
1.
Prepare a payroll register for Incorporation F for the week ended December 9, 20Y8.
1.
Answer to Problem 4PB
Prepare a payroll register for Incorporation F for the week ended December 9, 20Y8.
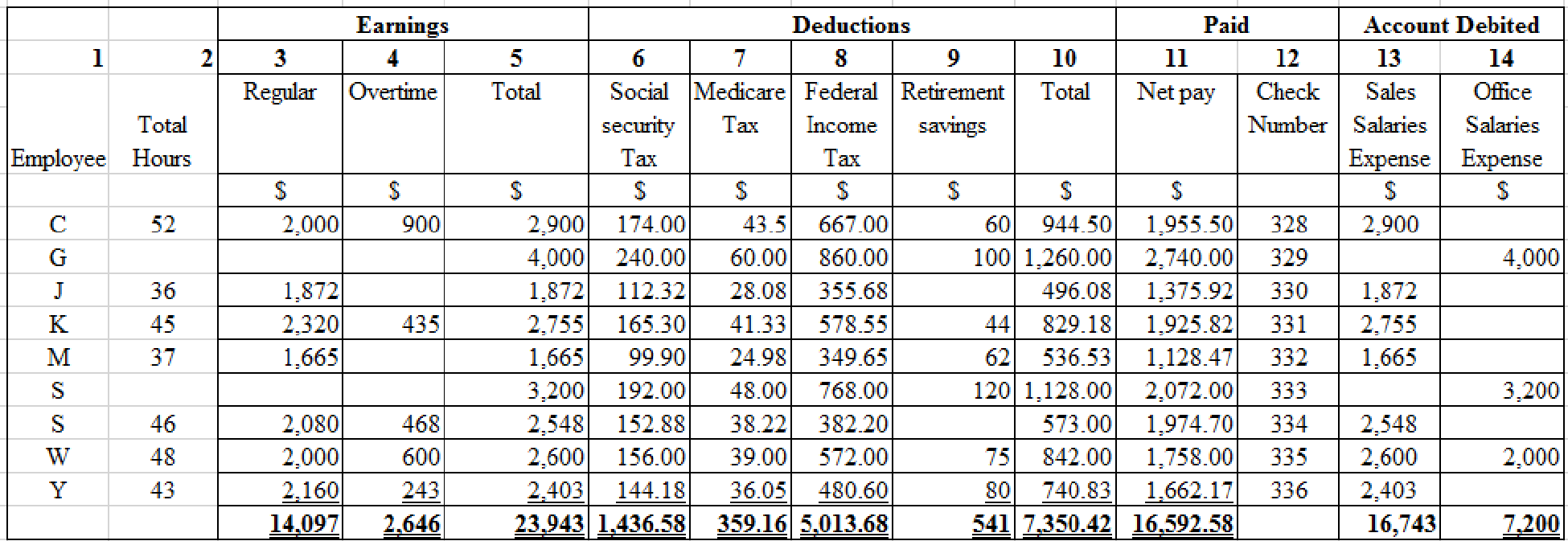
Table (1)
Explanation of Solution
Payroll: The total payment that a company is required to pay to its employee for the services received is called as payroll.
Payroll withholding deduction: The amounts which the employer withheld from employees’ gross pay to deduct taxes such as federal income tax, state income tax, local income tax, and social security tax are called payroll withholding deduction.
Payroll register: A schedule which is maintained by the company to record the earnings, earnings withholdings, and net pay of each employee is referred to as payroll register.
Working notes:
Calculate regular pay for C.
Regular pay = 40 hours ×$50 per hour=$2,000
Calculate overtime pay for C.
Overtime pay = (52 hours – 40 hours)×($50×1.5)= 12 hours×$75 per hour= $900
Calculate regular pay for J.
Regular pay = 36 hours ×$52 per hour=$1,872
Calculate regular pay for K.
Regular pay = 40 hours ×$58 per hour=$2,320
Calculate overtime pay for K.
Overtime pay = (45 hours – 40 hours)×($58×1.5)= 5 hours×$87 per hour= $435
Calculate regular pay for M.
Regular pay = 37 hours ×$45 per hour=$1,665
Calculate regular pay for S.
Regular pay = 40 hours ×$52 per hour=$2,080
Calculate overtime pay for S.
Overtime pay = (46 hours – 40 hours)×($52×1.5)= 6 hours×$78 per hour= $468
Calculate regular pay for W.
Regular pay = 40 hours ×$50 per hour=$2,000
Calculate overtime pay for W.
Overtime pay = (48 hours – 40 hours)×($50×1.5)= 8 hours×$75 per hour= $600
Calculate regular pay for Y.
Regular pay = 40 hours ×$54 per hour=$2,160
Calculate overtime pay for Y.
Overtime pay = (43 hours – 40 hours)×($54×1.5)= 3 hours×81 per hour= $243
Notes:
- • For calculating the value of total earnings (column 5), add the amounts of column 3, and column 4 of respective employee as given below:
Total earnings = (Regular pay + Overtime pay)
- • For calculating social security tax (column 6), multiply total earnings (column 5) by 6% of respective employee as given below:
Social security tax = 6% ×Total earnings
- • For calculating Medicare tax (column 7), multiply total earnings (column 5) by 1.5% of respective employee as given below:
Medicare tax = 1.5% ×Total earnings
- • For calculating the value of total deductions (column 10), add the amounts of column 6, column 7, column 8, and column 9 of respective employee as given below:
Total deductions = (Social security tax + Medicare tax + Federal income tax + Retirement savings)
- • For calculating the value of net pay(column 11), subtract total deductions (column 10) from total earnings (column 5) as given below:
Net pay = Total earnings – Total deductions
- • Sales salaries expense or office salaries expense (Column 13 or Column 14) = Total earnings (Column 5)
2.
Journalize the entry to record payroll for the week.
2.
Answer to Problem 4PB
Prepare
| Date | Accounts and Explanation | Post Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| Sales Salaries Expense | 16,743 | ||||||
| Office Salaries Expense | 7,200 | ||||||
| Social Security Taxes Payable | 1,436.58 | ||||||
| Medicare Taxes Payable | 359.16 | ||||||
| Federal Income Taxes Payable | 5,013.68 | ||||||
| Retirement Savings Deductions Payable | 541.00 | ||||||
| Salaries payable | 16.592.58 | ||||||
| (To record salaries expense and payroll deductions) | |||||||
Table (2)
Explanation of Solution
- ■ Sales salaries expense is an expense and it decreases the equity value. So, debit it by $16,743.
- ■ Office salaries expense is an expense and it decreases the equity value. So, debit it by $7,200.
- ■ Social Security taxes payable is a liability and it is increased. So, credit it by $359.16.
- ■ Medicare taxes payable is a liability and it is increased. So, credit it by $359.16.
- ■ Federal Income taxes payable is a liability and it is increased. So, credit it by $5,013.68.
- ■ Retirement savings deductions payable is a liability and it is increased. So, credit it by $541.00.
- ■ Salaries payable is a liability and it is increased. So, credit it by $16.592.58.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Financial and Managerial Accounting
- RK Co. sells snowboards. Each snowboard requires direct materials for $140, direct labor for $55, and variable overhead of $64. The company expects fixed overhead costs of $673,000 and fixed selling and administrative costs of $160,000 for the next year. It expects to produce and sell 11,900 snowboards in the next year. What will be the selling price per unit if RK uses a mark-up of 17% of the total cost? Answerarrow_forward5 PTSarrow_forwardHii teacher please provide for General accounting question answer do fastarrow_forward
- Accurate Answerarrow_forwardVanessa Enterprises reported pretax book income of $620,800. Included in the computation were favorable temporary differences of $15,500, unfavorable temporary differences of $88,200, and unfavorable permanent differences of $72,400. Assuming a tax rate of 35%, the Corporation's current income tax expense or benefit would be_. a. $225,304 b. $224,000 c. $221,000 d. $217,280arrow_forwardPlease don't answer if u don't know answer .arrow_forward
 Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning





