
To answer:
The questions based on the given situations
Concept Introduction:
Marginal utility: This is the additional benefit or satisfaction derived from the consumption of an additional unit of a commodity or service.
Utility: This is the benefit or satisfaction derived from the consumption of a good or service
Explanation of Solution
- Cal’s consumption bundle consists of the following
- The available consumption bundle for Cal is the following. These bundles lies on the budget line of Cal’s
- Cal’s consumption of Nikes increases from 1 to 2 as the price of Nikes falls. This is because of two effects, the substitution effect and income effect. The substitution effect says that as the price of Nikes falls, their
opportunity cost falls so Cal now has to give up fewer pairs of sunglasses for 1 Nike. This makes Nikes more attractive, and Cal substitutes Nikes in place of sunglasses. The income effect says that as Nikes become cheaper, Cal gets richer in a real sense; he can now buy more goods. Since Nikes are a normal good, when thepurchasing power of Cal’s income rises, he consumes more Nikes. Both effects contribute to the fact that as the price of Nikes falls, Cal’s consumption of Nikes increases.
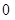 Nikes,
Nikes, 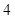 sunglasses
sunglasses
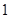 Nike,
Nike, 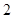 sunglasses
sunglasses
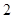 Nike,
Nike, 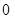 sunglasses
sunglasses
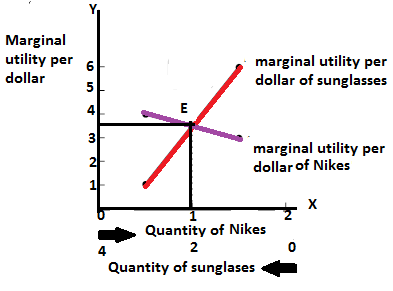
The above diagram shows the marginal utilities per dollar of Nikes and Sunglasses, the intersection between these points shows the optimal choice for Cal, the optimal point is denoted by the capital letter ‘E’. The quantity of Nikes is measured from left to right and the quantity of sunglasses measured from right to left on the horizontal axis. In the vertical axis the marginal utilities per dollar of both Nikes and Sunglasses are measured. Of the entire possible consumption bundle Cal could consume bundle that contains 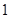 Nike and
Nike and 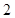 sunglasses. It is considered as the optimal consumption bundle, in this bundle the marginal utility per dollar spent on Nikes and marginal utility per dollar spent on Sunglasses are equal so it is the optimum consumption bundle.
sunglasses. It is considered as the optimal consumption bundle, in this bundle the marginal utility per dollar spent on Nikes and marginal utility per dollar spent on Sunglasses are equal so it is the optimum consumption bundle.
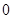 Nikes,
Nikes, 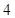 sunglasses
sunglasses
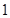 Nikes,
Nikes, 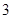 sunglasses
sunglasses
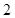 Nikes,
Nikes, 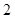 sunglasses
sunglasses
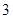 Nikes,
Nikes, 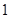 sunglasses
sunglasses
`4 Nikes, 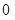 sunglasses
sunglasses
| Quantity of Nikes | Utility from Nikes | Marginal utility of Nikes | Marginal utility per dollar | Quantity of sunglasses | Utility of sunglasses | Marginal utility of sunglasses | Marginal utility per dollar |
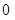 |
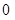 |
- | - | 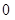 |
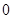 |
- | - |
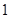 |
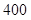 |
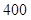 |
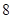 |
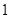 |
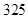 |
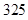 |
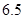 |
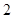 |
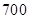 |
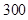 |
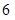 |
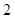 |
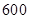 |
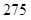 |
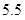 |
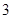 |
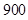 |
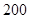 |
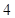 |
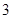 |
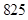 |
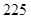 |
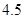 |
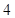 |
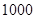 |
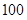 |
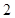 |
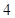 |
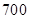 |
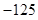 |
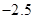 |
The above table shows the marginal utility of both Nikes and Sunglasses and the marginal utilities per dollar of Nikes and sunglasses.
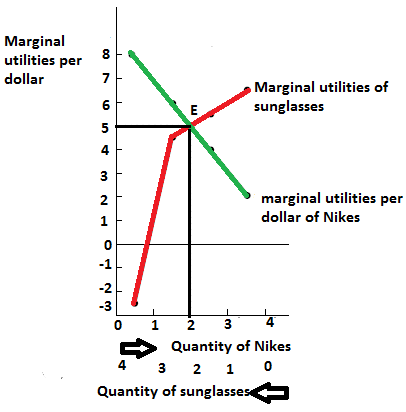
The above graph shows the marginal utilities per dollar spent on Nikes and Sunglasses, the intersection between these 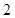 so it is considered as the optimal choice for him.
so it is considered as the optimal choice for him.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- a-c pleasearrow_forwardd-farrow_forwardPART II: Multipart Problems wood or solem of triflussd aidi 1. Assume that a society has a polluting industry comprising two firms, where the industry-level marginal abatement cost curve is given by: MAC = 24 - ()E and the marginal damage function is given by: MDF = 2E. What is the efficient level of emissions? b. What constant per-unit emissions tax could achieve the efficient emissions level? points) c. What is the net benefit to society of moving from the unregulated emissions level to the efficient level? In response to industry complaints about the costs of the tax, a cap-and-trade program is proposed. The marginal abatement cost curves for the two firms are given by: MAC=24-E and MAC2 = 24-2E2. d. How could a cap-and-trade program that achieves the same level of emissions as the tax be designed to reduce the costs of regulation to the two firms?arrow_forward
- Only #4 please, Use a graph please if needed to help provearrow_forwarda-carrow_forwardFor these questions, you must state "true," "false," or "uncertain" and argue your case (roughly 3 to 5 sentences). When appropriate, the use of graphs will make for stronger answers. Credit will depend entirely on the quality of your explanation. 1. If the industry facing regulation for its pollutant emissions has a lot of political capital, direct regulatory intervention will be more viable than an emissions tax to address this market failure. 2. A stated-preference method will provide a measure of the value of Komodo dragons that is more accurate than the value estimated through application of the travel cost model to visitation data for Komodo National Park in Indonesia. 3. A correlation between community demographics and the present location of polluting facilities is sufficient to claim a violation of distributive justice. olsvrc Q 4. When the damages from pollution are uncertain, a price-based mechanism is best equipped to manage the costs of the regulator's imperfect…arrow_forward
- For environmental economics, question number 2 only please-- thank you!arrow_forwardFor these questions, you must state "true," "false," or "uncertain" and argue your case (roughly 3 to 5 sentences). When appropriate, the use of graphs will make for stronger answers. Credit will depend entirely on the quality of your explanation. 1. If the industry facing regulation for its pollutant emissions has a lot of political capital, direct regulatory intervention will be more viable than an emissions tax to address this market failure. cullog iba linevoz ve bubivorearrow_forwardExercise 3 The production function of a firm is described by the following equation Q=10,000-3L2 where L stands for the units of labour. a) Draw a graph for this equation. Use the quantity produced in the y-axis, and the units of labour in the x-axis. b) What is the maximum production level? c) How many units of labour are needed at that point? d) Provide one reference with you answer.arrow_forward
- Exercise 1 Consider the market supply curve which passes through the intercept and from which the market equilibrium data is known, this is, the price and quantity of equilibrium PE=50 and QE=2000. Considering those two points, find the equation of the supply. Draw a graph of this line. Provide one reference with your answer. Exercise 2 Considering the previous supply line, determine if the following demand function corresponds to the market demand equilibrium stated above. QD=3000-2p.arrow_forwardConsider the market supply curve which passes through the intercept and from which the marketequilibrium data is known, this is, the price and quantity of equilibrium PE=50 and QE=2000.a. Considering those two points, find the equation of the supply. b. Draw a graph of this line.arrow_forwardGovernment Purchases and Tax Revenues A B GDP T₂ Refer to the diagram. Discretionary fiscal policy designed to slow the economy is illustrated by Multiple Choice the shift of curve T₁ to T2. a movement from d to balong curve T₁.arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





