
To find: The
Introduction:
The variation between the present value of the cash outflows and the present value of the cash inflows are known as the net present value. In capital budgeting the net present value is utilized to analyze the profitability of a project or investment. The rate of return which equates the initial investment and the present value of net cash inflows are referred to as internal rate of return. This is also called as actual rate of return.
Answer to Problem 32QP
The net
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Company A projects the unit sale for the new 7 octave voice emulation implant as follows:
- The year 1 unit sales is 84,000
- The year 2 unit sales is 98,000
- The year 3 unit sales is 113,000
- The year 4 unit sales is 106,000
- The year 5 unit sales is 79,000
The production implant needs $1,500,000 in the net working capital to begin their production activities. The extra net working capital investment for every year is equivalent to the 15% of the sales that is projected has to rise for the following year. The total fixed cost is $3,400,000 for a year, the unit price is $395, and the variable production cost is $265. The installation cost of the equipment is $17,000,000.
The equipment is qualified in the 7 Year MACRS
MACRS depreciation table for year 7:
| MACRS Depreciation table for seven year | |
| Year | Seven year |
| 1 | 14.29% |
| 2 | 24.49% |
| 3 | 17.49% |
| 4 | 12.49% |
| 5 | 8.93% |
| 6 | 8.92% |
| 7 | 8.93% |
| 8 | 4.46% |
Computation of the net present value:
Computation of the
Table showing the cash inflows:
| Year | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Ending book value | $14,570,700 | $10,407,400 | $7,434,100 | $5,310,800 | $3,792,700 |
| Sales | $33,180,000 | $38,710,000 | $44,635,000 | $41,870,000 | $31,205,000 |
| Less: Variable costs | -$22,260,000 | -$25,970,000 | -$29,945,000 | -$28,090,000 | -$20,935,000 |
| Fixed costs | -$3,400,000 | -$3,400,000 | -$3,400,000 | -$3,400,000 | -$3,400,000 |
| Depreciation | -$2,429,300 | -$4,163,300 | -$2,973,300 | -$2,123,300 | -$1,518,100 |
| EBIT | $5,090,700 | $5,176,700 | $8,316,700 | $8,256,700 | $5,351,900 |
| Less: Taxes | -$1,781,745 | -$1,811,845 | -$2,910,845 | -$2,889,845 | -$1,873,165 |
| Net income | $3,308,955 | $3,364,855 | $5,405,855 | $5,366,855 | $3,478,735 |
| Add: Depreciation | $2,429,300 | $4,163,300 | $2,973,300 | $2,123,300 | $1,518,100 |
| Operating cash flow | $5,738,255 | $7,528,155 | $8,379,155 | $7,490,155 | $4,996,835 |
| Net cash inflows: | |||||
| Operating cash flow | $5,738,255 | $7,528,155 | $8,379,155 | $7,490,155 | $4,996,835 |
| Change in net working capital | –829,500 | –888,750 | $414,750 | $1,599,750 | $1,203,750 |
| Capital spending | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $3,537,445 |
| Total cash inflows | $4,908,755 | $6,639,405 | $8,793,905 | $9,089,905 | $9,738,030 |
Computations for the above table:
Formula to calculate the ending book value:
Computation of the ending book value for year 1:
Formula to calculate the sales:
Computation of the sales:
Computation of the depreciation:
The depreciation amount is calculated by using the MACRS depreciation table for seven years.
Formula to calculate depreciation:
Computation of the depreciation:
Formula to calculate the taxes:
Computation of the taxes:
Formula to calculate the net working capital:
Computation of the net working capital:
Computation of the net working capital for the year 5:
Computation of the ending book value:
Formula to calculate the after-tax salvage value:
Computation of the after-tax salvage value:
Formula to calculate the net present value:
Computation of the net present value:
Hence, the net present value is $4,725,575.74.
Computation of the internal rate of return:
The internal rate of return is calculated by the spreadsheet method.
Step 1:
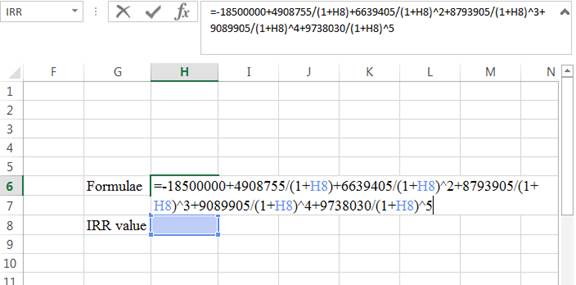
- Type the formulae of the internal rate of return in H6 in the spreadsheet and consider the IRR value as H8
Step 2:
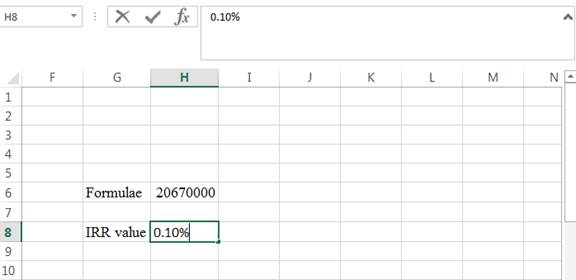
- Assume the IRR value as 0.10%
Step 3:
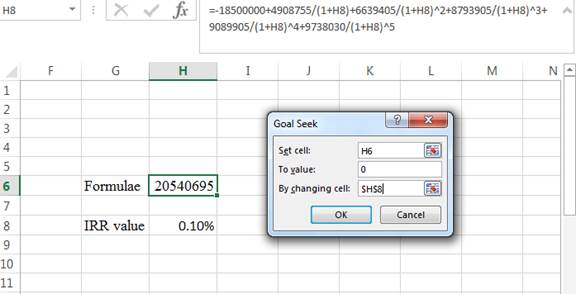
- In the spreadsheet go to data and select the what-if analysis.
- In what-if analysis select goal seek
- In set cell select H6 (the formulae)
- The To value is considered as 0
- The H8 cell is selected for the by changing cell.
Step 4:
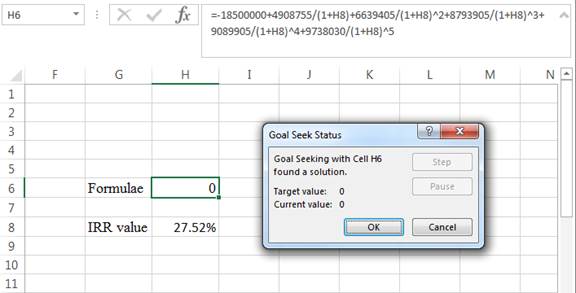
- Following the previous step click OK in the goal seek. The goal seek status appears
Step 5:
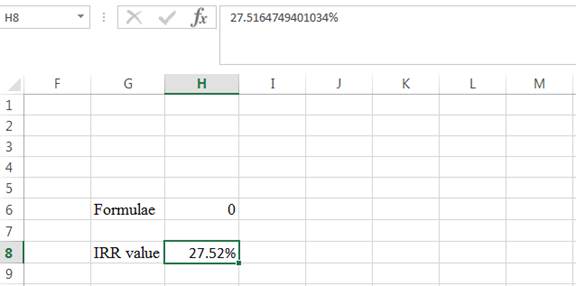
- The IRR value appears to be 27.5164749401034%
Hence, the internal rate of return is 27.52%.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Fundamentals of Corporate Finance (Special Edition for Rutgers Business School)
- Chee Chew's portfolio has a beta of 1.27 and earned a return of 13.6% during the year just ended. The risk-free rate is currently 4.6%. The return on the market portfolio during the year just ended was 10.5%. a. Calculate Jensen's measure (Jensen's alpha) for Chee's portfolio for the year just ended. b. Compare the performance of Chee's portfolio found in part a to that of Carri Uhl's portfolio, which has a Jensen's measure of -0.25. Which portfolio performed better? Explain. c. Use your findings in part a to discuss the performance of Chee's portfolio during the period just ended.arrow_forwardDuring the year just ended, Anna Schultz's portfolio, which has a beta of 0.91, earned a return of 8.1%. The risk-free rate is currently 4.1%, and the return on the market portfolio during the year just ended was 9.4%. a. Calculate Treynor's measure for Anna's portfolio for the year just ended. b. Compare the performance of Anna's portfolio found in part a to that of Stacey Quant's portfolio, which has a Treynor's measure of 1.39%. Which portfolio performed better? Explain. c. Calculate Treynor's measure for the market portfolio for the year just ended. d. Use your findings in parts a and c to discuss the performance of Anna's portfolio relative to the market during the year just ended.arrow_forwardNeed answer.arrow_forward
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT





