
1.
Prepare a table to allocate the costs incurred by Company P.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Lump-Sum purchase:
If a company purchases a group of assets collectively and a lump sum amount is paid for such purchase, then it is referred to as basket purchase. The accounting term for this type of acquisition is the lump-sum purchase.
Compute the total cost of the assets as follows:
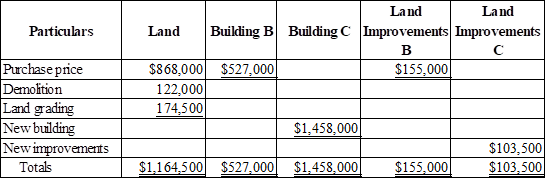
Table (1)
Note: Refer table-2 for the purchase price of each asset.
Working note:
Prepare a table to allocate the costs incurred by Company P as follows:
| Assets | Fair Market Value (in $) | Percent of total= | Allocation of the purchase price based on the percentage of total |
| Land | 795,200 | 868,000 | |
| Building B | 482,800 | 527,000 | |
| Land Improvements B | 142,000 | 155,000 | |
| Total | $1,420,000 | $1,550,000 |
…… (1)
2.
Prepare a single
2.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a single journal entry to record all the incurred costs as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| January 1 | Land | 1,164,500 | |
| Land improvements B | 155,000 | ||
| Land Improvements C | 103,500 | ||
| Building B | 527,000 | ||
| Building C | 1,458,000 | ||
| Cash | 3,408,000 | ||
| (To record the costs of lump-sum purchase) |
Table (2)
- Land is an asset account and it is increased. Therefore, debit land account.
- Land Improvements are the asset account and they are increased. Therefore, debit land improvements account.
- Building is an asset account and it is increased. Therefore debit building account.
- Cash is an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore credit cash account.
3.
Prepare the December 31
3.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the December 31 adjusting entries to record depreciation of the assets for the first year as follows:
Building B:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31 | Depreciation expense (2) | 28,500 | ||
| | 28,500 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) |
Table (3)
- Depreciation expense is an expense account, and it decreases the value of equity. Hence, debit the depreciation expense by $28,500.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra asset, and it decreases the value of assets. Therefore, credit the accumulated depreciation by $28,500.
Working Note:
Calculate the depreciation expense.
Building C:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ( $) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31 | Depreciation expense (3) | 60,000 | ||
| Accumulated depreciation | 60,000 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) |
Table (4)
- Depreciation expense is an expense account, and it decreases the value of equity. Hence, debit the depreciation expense by $60,000.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra asset, and it decreases the value of assets. Therefore, credit the accumulated depreciation by $60,000.
Working Note:
Calculate the depreciation expense.
Land Improvements B:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ( $) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31 | Depreciation expense (4) | 31,000 | ||
| Accumulated depreciation | 31,000 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) |
Table (5)
- Depreciation expense is an expense account, and it decreases the value of equity. Hence, debit the depreciation expense by $31,000.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra asset, and it decreases the value of assets. Therefore, credit the accumulated depreciation by $31,000.
Working Note:
Calculate the depreciation expense.
Land Improvements C:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31 | Depreciation expense (5) | 10,350 | ||
| Accumulated depreciation | 10,350 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) |
Table (6)
- Depreciation expense is an expense account, and it decreases the value of equity. Hence, debit the depreciation expense by $10,350.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra asset, and it decreases the value of assets. Therefore, credit the accumulated depreciation by $10,350.
Working Note:
Calculate the depreciation expense.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Principles of Financial Accounting.
- Can you solve this general accounting problem using appropriate accounting principles?arrow_forwardIf the average age of inventory is 80 days, the average age of accounts payable is 55 days, and the average age of accounts receivable is 70 days, the number of days in the cash flow cycle is__.arrow_forwardAnswerarrow_forward
- Can you help me solve this financial accounting question using the correct financial procedures?arrow_forwardWhat is the direct labor time variance?arrow_forwardSunset Crafts Company sells handmade scarves for $28.50 per scarf. In FY 2023, total fixed costs are expected to be $185,000, and variable costs are estimated at $19.75 a unit. Sunset Crafts Company wants to have an FY 2023 operating income of $92,000. Use this information to determine the number of units of scarves that Sunset Crafts Company must sell in FY 2023 to meet this goal. (Don't round-up unit calculation)arrow_forward
- Please explain the correct approach for solving this general accounting question.arrow_forwardQuestion: 22 - Hader company has actual sales of $82,000 in April and $63,000 in May. It expects sales of $78,000 in June and $92,000 in July and in August. Assuming that sales are the only source of cash inflows and that half of them are for cash and the remainder are collected evenly over the following 2 months, what are the firm's expected cash receipts for June, July, and August?arrow_forwardCalculate the sales revenue to achieve a target profit of 375000arrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT





