
a.
Prepare journey to record the given transactions.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Liabilities:
The claims creditors have over assets or resources of a company are referred to as liabilities. These are the debt obligations owed by company to creditors. Liabilities are classified on the
Prepare journal entry to record borrowing of $20,000 from Bank W, signing a 90-day, 12 percent note payable.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| July 1 | Cash | 20,000 | |
| Notes payable | 20,000 | ||
| (To record the borrowing of $20,000 from Bank W, signing a 90-day promissory note) |
(Table 1)
- Cash is an asset and there is an increase in the value of an asset. Hence, debit the cash by $20,000.
- Notes payable is a liability and there is an increase in the value of liability. Hence, credit the notes payable by $20,000.
Prepare journal entry to record purchased office equipment from Company M.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| September 16 | Office equipment | 30,000 | |
| Notes payable | 30,000 | ||
| (To record the purchase of equipment) |
(Table 2)
- Office equipment is an asset and there is an increase in the value of an asset. Hence, debit the office equipment by $30,000.
- Notes payable is a liability and there is an increase in the value of liability. Hence, credit the notes payable by $30,000.
Prepare journal entry to record the payment made on bank W’s note along with accrued interest.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| October 1 | Note payable | 20,000 | |
| Interest Expense (1) | 600 | ||
| Cash | 20,600 | ||
| (To record the payment of Bank W’s note with accrued interest) |
(Table 3)
- Notes payable is a liability and there is decrease in the value of liability. Hence, debit the notes payable by $20,000.
- Interest expense is a component of
stockholder’s equity and there is an increase in the value of expense. Hence, debit the interest expense by $600. - Cash is an asset and there is a decrease in the value of an asset. Hence, credit the office equipment by $20,600.
Prepare journal entry to record borrowing of $170,000 from Company J.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 1 | Cash | 170,000 | |
| Notes payable | 170,000 | ||
| (To record the borrowing of $170,000 from Company J) |
(Table 4)
- Cash is an asset and there is an increase in the value of an asset. Hence, debit the cash by $170,000.
- Notes payable is a liability and there is an increase in the value of liability. Hence, credit the notes payable by $170,000.
Prepare journal entry to record purchase of merchandise inventory on account from Corporation L.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 1 | Merchandise inventory | 10,000 | |
| Notes payable | 10,000 | ||
| (To record the purchase of merchandise inventory on account) |
(Table 5)
- Merchandise inventory is an asset and there is an increase in the value of an asset. Hence, debit the merchandise inventory by $10,000.
- Notes payable is a liability and there is an increase in the value of liability. Hence, credit the notes payable by $10,000.
Prepare journal entry to record the payment of note payable to Company M along with the accrued interest and issued a new 60-day, 12 percent note payable in the amount of $30,000 to replace the note that matured.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 16 | Note payable | 30,000 | |
| Interest Expense (2) | 750 | ||
| Cash | 750 | ||
| Notes payable | 30,000 | ||
| (To record the payment made to Company M on note along with the interest and issued a 60-day, 12%, renewal note ) |
(Table 6)
- Notes payable is a liability and there is decrease in the value of liability. Hence, debit the notes payable by $30,000.
- Interest expense is a component of stockholder’s equity and there is an increase in the value of expense. Hence, debit the interest expense by $750.
- Cash is an asset and there is a decrease in the value of an asset. Hence, credit the office equipment by $750.
- Notes payable is a liability and there is an increase in the value of liability. Hence, credit the notes payable by $30,000.
Working Notes:
Calculate the amount of interest expense:
Calculate the value of interest expense that is to be paid to Company M on purchase of office equipment.
b.
Prepare the adjusting entry needed at December 31, prior to closing the accounts.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries are those entries which are recorded at the end of the year, to update the income statement accounts (revenue and expenses) and balance sheet accounts (assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity) to maintain the records according to accrual basis principle.
Prepare the adjusting entry needed at December 31, prior to closing the accounts.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31 | Interest expense (3) | 958 | |
| Interest payable | 958 | ||
| (To record interest accrued on notes payable) |
(Table 7)
- Debit to increase the interest expense account (Increase in interest expense decreases stockholders’ equity account).
- Credit to increase the interest payable account (liability account).
Working Note:
Calculate the interest accrued on notes payable.
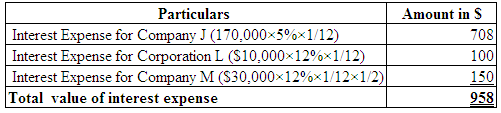
(Table 8)
(3)
c.
Provide reason to explain why the new 60-day note payable to Company M pays 16 percent interest instead of the 10 percent rate charged on the September 16 note.
c.
Explanation of Solution
The note made by Company M on September 16, is to be collected in full amount by December 16. The interest rate has increased on the new note, because due to the risk involved in collecting $30,000 in 60 days along with the accrued interest that is in due.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Connect Access Card for Financial and Managerial Accounting
- Hello tutor please given General accounting question answer do fast and properly explain all answerarrow_forwardOn March 1, 20X1, your company,which uses Units-of-Production (UOP) Depreciation, purchases a machine for $300,000.arrow_forwardPlease provide the accurate answer to this general accounting problem using valid techniques.arrow_forward
- Can you explain the correct methodology to solve this general accounting problem?arrow_forwardPlease explain the solution to this general accounting problem with accurate principles.arrow_forwardI am searching for the correct answer to this general accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





