
(a)
To calculate:
The implied one-year forward rates when yield to maturity for
Introduction:
The implied forward rate is the rate which helps in determining the movements of the interest rate.
The yield to maturity is the rate which provides the amount of expected return on a bond held till its maturity.
Answer to Problem 40PS
The implied one-year forward rate for
Given:
The yield to maturity for
Explanation:
The formula for computing forward rate as follows:
For computing forward rate of zero-coupon bond with
For computing forward rate of zero-coupon bond with
Thus, the implied one-year forward rate for
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The yield to maturity for
The formula for computing forward rate as follows:
For computing forward rate of zero-coupon bond with
For computing forward rate of zero-coupon bond with
Thus, the implied one-year forward rate for
(b)
To calculate:
The yield to maturity of a zero-coupon bond having maturity of one year for the next year i.e.
Introduction:
The implied forward rate is the rate which helps in determining the movements of the interest rate.
The yield to maturity is the rate which provides the amount of expected return on a bond held till its maturity.
Answer to Problem 40PS
The yield to maturity of zero-coupon bond for
Explanation:
The formula for computing yield to maturity as follows:
Here,
PV is Current price of the bond
FV is Face value of the bond
For computing Price of the bond
For computing yield to maturity:
Using function in excel, effective yield is calculated.
Enter the data as shown below:
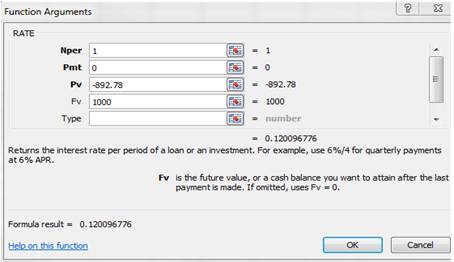
Thus, the yield to maturity of zero-coupon bond for
Explanation of Solution
The formula for computing yield to maturity as follows:
Here,
PV is Current price of the bond
FV is Face value of the bond
For computing Price of the bond
For computing yield to maturity:
Using function in excel, effective yield is calculated.
Enter the data as shown below:

Thus, the yield to maturity of zero-coupon bond for
(c)
To calculate:
The yield to maturity of a zero-coupon bond having maturity of two year for the next year i.e.
Introduction:
The implied forward rate is the rate which helps in determining the movements of the interest rate.
The yield to maturity is the rate which provides the amount of expected return on a bond held till its maturity.
Answer to Problem 40PS
The yield to maturity of zero-coupon bond for
Explanation:
The formula for computing yield to maturity as follows:
Here,
PV is Current price of the bond
FV is Face value of the bond
For computing Price of the bond
For computing yield to maturity:
Using function in excel, effective yield is calculated.
Enter the data as shown below:
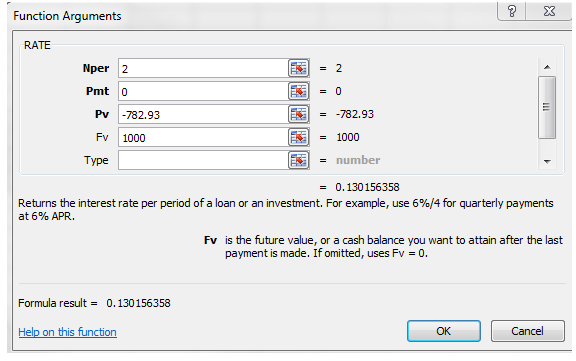
Thus, the yield to maturity of zero-coupon bond for
Explanation of Solution
The formula for computing yield to maturity as follows:
Here,
PV is Current price of the bond
FV is Face value of the bond
For computing Price of the bond
For computing yield to maturity:
Using function in excel, effective yield is calculated.
Enter the data as shown below:

Thus, the yield to maturity of zero-coupon bond for
(d)
To calculate:
The expected total
Introduction:
The expected rate of return is used to determine the total expected return on the bond for the holding period.
The yield to maturity is the rate which provides the amount of expected return on a bond held till its maturity.
Answer to Problem 40PS
The expected rate of return for two year bond is
Explanation:
The formula for computing price of the bond as follows:
For computing price of the bond with
For computing price of the bond with
Price at which the bond will sell in the next year:
The expected rate of return for two-year bond is as follows:
Thus, the expected rate of return for two-year bond is
Explanation of Solution
The formula for computing price of the bond as follows:
For computing price of the bond with
For computing price of the bond with
Price at which the bond will sell in the next year:
The expected rate of return for two-year bond is as follows:
Thus, the expected rate of return for two-year bond is
(e)
To calculate:
The expected total rate of return over the next year when purchase of a three-year zero-coupon bond on current day.
Introduction:
The expected rate of return is used to determine the total expected return on the bond for the holding period.
The yield to maturity is the rate which provides the amount of expected return on a bond held till its maturity.
Answer to Problem 40PS
The expected rate of return for three-year bond is
Explanation:
The formula for computing price of the bond as follows:
For computing price of the bond with
Price at which the bond will sell in the next year:
The expected rate of return for two-year bond is as follows:
Thus, the expected rate of return for three-year bond is
Explanation of Solution
The formula for computing price of the bond as follows:
For computing price of the bond with
Price at which the bond will sell in the next year:
The expected rate of return for two-year bond is as follows:
Thus, the expected rate of return for three-year bond is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
ESSENTIALS OF INVESTMENTS - CONNECT ACCE
- 7. What is a par value of a bond?* The amount borrowed by the issuer of the bond and returned to the investors when the bond matures The overall return earned by the bond investor when the bond matures The difference between the amount borrowed by the issuer of bond and the amount returned to investors at maturity The size of the coupon investors receive on an annual basisarrow_forwardWhat is an annuity?* An investment that has no definite end and a stream of cash payments that continues forever A stream of cash flows that start one year from today and continue while growing by a constant growth rate A series of equal payments at equal time periods and guaranteed for a fixed number of years A series of unequal payments at equal time periods which are guaranteed for a fixed number of yearsarrow_forwardIf you were able to earn interest at 3% and you started with $100, how much would you have after 3 years?* $91.51 $109.27 $291.26 $103.00arrow_forward
- A proxy is an authorization that doesn’t allows one shareholder to vote on behalf of another shareholder. TRUE OR FALSEarrow_forwardNon-Investment-grade bonds are rated at least BBB by Standard and Poor’s. TRUE OR FALSEarrow_forwardNon-Investment-grade bonds are rated at least BBB by Standard and Poor’s. TRUE OR FALSEarrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





