
Concept explainers
a.
To calculate: The estimated value of dividend for Martin Office Supplies in the next four years.
Introduction:
Dividends:
It refers to the distribution of profits to the shareholders of a company and can be paid in terms of cash and stock.
a.
Answer to Problem 34P
The calculation of the next four anticipated values of dividend is shown below.
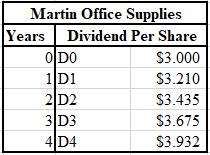
Explanation of Solution
The formulae used for the calculation of the anticipated values of dividend are shown below.
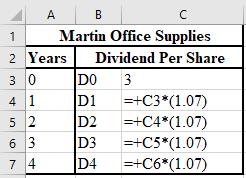
b.
To calculate: The summation of the present values of the four anticipated values of dividend discounted at the rate of 14% of Martin Office Supplies.
Introduction:
Present value (PV):
The current value of an investment or an asset is termed as its PV. It is calculated by discounting the
b.
Answer to Problem 34P
The calculation of the PV of the next four values of dividend is shown below.
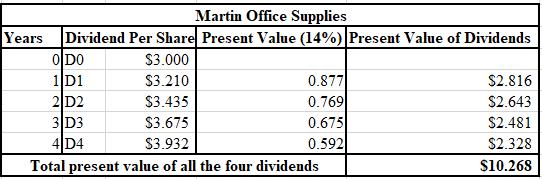
Hence, the sum of the PV of the next four anticipated values of dividend is $10.268.
Explanation of Solution
The formulae used for the calculation of the PV of the anticipated values of dividend are shown below.
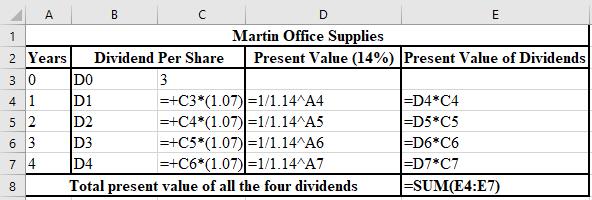
c.
To calculate: The price of the stock at the end of fourth year (P4) of Martin Office Supplies.
Introduction:
Share Price:
The highest price of one share of a company that an investor is willing to pay is termed as share price. It is the current price used for the trading of such shares.
c.
Answer to Problem 34P
The price of the stock at the end of fourth year (P4) of Martin Office Supplies will be $60.10.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of the stock price:
Working note:
Calculation of the expected dividend in the fifth year:
d.
To calculate: The PV of P4 at a discount rate of 14% for Martin Office Supplies.
Introduction:
Present value (PV):
The current value of an investment or an asset is termed as its PV. It is calculated by discounting the future value of the investment or asset.
d.
Answer to Problem 34P
The PV of P4 discounted at 14% is $35.579.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of the present value of the stock price calculated in part (c):
e.
To calculate: The current value of the stock of Martin Office Supplies.
Introduction:
Present value (PV):
The current value of an investment or an asset is termed as its present value. It is calculated by discounting the future value of the investment or asset.
Share Price:
The highest price of one share of a company that an investor is willing to pay is termed as share price. It is the current price used for the trading of such shares.
e.
Answer to Problem 34P
The current value of the stock is $45.845.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of the current price of stock:
f.
To calculate: The current value of the stock of Martin Office Supplies.
Introduction:
Share Price:
The highest price of one share of a company that an investor is willing to pay is termed as share price. It is the current price used for the trading of such shares.
f.
Answer to Problem 34P
The price of the stock is the same as that computed in part (e), that is, $45.857.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of the stock price by using formula 10-8:
g.
To calculate: The current value of the stock of Trump Office Supplies if EPS is $5.32 and the P/E ratio is 1.1, which is higher than the industry average.
Introduction:
Share Price:
The highest price of one share of a company that an investor is willing to pay is termed as share price. It is the current price used for the trading of such shares.
g.
Answer to Problem 34P
The current value of the stock of Trump Office Supplies is $46.816 if EPS is $5.32 and the P/E ratio is 1.1, which is higher than the industry average.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of the price of the stock:
Working Note:
Calculation of the P/E ratio of the firm:
h.
To calculate: The difference between the stock prices calculated in parts (g) and (f) for Martin Office Supplies.
Introduction:
Share Price:
The highest price of one share of a company that an investor is willing to pay is termed as share price. It is the current price used for the trading of such shares.
h.
Answer to Problem 34P
The dollar difference between the stock prices in parts (g) and (f) is $0.959.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of the difference between the stock prices in parts (g) and (f):
i.
To calculate: The effect of changing variables on the stock price if dividend increases, Ke increases, and g decreases of Martin Office Supplies.
Introduction:
Share Price:
The highest price of one share of a company that an investor is willing to pay is termed as share price. It is the current price used for the trading of such shares.
i.
Answer to Problem 34P
The price of the stock will increase in the 1st and 3rd parts, and decrease in the 2nd part.
Explanation of Solution
(1) If D1 increases, the stock price will go up. The stock price and amount of dividend are positively related to one another.
(2) If the required
(3) If the growth rate (g) increases, the price of the stock will also increase. They have a positive relationship.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Foundations of Financial Management Format: Loose-leaf
- Wilbur and Orville are brothers. They're both serious investors, but they have different approaches to valuing stocks. Wilbur, the older brother, likes to use the dividend valuation model. Orville prefers the free cash flow to equity valuation model. As it turns out, right now, both of them are looking at the same stock-Wright First Aerodynmaics, Inc. (WFA). The company has been listed on the NYSE for over 50 years and is widely regarded as a mature, rock-solid, dividend-paying stock. The brothers have gathered the following information about WFA's stock: Current dividend (D) = $2.30/share Current free cash flow (FCF) = $1.5 million Expected growth rate of dividends and cash flows (g) = 5% Required rate of return (r) = 14% Shares outstanding 500,000 shares How would Wilbur and Orville each value this stock?arrow_forwardCompany P/S Multiples Facebook 13.33 Snap 18.22 Twitter 13.27arrow_forwardThe Perez Company has the opportunity to invest in one of two mutually exclusive machines that will produce a product it will need for the foreseeable future. Machine A costs $8 million but realizes after-tax inflows of $4.5 million per year for 4 years. After 4 years, the machine must be replaced. Machine B costs $17 million and realizes after-tax inflows of $4 million per year for 8 years, after which it must be replaced. Assume that machine prices are not expected to rise because inflation will be offset by cheaper components used in the machines. The cost of capital is 13%. Using the replacement chain approach to project analysis, by how much would the value of the company increase if it accepted the better machine? Round your answer to two decimal places. 1.) $ millionarrow_forward
- Wilbur and Orville are brothers. They're both serious investors, but they have different approaches to valuing stocks. Wilbur, the older brother, likes to use the dividend valuation model. Orville prefers the free cash flow to equity valuation model. As it turns out, right now, both of them are looking at the same stock-Wright First Aerodynmaics, Inc. (WFA). The company has been listed on the NYSE for over 50 years and is widely regarded as a mature, rock-solid, dividend-paying stock. The brothers have gathered the following information about WFA's stock: Current dividend (D) = $3.30/share Current free cash flow (FCF) = $1.5 million Expected growth rate of dividends and cash flows (g)=8% Required rate of return (r) = 13% Shares outstanding 500,000 shares How would Wilbur and Orville each value this stock? The stock price from Wilbur's valuation is $ (Round to the nearest cent.)arrow_forwardThe Perez Company has the opportunity to invest in one of two mutually exclusive machines that will produce a product it will need for the foreseeable future. Machine A costs $8 million but realizes after-tax inflows of $4.5 million per year for 4 years. After 4 years, the machine must be replaced. Machine B costs $17 million and realizes after-tax inflows of $4 million per year for 8 years, after which it must be replaced. Assume that machine prices are not expected to rise because inflation will be offset by cheaper components used in the machines. The cost of capital is 13%. Using the replacement chain approach to project analysis, by how much would the value of the company increase if it accepted the better machine? Round your answer to two decimal places. 1.) $ million What is the equivalent annual annuity for each machine? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places. 2.) Machine A: $ million 3.) Machine B: $ millionarrow_forwardYou expect to have $29,865. You plan to make X savings contribution of $1,690 per month. The expected return is 0.92 percent per month and the first regular savings contribution will be made later today. What is X? Round to 2 decimal places.arrow_forward
- Company P/S Multiples Facebook 13.67 Snap 18.76 Twitter 13.55arrow_forwardEnergy Resources generated an EPS of $4.38 over the last 12 months. The company's earnings are expected to grow by 30.7% next year, and because there will be no significant change in the number of shares outstanding, EPS should grow at about the same rate. You feel the stock should trade at a P/E of around 30 times earnings. Use the P/E approach to set a value on this stock. Using the P/E approach, the value on this stock is $ (Round to the nearest cent.)arrow_forwardThe Anderson Company has a net profits of $20 million, sales of $226 million, and 3.9 million shares of common stock outstanding. The company has total assets of $139 million and total stockholders' equity of $74 million. It pays $2.31 per share in common dividends, and the stock trades at $40 per share. Given this information, determine the following: a. Anderson's EPS. b. Anderson's book value per share and price-to-book-value ratio. c. The firm's P/E ratio. d. The company's net profit margin. e. The stock's dividend payout ratio and its dividend yield. f. The stock's PEG ratio, given that the company's earnings have been growing at an average annual rate of 8.2%. a. Anderson's EPS is $ (Round to the nearest cent.)arrow_forward
- Davis Industries must choose between a gas-powered and an electric-powered forklift truck for moving materials in its factory. Because both forklifts perform the same function, the firm will choose only one. (They are mutually exclusive investments.) The electric-powered truck will cost more, but it will be less expensive to operate; it will cost $23,000, whereas the gas-powered truck will cost $17,100. The cost of capital that applies to both investments is 11%. The life for both types of truck is estimated to be 6 years, during which time the net cash flows for the electric-powered truck will be $6,500 per year, and those for the gas-powered truck will be $4,750 per year. Annual net cash flows include depreciation expenses. Calculate the NPV and IRR for each type of truck, and decide which to recommend. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round the monetary values to the nearest dollar and percentage values to two decimal places. Electric-poweredforklift truck…arrow_forwardA project has an initial cost of $45,000, expected net cash inflows of $9,000 per year for 11 years, and a cost of capital of 14%. What is the project's NPV? (Hint: Begin by constructing a time line.) Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest cent.arrow_forwardA project has an initial cost of $45,000, expected net cash inflows of $9,000 per year for 11 years, and a cost of capital of 14%. What is the project's NPV? (Hint: Begin by constructing a time line.) Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest cent.arrow_forward
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
