
Concept introduction:
Budget line:
This is defined as the combination of all goods that a consumer can purchase exhausting all his income. Formula for the budget line is:
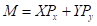
Here,
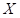 is the quantity of good X.
is the quantity of good X.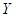 is the quantity of good Y.
is the quantity of good Y.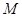 is the total income.
is the total income.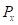 is the
is the price of good X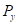 is the price of good Y.
is the price of good Y.
It is defined as the change in the total utility due to a change in an additional unit of a good. It may be diminishing, increasing, or constant.
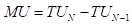 Or
Or
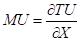
Here,
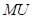 is the marginal utility.
is the marginal utility.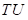 is the total utility.
is the total utility.- X is the quantity of any good.
Maximizing utility Principle:
Maximizing utility in the case of two goods state that the equilibrium level of consumption of the two goods for a consumer is achieved when the Marginal Utility per dollar of the two goods are equal, provided the marginal utility of money is constant. This means that the following conditions must be fulfilled:
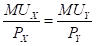
Here,
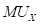 is the marginal utility of good X.
is the marginal utility of good X.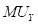 is the marginal utility of good Y.
is the marginal utility of good Y.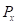 is the price of good X.
is the price of good X.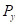 is the price of good Y.
is the price of good Y.
Substitution effects:
In this case, the
Income effects:
It states that the demand for normal goods and the income are directly related which means that when income increases, the demand for normal goods also increases and vice versa.
Explanation of Solution
a. Mr. Cal’s budget line and optimal bundle Case I.
The total money with Cal is 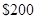 the cost of a cell phone is
the cost of a cell phone is 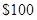 the cost of a pair of sun glasses is
the cost of a pair of sun glasses is 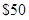 Mr. Cal’s budget line is given as:
Mr. Cal’s budget line is given as:
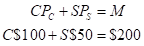
Here,
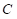 is the cell phone.
is the cell phone.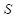 is the sun glasses.
is the sun glasses.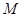 is the total income.
is the total income.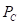 is the price of good
is the price of good 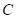 .
.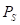 is the price of good
is the price of good 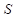
From the above formula, the consumption bundle is calculated as follows:
| Consumption bundle | Quantity of cell phones | Quantity of sun glasses |
| A | 0 | 4 |
| B | 1 | 2 |
| C | 2 | 0 |
Table(1)
| Quantity of cell phones | Total Utility | Marginal Utility | Marginal Utility per dollar |
| 0 | 0 | - | - |
| 1 | 400 | 400 | 4 |
| 2 | 700 | 300 | 3 |
Table(2)
| Quantity of sun glasses | Total Utility (utils) | Marginal Utility (utils) | Marginal Utility per dollar |
| 0 | 0 | - | - |
| 2 | 600 | 300 | 6 |
| 4 | 700 | 50 | 1 |
Table(3)
By the optimal consumption rule, Mr. Cal should consume bundles where,
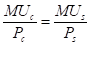
Here,
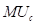 is the marginal utility of good
is the marginal utility of good 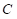
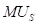 is the marginal utility of good
is the marginal utility of good 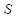
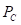 is the price of good
is the price of good 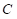
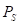 is the price of good
is the price of good 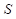
From Table 2 and 3, the above condition is satisfied at (1, 2). Hence, the optimal consumption bundle is 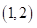
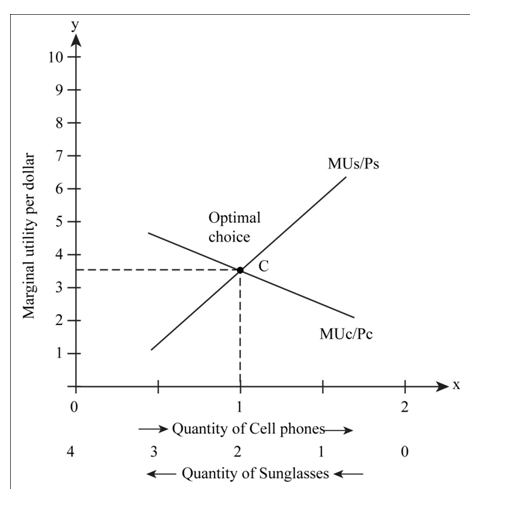
Fig 1
- In the above figure, the x-axis represents the quantity of sun glasses and cell phones from right to left and from left to right respectively.
- The Y-axis represents marginal utility per dollar.
- As shown in Fig 1, the marginal per dollar of cell phone and sun glasses are equal at the consumption bundle
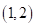
Conclusion:
The bundles that lie on the budget line are 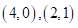
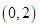 and the optimal bundle is
and the optimal bundle is 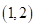 that is one pair of sun glasses and 2 cell phones.
that is one pair of sun glasses and 2 cell phones.
Concept introduction:
Budget line:
This is defined as the combination of all goods that a consumer can purchase exhausting all his income. Formula for the budget line is:
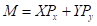
Here,
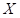 is the quantity of good X.
is the quantity of good X.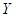 is the quantity of good Y.
is the quantity of good Y.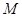 is the total income.
is the total income.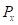 is the price of good X
is the price of good X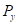 is the price of good Y.
is the price of good Y.
Marginal Utility:
It is defined as the change in the total utility due to a change in an additional unit of a good. It may be diminishing, increasing, or constant.
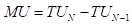 Or
Or
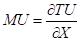
Here,
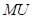 is the marginal utility.
is the marginal utility.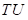 is the total utility.
is the total utility.- X is the quantity of any good.
Maximizing utility Principle:
Maximizing utility in the case of two goods state that the equilibrium level of consumption of the two goods for a consumer is achieved when the Marginal Utility per dollar of the two goods are equal, provided the marginal utility of money is constant. This means that the following conditions must be fulfilled:
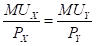
Here,
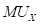 is the marginal utility of good X.
is the marginal utility of good X.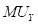 is the marginal utility of good Y.
is the marginal utility of good Y.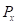 is the price of good X.
is the price of good X.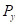 is the price of good Y.
is the price of good Y.
Substitution effects:
In this case, the demand of a good increases if the price of its substitute goods increase and the demand of a good decreases if the price of its substitute goods decrease. Take an example of tea and coffee, if the prices of tea increase, then the demand for coffee will increase.
Income effects:
It states that the demand for normal goods and the income are directly related which means that when income increases, the demand for normal goods also increases and vice versa.
Explanation of Solution
b. Mr. Cal’s budget line and optimal bundle Case II.
The total money with Cal is 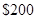 the cost of a cell phone is
the cost of a cell phone is 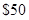 the cost of a pair of sun glasses is
the cost of a pair of sun glasses is 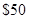 Mr. Cal’s budget line is given as follows:
Mr. Cal’s budget line is given as follows:
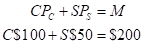
Using the above formula, the consumption bundles of Mr. Cal are:
| Interpretation: | Consumption bundle | Quantity of cell phones | Quantity of sun glasses |
| A | 0 | 4 | |
| B | 1 | 3 | |
| C | 2 | 2 | |
| D | 3 | 1 | |
| E | 4 | 0 |
Table(4)
| Quantity of cell phones | Total Utility (utils) | Marginal Utility (utils) | Marginal Utility per dollar |
| 0 | 0 | - | - |
| 1 | 400 | 400 | 8 |
| 2 | 700 | 300 | 6 |
| 3 | 900 | 200 | 4 |
| 4 | 1000 | 100 | 2 |
Table(5)
| Quantity of sun glasses | Total Utility (utils) | Marginal Utility (utils) | Marginal Utility per dollar |
| 0 | 0 | - | - |
| 1 | 325 | 325 | 6.5 |
| 2 | 600 | 275 | 5.5 |
| 3 | 825 | 225 | 4.5 |
| 4 | 700 | 125 | -2.5 |
Table(6)
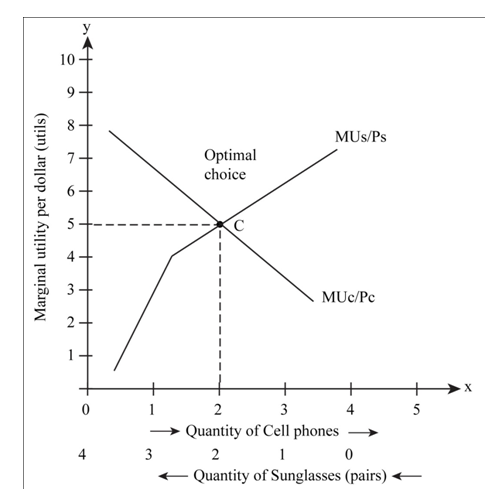
Fig 2
- In the above figure, the x-axis represents the quantity of sun glasses and cell phones from right to left and from left to right respectively.
- The Y-axis represents the marginal utility per dollar.
- The optimum bundle is at the intersection level, which is (2,2).
Conclusion:
Thus, the optimum bundle is (2,2).
Concept introduction:
Budget line:
This is defined as the combination of all goods that a consumer can purchase exhausting all his income. Formula for the budget line is:
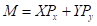
Here,
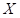 is the quantity of good X.
is the quantity of good X.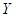 is the quantity of good Y.
is the quantity of good Y.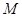 is the total income.
is the total income.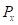 is the price of good X
is the price of good X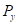 is the price of good Y.
is the price of good Y.
Marginal Utility:
It is defined as the change in the total utility due to a change in an additional unit of a good. It may be diminishing, increasing, or constant.
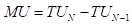 Or
Or
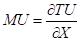
Here,
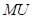 is the marginal utility.
is the marginal utility.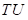 is the total utility.
is the total utility.- X is the quantity of any good.
Maximizing utility Principle:
Maximizing utility in the case of two goods state that the equilibrium level of consumption of the two goods for a consumer is achieved when the Marginal Utility per dollar of the two goods are equal, provided the marginal utility of money is constant. This means that the following conditions must be fulfilled:
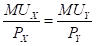
Here,
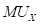 is the marginal utility of good X.
is the marginal utility of good X.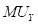 is the marginal utility of good Y.
is the marginal utility of good Y.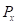 is the price of good X.
is the price of good X.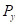 is the price of good Y.
is the price of good Y.
Substitution effects:
In this case, the demand of a good increases if the price of its substitute goods increase and the demand of a good decreases if the price of its substitute goods decrease. Take an example of tea and coffee, if the prices of tea increase, then the demand for coffee will increase.
Income effects:
It states that the demand for normal goods and the income are directly related which means that when income increases, the demand for normal goods also increases and vice versa.
Explanation of Solution
c. Income and substitution effects of a price change.
- Due to a change in the price of a cell phone from $100 to $50, the consumption changed from 1 to 2. It is due to the total price effect which has two parts one is substitution effect and other is income effect.
- Due to the substitution effect, Mr. Cal has an additional cell phone by sacrificing a less number of sunglasses. This has happened due to the
law of demand . - Due to the income effect, Mr. Cal has more money with him to buy more cell phones and less sun glasses.
Conclusion:
The consumption of the cell phone has increased due to a fall in its prices, due to the substitution and income effect.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Economics
- Critically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forwardCritically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forwardOutline the nine (9) consumer rights as specified in the Consumer Rights Act in South Africa.arrow_forward
- In what ways could you show the attractiveness of Philippines in the form of videos/campaigns to foreign investors? Cite 10 examples.arrow_forwardExplain the following terms and provide an example for each term: • Corruption • Fraud • Briberyarrow_forwardIn what ways could you show the attractiveness of a country in the form of videos/campaigns?arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





