
Concept explainers
To find: The
Introduction:
The variation between the present value of the cash outflows and the present value of the cash inflows are known as the net present value. In capital budgeting, the net present value is utilized to analyze the profitability of a project or investment. The rate of return (which compares the initial investment and the present value of net cash inflows)isreferred to as internal rate of return. This is also called actual rate of return.
Answer to Problem 32QP
The net
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Company A projects the unit sale for the new 7 octave voice emulation implant as follows:
- Year 1’s unit sales is 81,000
- Year 2’s unit sales is 94,000
- Year 3’s unit sales is 108,000
- Year 4’s unit sales is 103,000
- Year 5’s unit sales is 84,000
The production implant needs $1,600,000 in the net working capital to begin their production activities. The extra net working capital investment for every year is equivalent to the 15% of the sales that is projected, which has to rise for the following year. The total fixed cost is $1,500,000 for a year, the unit price is $380, and the variable production cost is $265. The installation cost of the equipment is $21,000,000.
The equipment is qualified in the 7 Year MACRS
MACRS depreciation table for 7 year:
| MACRS Depreciation table for seven year | |
| Year | Seven year |
| 1 | 14.29% |
| 2 | 24.49% |
| 3 | 17.49% |
| 4 | 12.49% |
| 5 | 8.93% |
| 6 | 8.92% |
| 7 | 8.93% |
| 8 | 4.46% |
Computation of the net present value:
Computation of the
Table showing the cash inflows:
| Year | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Ending book value | $17,999,100 | $12,856,200 | $9,183,300 | $6,560,400 | $4,685,100 |
| Sales | $30,780,000 | $35,720,000 | $41,040,000 | $39,140,000 | $31,920,000 |
| Less: Variable costs | $21,465,000 | $24,910,000 | $28,620,000 | $27,295,000 | $22,260,000 |
| Fixed costs | $1,500,000 | $1,500,000 | $1,500,000 | $1,500,000 | $1,500,000 |
| Depreciation | $3,000,900 | $5,142,900 | $3,672,900 | $2,622,900 | $1,875,300 |
| EBIT | $4,814,100 | $4,167,100 | $7,247,100 | $7,722,100 | $6,284,700 |
| Less: Taxes | $1,684,935 | $1,458,485 | $2,536,485 | $2,702,735 | $2,199,645 |
| Net income | $3,129,165 | $2,708,615 | $4,710,615 | $5,019,365 | $4,085,055 |
| Add: Depreciation | $3,000,900 | $5,142,900 | $3,672,900 | $2,622,900 | $1,875,300 |
| Operating cash flow | $6,130,065 | $7,851,515 | $8,383,515 | $7,642,265 | $5,960,355 |
| Net cash inflows: | |||||
| Operating cash flow | $6,130,065 | $7,851,515 | $8,383,515 | $7,642,265 | $5,960,355 |
| Change in net working capital | -$741,000 | -$798,000 | $285,000 | $1,083,000 | $1,771,000 |
| Capital spending | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $4,369,785 |
| Total cash inflows | $5,389,065 | $7,053,515 | $8,668,515 | $8,725,265 | $12,101,140 |
Computations for the above table:
Formula to calculate the ending book value:
Computation of the ending book value for year 1:
Note:
- Sales are calculated by multiplying the price per unit with the unit sales of each year.
- Depreciation is calculated by multiplying the equipment’s installation cost with the MACRS depreciation rate for the particular year.
- The taxes are calculated by multiplying the earnings before tax for the specific year with the marginal tax rate.
- The change in the net working capital is calculated by subtracting the current year’s sales with the next year’s sales and multiplying it with the 15% (increased percentage).
Computation of the net working capital for year 5:
Computation of the ending book value:
Formula to calculate the after-tax salvage value:
Computation of the after-tax salvage value:
Formula to calculate the net present value:
Computation of the net present value:
Hence, the net present value is $2,098,569.18.
Computation of the internal rate of return:
The internal rate of return is calculated by the spreadsheet method.
Step 1:
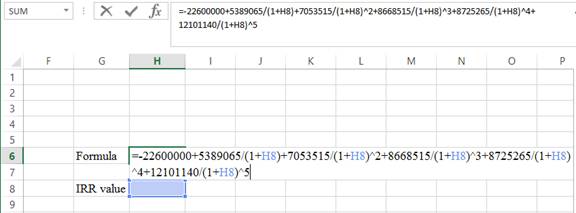
- Type the formula of the internal rate of return in H6 in the spreadsheet and consider the IRRvalue as H8.
Step 2:
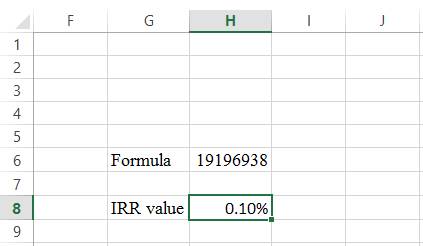
- Assume the IRRvalue as 0.10%.
Step 3:
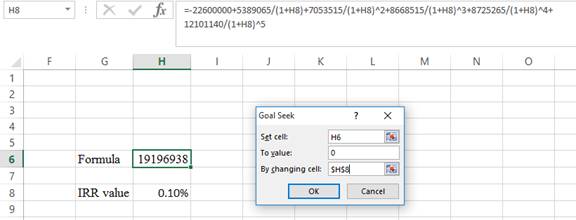
- In the spreadsheet, go to data, and select the what-if analysis.
- In what-if analysis, select goal seek.
- In set cell, select H6 (the formula).
- The To value is considered as 0.
- The H8 cell is selected for the by changing cell.
Step 4:
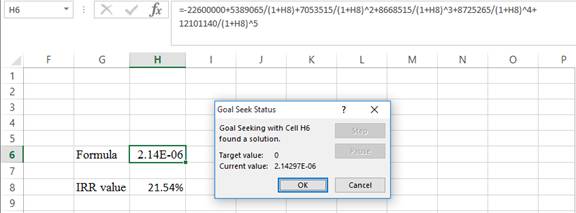
- Following the previous step, click OK in the goal seek. The goal seek status appears.
Step 5:
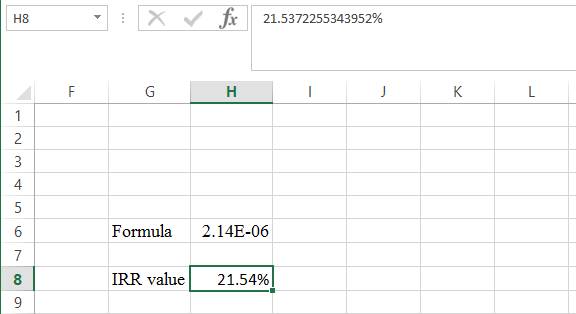
- The IRRvalue appears to be 21.5372255343952%.
Hence, the internal rate of return is 21.54%.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Corporate Finance, Tenth Standard Edition
- (Annual percentage yield) Compute the cost of the following trade credit terms using the compounding formula, or effective annual rate. Note: Assume a 30-day month and 360-day year. a. 3/5, net 30 b. 3/15, net 45 c. 4/10, net 75 d. 3/15, net 45 ... a. When payment is made on the net due date, the APR of the credit terms of 3/5, net 30 is decimal places.) %. (Round to twoarrow_forwardSuppose XYZ is a non-dividend-paying stock. Suppose S = $100, σ = 40%, δ = 0, and r = 0.06. What is the price of a 105-strike call option with 1 year to expiration? What is the 1-year forward price for the stock? What is the price of a 1-year 105-strike option, where the underlying asset is a futures contract maturing at the same time as the option?arrow_forwardCalifornia Construction Inc. is considering a 15 percent stock dividend. The capital accounts are: Common stock (6,000,000 shares at $10 par) ....... $60,000,000 Capital in excess of par* ...................................... 35,000,000 Retained earnings ................................................ 75,000,000 Net worth ......................................................... $170,000,000 *The increase in capital in excess of par as a result of a stock dividend is equal to the shares created times (Market price – Par value). The company’s stock is selling for $32 per share. The company had total earnings of $19,200,000 with 6,000,000 shares outstanding and earnings per share were $3.20. The firm has a P/E ratio of 10. a. Show the new capital accounts if a 15 percent stock dividend is given. b. What adjustments would be made to EPS and the stock price? (Assume the P/E ratio remains constant.) c. How many shares would an investor have if they originally had 80 shares? d. What…arrow_forward
- Refer to Table 10–6. Price quotes are stated in 1/64ths. What was the closing price of a May 3,990 call option on the S&P 500 Stock Index futures contract on January 13, 2023? Round your closing price answer to 1 decimal place and dollar price answer to the nearest whole number. TABLE 10-6 Option Quotes, January 13, 2023 Underlying Asset: S&P 500 Index (SPX) Closing Value: 3,999.09 Expiration Strike Price Calls Puts Last Volume Open Interest Last Volume Open Interest 04-21-23 3990 140 0 258 164.6 0 223 04-21-23 4010 164.3 257 18,244 144.3 100 17,166 05-19-23 3990 200.7 210 30 169.1 210 52 05-19-23 4010 186.1 303 3,552 279.2 2 3,965 06-16-23 3990 223.3 1 16 178.8 1 1 06-16-23 4010 152.9 0 46 183 1,665 42,159 12-15-23 3975 361 100 2,555 250.1 32 2,438 12-15-23 4025 349.3 0 2,416 268.2 4 2,149 OPTIONS ON INTEREST RATE FUTURES Underlying Asset: March 2023 30-Year Treasury Bond Future Prior Settle: 130'02 Expiration Strike Price Calls Puts…arrow_forwardTerrill Machining Inc. sells machine parts to auto mechanics. It has not paid a dividend in many years but is currently contemplating some kind of dividend. The capital accounts for the firm are as follows: Common stock (2,400,000 shares at $5 par) . Capital in excess of par* ............................... Retained earnings ......................................... Net worth ................................................... $12,000,000 5,000,000 23,000,000 $40,000,000 *The increase in capital in excess of par as a result of a stock dividend is equal to the new shares created times (Market price – Par value). The company’s stock is selling for $20 per share. The company had total earnings of $4,800,000 during the year. With 2,400,000 shares outstanding, earnings per share were $2.00. The firm has a P/E ratio of 10. a. What adjustments would have to be made to the capital accounts for a 10 percent stock dividend? Show the new capital accounts. b. What adjustments would be made to…arrow_forwardPat’s Video Games has been struggling recently as it has been rumored that the owners are secret Dodgers fans. As a result, its stock price is now only $4 per share. It is going to declare a one-for-two reverse stock split to increase the stock value. a. If an investor owns 90 shares, how many shares will he own after the reverse stock split? b. What is the anticipated price of the stock after the reverse stock split? c. Because it became public knowledge that the owners of Pat’s Video Games were Dodgers fans (and used company proceeds to purchase Dodger paraphernalia, the stock price continued to drop even after the stock split. If the stock price only goes up to 75 percent of the value computed in part b. What will the stock’s price be? d. How has the total value of an investor’s holdings changed from before the reverse stock split to after the reverse stock split (based on the stock value computed in part c)? e. What important lesson did the investor learn?arrow_forward
- Purrogi Cat Treats Inc. earned $500 million last year and retained $290 million in earnings. What is the payout ratio?arrow_forwardEthical dilemma: Republic Communications Corporation (RCC) has offered you an attractive position in its financial planning division. The new position would constitute a promotion with a $30,000 increase in salary compared to the job you now have at National Telecommunications, Inc. (NTI). The problem is that RCC wants you to bring the rate-setting software you developed at NTI, along with some rate data, with you to the new job. Even though NTI sells its software to other companies and information concerning telephone rates is available to the public, you know that such knowledge will help RCC significantly in its attempt to redesign its rate-setting system. In fact, according to the situation presented in the text, a new and improved rate-setting program could be worth as much as $200 million per year for RCC. Therefore, the question is whether the information RCC wants you to take with you to your new job is proprietary to NTI. Should the rate-setting program and the rate data be…arrow_forwardYour traditional IRA account has stock of GFH, which cost $2,000 20 years ago when you were 50 years old. You have been very fortunate, and the stock is now worth $23,000. You are in the 32 percent income tax bracket and pay 15 percent on long-term capital gains. a. What was the annual rate of growth in the value of the stock? b. What are the taxes owed if you withdraw the funds? Answer to part b. is $8,050 *Please display all work & needed formulasarrow_forward
- Can anyone figure this out correctly? I keep getting the wrong answers over and over? Cost of Trade Credit Grunewald Industries sells on terms of 3/10, net 40. Gross sales last year were $4,161,000 and accounts receivable averaged $370,500. Half of Grunewald's customers paid on the 10th day and took discounts. What are the nominal and effective costs of trade credit to Grunewald's nondiscount customers? (Hint: Calculate daily sales based on a 365-day year, calculate the average receivables for discount customers, and then find the DSO for the nondiscount customers.) Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places. 1.) Effective cost of trade credit:arrow_forwardExplain how an increase in interest rates by a central bank could affect bond prices and stock market performance. Explanation.arrow_forwardWhat is the purpose of diversification in an investment portfolio, and how does it reduce risk?arrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





