
(a)
To calculate:
The implied one-year forward rates when yield to maturity for
Introduction:
The implied forward rate is the rate which helps in determining the movements of the interest rate.
The yield to maturity is the rate which provides the amount of expected return on a bond held till its maturity.
Answer to Problem 40PS
The implied one-year forward rate for
Given:
The yield to maturity for
Explanation:
The formula for computing forward rate as follows:
For computing forward rate of zero-coupon bond with
For computing forward rate of zero-coupon bond with
Thus, the implied one-year forward rate for
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The yield to maturity for
The formula for computing forward rate as follows:
For computing forward rate of zero-coupon bond with
For computing forward rate of zero-coupon bond with
Thus, the implied one-year forward rate for
(b)
To calculate:
The yield to maturity of a zero-coupon bond having maturity of one year for the next year i.e.
Introduction:
The implied forward rate is the rate which helps in determining the movements of the interest rate.
The yield to maturity is the rate which provides the amount of expected return on a bond held till its maturity.
Answer to Problem 40PS
The yield to maturity of zero-coupon bond for
Explanation:
The formula for computing yield to maturity as follows:
Here,
PV is Current price of the bond
FV is Face value of the bond
For computing Price of the bond
For computing yield to maturity:
Using function in excel, effective yield is calculated.
Enter the data as shown below:
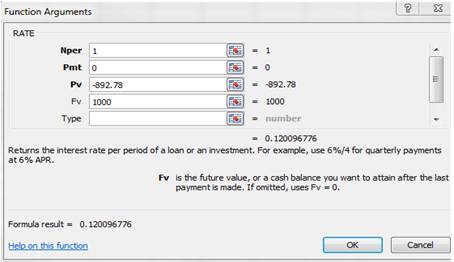
Thus, the yield to maturity of zero-coupon bond for
Explanation of Solution
The formula for computing yield to maturity as follows:
Here,
PV is Current price of the bond
FV is Face value of the bond
For computing Price of the bond
For computing yield to maturity:
Using function in excel, effective yield is calculated.
Enter the data as shown below:

Thus, the yield to maturity of zero-coupon bond for
(c)
To calculate:
The yield to maturity of a zero-coupon bond having maturity of two year for the next year i.e.
Introduction:
The implied forward rate is the rate which helps in determining the movements of the interest rate.
The yield to maturity is the rate which provides the amount of expected return on a bond held till its maturity.
Answer to Problem 40PS
The yield to maturity of zero-coupon bond for
Explanation:
The formula for computing yield to maturity as follows:
Here,
PV is Current price of the bond
FV is Face value of the bond
For computing Price of the bond
For computing yield to maturity:
Using function in excel, effective yield is calculated.
Enter the data as shown below:
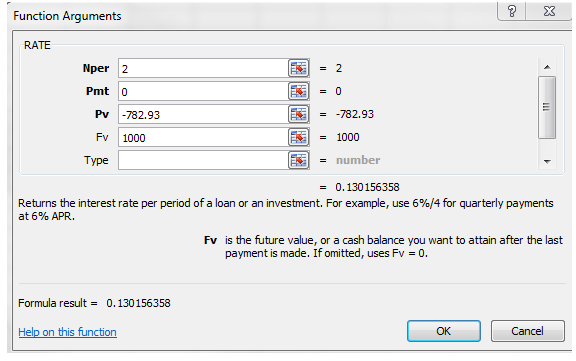
Thus, the yield to maturity of zero-coupon bond for
Explanation of Solution
The formula for computing yield to maturity as follows:
Here,
PV is Current price of the bond
FV is Face value of the bond
For computing Price of the bond
For computing yield to maturity:
Using function in excel, effective yield is calculated.
Enter the data as shown below:

Thus, the yield to maturity of zero-coupon bond for
(d)
To calculate:
The expected total
Introduction:
The expected rate of return is used to determine the total expected return on the bond for the holding period.
The yield to maturity is the rate which provides the amount of expected return on a bond held till its maturity.
Answer to Problem 40PS
The expected rate of return for two year bond is
Explanation:
The formula for computing price of the bond as follows:
For computing price of the bond with
For computing price of the bond with
Price at which the bond will sell in the next year:
The expected rate of return for two-year bond is as follows:
Thus, the expected rate of return for two-year bond is
Explanation of Solution
The formula for computing price of the bond as follows:
For computing price of the bond with
For computing price of the bond with
Price at which the bond will sell in the next year:
The expected rate of return for two-year bond is as follows:
Thus, the expected rate of return for two-year bond is
(e)
To calculate:
The expected total rate of return over the next year when purchase of a three-year zero-coupon bond on current day.
Introduction:
The expected rate of return is used to determine the total expected return on the bond for the holding period.
The yield to maturity is the rate which provides the amount of expected return on a bond held till its maturity.
Answer to Problem 40PS
The expected rate of return for three-year bond is
Explanation:
The formula for computing price of the bond as follows:
For computing price of the bond with
Price at which the bond will sell in the next year:
The expected rate of return for two-year bond is as follows:
Thus, the expected rate of return for three-year bond is
Explanation of Solution
The formula for computing price of the bond as follows:
For computing price of the bond with
Price at which the bond will sell in the next year:
The expected rate of return for two-year bond is as follows:
Thus, the expected rate of return for three-year bond is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
CONNECT WITH LEARNSMART FOR BODIE: ESSE
- Lara Fredericks is interested in two mutually exclusive investments. Both investments cover the same time horizon of 5 years. The cost of the first investment is $9900, and Lara expects equal and consecutive year-end payments of $3400. The second investment promises equal and consecutive payments of $4100 with an initial outlay of $12500 required. The current required return on the first investment is 8.4 %, and the second carries a required return of 10.4 %.a. What is the net present value of the first investment?b. What is the net present value of the second investment?c. Being mutually exclusive, which investment should Lara choose? d. Which investment is relatively more risky? Explain.arrow_forwardWhat are some of the characteristics of a firm with a long operating cycle?arrow_forwardAbout this Assignment For this Corporate Finance 301 assignment, you will submit a research paper that analyzes the types of organizational business structures. You will apply knowledge of business structure concepts as acquired in the course. The research paper should follow APA formatting style. Project Prompts The written research paper should be at least 1,000 to 1,200 words in length and should include four sections based on the business structures studied throughout the course. Define each business structure, compare the corporate finance strategies of the four business structures, discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each business structure, and how each varies in taxation. Research Paper Sections ⚫ Sole Proprietorship ⚫ Partnership • Corporation ⚫ Limited Liability Company (LLC)arrow_forward
- PLEASE ANSWER THE COLUMN FULLY AND CORRECTLY PLEASE DO THE RIGHT CALCULATION DOUBLE CHECK AS WELL TO GIVE ME THE RIGHT ANSWER REQUIRED: Given the following information, what are the NZD/SGD currency against currency bid-ask quotations? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 4 decimal places. Bank Quotations American Terms European Terms Bid Ask Bid Ask New Zealand dollar 0.733 0.7340 1.3870 1.3884 Singapore dollar 0.6186 0.6191 1.6423 1.6436 answer Bid Ask New Zealand dollar ? ? Singapore dollar ? ?arrow_forwardAbout this Assignment For the Corporate Finance 301 assignment, you will submit a research paper that analyzes and discusses organizational financial risks. You will apply knowledge acquired in the course and use the concepts of multiple financial risks as the basis of research and analysis. The research paper should follow APA formatting style. Audience: upper-level business students. Project Prompt Write a 1,000-1,200-word analysis discussing financial risk concepts and assess the impact of the different financial risks on an organization. For this assignment, you will structure your assignment using four research paper sections associated with corporate risk management, as studied in the course. Base your research paper on the financial statements analyzed in Corporate Finance 301 assignment 2 and apply the knowledge acquired in the analysis. Define each financial risk, discuss the risk associated components, and evaluate the financial risks and how they affect the corporation's…arrow_forwardBobby Nelson, made deposits of $880 at the end of each year for 6 years. Interest is 6% compounded annually. What is the value of Bobby’s annuity at the end of 6 years?arrow_forward
- 1. Find the future value if $1,250 is invested in Simple interest account paying 6.5%: a. for 5 years b. for 20 years 2. Find the future amount $ 35,000 is invested for 30 years at 4.25% compounded: a. annually b. Quarterly c. monthly d. weekly 3. How much should be put into an account today that pays 7.75% compounded monthly if you need $10,000 in 5 years. 4. Find the effective rate for: a. 5.75% compounded quarterly b. 6.25% compounded daily. 5. $50 is invested at the end of each month into an account paying 7.5% compounded monthly. How much will be in the account after 5 years?…arrow_forwardSolve step by step no aiarrow_forwardDont use ai solve itarrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





