are: Accident Year Premium 2018 306 2019 312 2020 318 2021 326 2022 330 You do not need to make any allowance for inflation. 1. (a) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the basic chain ladder method. (b) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the Bornhuetter-Ferguson method. 2. Comment on the differences in the reserves produced by the methods in Part 1.arrow_forwardUse the accompanying Grade Point Averages data to find 80%,85%, and 99%confidence intervals for the mean GPA. view the Grade Point Averages data. Gender College GPAFemale Arts and Sciences 3.21Male Engineering 3.87Female Health Science 3.85Male Engineering 3.20Female Nursing 3.40Male Engineering 3.01Female Nursing 3.48Female Nursing 3.26Female Arts and Sciences 3.50Male Engineering 3.00Female Arts and Sciences 3.13Female Nursing 3.34Female Nursing 3.67Female Education 3.45Female Engineering 3.17Female Health Science 3.28Female Nursing 3.25Male Engineering 3.72Female Arts and Sciences 2.68Female Nursing 3.40Female Health Science 3.76Female Arts and Sciences 3.72Female Education 3.44Female Arts and Sciences 3.61Female Education 3.29Female Nursing 3.20Female Education 3.80Female Business 3.26Male…arrow_forward
- Business Discussarrow_forwardCould you please answer this question using excel. For 1a) I got 84.75 and for part 1b) I got 85.33 and was wondering if you could check if my answers were correct. Thanksarrow_forwardWhat is one sample T-test? Give an example of business application of this test? What is Two-Sample T-Test. Give an example of business application of this test? .What is paired T-test. Give an example of business application of this test? What is one way ANOVA test. Give an example of business application of this test? 1. One Sample T-Test: Determine whether the average satisfaction rating of customers for a product is significantly different from a hypothetical mean of 75. (Hints: The null can be about maintaining status-quo or no difference; If your alternative hypothesis is non-directional (e.g., μ≠75), you should use the two-tailed p-value from excel file to make a decision about rejecting or not rejecting null. If alternative is directional (e.g., μ < 75), you should use the lower-tailed p-value. For alternative hypothesis μ > 75, you should use the upper-tailed p-value.) H0 = H1= Conclusion: The p value from one sample t-test is _______. Since the two-tailed p-value…arrow_forward
- Using the accompanying Accounting Professionals data to answer the following questions. a. Find and interpret a 90% confidence interval for the mean years of service. b. Find and interpret a 90% confidence interval for the proportion of employees who have a graduate degree. view the Accounting Professionals data. Employee Years of Service Graduate Degree?1 26 Y2 8 N3 10 N4 6 N5 23 N6 5 N7 8 Y8 5 N9 26 N10 14 Y11 10 N12 8 Y13 7 Y14 27 N15 16 Y16 17 N17 21 N18 9 Y19 9 N20 9 N Question content area bottom Part 1 a. A 90% confidence interval for the mean years of service is (Use ascending order. Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardIf, based on a sample size of 900,a political candidate finds that 509people would vote for him in a two-person race, what is the 95%confidence interval for his expected proportion of the vote? Would he be confident of winning based on this poll? Question content area bottom Part 1 A 9595% confidence interval for his expected proportion of the vote is (Use ascending order. Round to four decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardQuestions An insurance company's cumulative incurred claims for the last 5 accident years are given in the following table: Development Year Accident Year 0 2018 1 2 3 4 245 267 274 289 292 2019 255 276 288 294 2020 265 283 292 2021 263 278 2022 271 It can be assumed that claims are fully run off after 4 years. The premiums received for each year are: Accident Year Premium 2018 306 2019 312 2020 318 2021 326 2022 330 You do not need to make any allowance for inflation. 1. (a) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the basic chain ladder method. (b) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the Bornhuetter-Ferguson method. 2. Comment on the differences in the reserves produced by the methods in Part 1.arrow_forward
- A population that is uniformly distributed between a=0and b=10 is given in sample sizes 50( ), 100( ), 250( ), and 500( ). Find the sample mean and the sample standard deviations for the given data. Compare your results to the average of means for a sample of size 10, and use the empirical rules to analyze the sampling error. For each sample, also find the standard error of the mean using formula given below. Standard Error of the Mean =sigma/Root Complete the following table with the results from the sampling experiment. (Round to four decimal places as needed.) Sample Size Average of 8 Sample Means Standard Deviation of 8 Sample Means Standard Error 50 100 250 500arrow_forwardA survey of 250250 young professionals found that two dash thirdstwo-thirds of them use their cell phones primarily for e-mail. Can you conclude statistically that the population proportion who use cell phones primarily for e-mail is less than 0.720.72? Use a 95% confidence interval. Question content area bottom Part 1 The 95% confidence interval is left bracket nothing comma nothing right bracket0.60820.6082, 0.72510.7251. As 0.720.72 is within the limits of the confidence interval, we cannot conclude that the population proportion is less than 0.720.72. (Use ascending order. Round to four decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





