
1.
Calculate the bond issue price.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Bonds: Bonds are long-term promissory notes that are issued by a company while borrowing money from investors to raise fund for financing the operations.
Bonds Payable: Bonds payable are referred to long-term debts of the business, issued to various lenders known as bondholders, generally in multiples of $1,000 per bond, to raise fund for financing the operations.
Present Value: The current value of an amount that is to be paid or received in future is called as present value.
Determine the bond issue price.
Step 1: Calculate the cash interest payment for bonds.
Step 2: Calculate the present value of cash interest payment.
| Particulars | Amount |
| Interest payment (a) | $64,000 |
| PV factor at annual market interest rate of 12% for 5 periods (b) | 3.6048 |
| Present value | $230,707 |
Table (1)
Note: The present value factor for 5periods at 12% interest would be 3.6048 (Refer Appendix A (Table A.2) in the book for present value factor).
Step 3: Calculate the present value of single principal payment of $800,000 (principal amount) at 12% for 5 periods.
| Particulars | Amount |
| Single principal payment (a) | $800,000 |
| PV factor at annual market interest rate of 12% for 5 periods (b) | 0.5674 |
| Present value | $453,920 |
Table (2)
Note: The present value factor for 5periods at 12% interest would be 0.5674 (Refer Appendix A (Table A.1) in the book for present value factor).
Step 4: Calculate the issue price of the bonds.
Hence, the bond issue price on January 1, 2014 is $684,627.
State the reason for using of both the stated rate and effective-interest rate in calculation of issue
Explanation of Solution
Bonds Payable: Bonds payable are referred to long-term debts of the business, issued to various lenders known as bondholders, generally in multiples of $1,000 per bond, to raise fund for financing the operations.
Stated interest rate: It refers to the interest rate that is stated on the face of the bonds.
Market interest rate: It refers to the interest rate that the lenders expect, or demands from the borrower to part with their money as loan to them.
The price of the bond is calculated by adding the present value of the principal amount of bond and present value of the interest payment of the bond. The stated interest rate is used to calculate the cash interest payment of $64,000. The amount is required because it is discounted at the present value of the effective interest rate of the bonds. The effective interest rate is used to discount the principal and cash interest payment. The discounting should be based on the effective-interest rate because the issue price of bond is equal to the present value of principal and cash interest payment.
2.
a.
Calculate the amount of cash payment for bond interest for 2014 through 2018, if company used straight-line amortization method.
2.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Bonds: Bonds are long-term promissory notes that are issued by a company while borrowing money from investors to raise fund for financing the operations.
Bonds Payable: Bonds payable are referred to long-term debts of the business, issued to various lenders known as bondholders, generally in multiples of $1,000 per bond, to raise fund for financing the operations.
Bond discount: It occurs when the bonds are issued at a lower price than the face value.
Straight-line amortization method: It is a method of bond amortization that spreads the amount of the bond discount or bond premium equally over the interest period.
Interest Expense: The cost of debt which is occurred during a particular period of time is called interest expense. The interest amount is payable on the principal amount of debt at a fixed interest rate.
Calculate the amount of cash payment for bond interest for 2014 through 2018.
Hence, cash payment for bond interest for 2014 through 2018 is $64,000.
2.
b.
Calculate the amount of amortization of bond discount or premium for 2014 through 2018, if company used straight-line amortization method.
2.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Bonds: Bonds are long-term promissory notes that are issued by a company while borrowing money from investors to raise fund for financing the operations.
Bonds Payable: Bonds payable are referred to long-term debts of the business, issued to various lenders known as bondholders, generally in multiples of $1,000 per bond, to raise fund for financing the operations.
Bond discount: It occurs when the bonds are issued at a lower price than the face value.
Straight-line amortization method: It is a method of bond amortization that spreads the amount of the bond discount or bond premium equally over the interest period.
Calculate the amount of amortization of bond discount or premium for 2014 through 2018.
Working note:
Calculate the amount of bond discount.
Hence, the amount of amortization of bond discount or premium for 2014 through 2018 is $23,075.
2.
c.
Calculate the amount of bond interest expense for 2014 through 2018, if company used straight-line amortization method.
2.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Bonds: Bonds are long-term promissory notes that are issued by a company while borrowing money from investors to raise fund for financing the operations.
Bonds Payable: Bonds payable are referred to long-term debts of the business, issued to various lenders known as bondholders, generally in multiples of $1,000 per bond, to raise fund for financing the operations.
Bond discount: It occurs when the bonds are issued at a lowerprice than the face value.
Straight-line amortization method: It is a method of bond amortization that spreads the amount of the bond discount or bond premium equally over the interest period.
Interest Expense: The cost of debt which is occurred during a particular period of time is called interest expense. The interest amount is payable on the principal amount of debt at a fixed interest rate.
Calculate the amount of bond interest expense for 2014 through 2018.
Hence, the amount of bond interest expense for 2014 through 2018 is $87,075.
3.
Prepare an effective –interest bond amortization schedule.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Bonds: Bonds are long-term promissory notes that are issued by a company while borrowing money from investors to raise fund for financing the operations.
Bonds Payable: Bonds payable are referred to long-term debts of the business, issued to various lenders known as bondholders, generally in multiples of $1,000 per bond, to raise fund for financing the operations.
Bond discount: It occurs when the bonds are issued at a lower price than the face value.
Effective-interest method of amortization: It is an amortization model that apportions the amount of bond discount or premium based on the market interest rate.
Amortization Schedule: An amortization schedule is a table that shows the details of each loan payment allocated between the principal amount and the overdue interest along with the beginning and ending balance of the loan. From the amortization schedule of the loan, the periodical interest expense, total interest expense and total payment made are known.
Prepare an effective –interest bond amortization schedule.
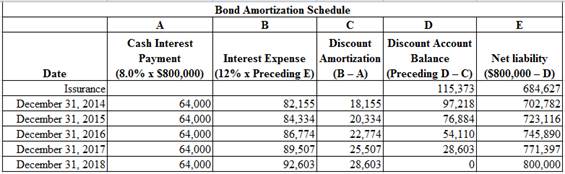
Figure (1)
Explain about a constant interest rate when interest expense is related to the net liability.
Explanation of Solution
Bonds Payable: Bonds payable are referred to long-term debts of the business, issued to various lenders known as bondholders, generally in multiples of $1,000 per bond, to raise fund for financing the operations.
Market interest rate: It refers to the interest rate that the lenders expect, or demands from the borrower to part with their money as loan to them.
Interest Expense: The cost of debt which is occurred during a particular period of time is called interest expense. The interest amount is payable on the principal amount of debt at a fixed interest rate.
A contract interest rate for each year can be demonstrated by dividing the interest expense by preceding year net liability. The constant interest rate for all the year would be 12% (equal to effective-interest rate).
4.
Explain the method that the company should use to amortize the bond discount.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Effective-interest amortization method: Effective-interest amortization method it is an amortization model that apportions the amount of bond discount or premium based on the market interest rate.
Straight-line amortization method: It is a method of bond amortization that spreads the amount of the bond discount or bond premium equally over the interest period.
The company should prefer the effective-interest amortization method instead of straight-line method to amortize the bonds because effective-interest method well measures the interest expense (to report on income statement) and the net liability (to report on the
The straight-line method should be used only when the results of straight-line method are not significantly different from the results of the effective-interest method.
Explain whether a financial analyst would prefer the straight-line or effective-interest method of amortization.
Explanation of Solution
Effective-interest amortization method: Effective-interest amortization method it is an amortization model that apportions the amount of bond discount or premium based on the market interest rate.
Straight-line amortization method: It is a method of bond amortization that spreads the amount of the bond discount or bond premium equally over the interest period.
The financial results produce by both the methods are typically similar. Hence, due to simple computation and materiality concept, a financial analyst of a company practically would prefer straight-line amortization method.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Financial Accounting, 8th Edition
- Provide correct optionarrow_forwardA machine has a cost of $18,500, an estimated residual value of $4,500, and an estimated useful life of five years. The machine is being depreciated on a straight-line basis. At the end of the second year, what amount will be reported for accumulated depreciation? Need helparrow_forwardOn December 31, 2014, Santiago's common stock sold for $34 per share, and dividends per share were 0.60. Compute Santiago's dividend yield during 2014. A. 1.8% B. 3.6% C. 1.4% D. 6%arrow_forward
- What is the correct option? For general accounting question give me step by step explanationarrow_forwardThurman Industries expects to incur overhead costs of $18,000 per month and direct production costs of $155 per unit. The estimated production activity for the upcoming year is 1,800 units. If the company desires to earn a gross profit of $72 per unit, the sales price per unit would be which of the following amounts? A. $327 B. $240 C. $273 D. $347 helparrow_forwardAccounting answerarrow_forward
- A machine has a cost of $18,500, an estimated residual value of $4,500, and an estimated useful life of five years. The machine is being depreciated on a straight-line basis. At the end of the second year, what amount will be reported for accumulated depreciation?arrow_forwardWhat will be it's net operating incomearrow_forwardNonearrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





