
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure formula with all valence electrons should be drawn for a carbonyl group.
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structures can be drawn by following some point for any compound as mentioned below:
- Find out number of valence electrons present in the molecule
- The connectivity of atoms need to be understood like which atoms are linked with each other and connect them with covalnet bonds
- The arrangements of electrons in proper manner to achieve complete outer shell
Answer to Problem 23P
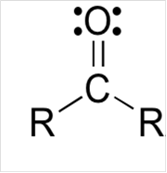
Lewis structure for a carbonyl group:
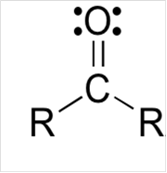
Explanation of Solution
The structure of any atom of prepared with the help of Lewis model which explains guideline for bonding of atom. It guides about the covalent bonds which are formed in various combinations of single, double and triple bonds.
Single covalent bond occurs by sharing one pair of electrons and can be represented by single line in between atoms.
Double and triple bonds are formed when two and three pairs of electrons are shared in between atoms respectively and can be represented by two or three lines in between the atoms.
For several covalent bonds in organic compound containing carbon bonded to hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine and oxygen shows some important points to be noted for structure are as follow:
- Carbon forms four covalent bonds while hydrogen form one covalent bond and both has no unshared pair of electrons.
- Three covalent bonds are formed in nitrogen atom with only one unshared pair of electron left behind.
- Oxygen can form two covalent bonds and have further more two unshared pair of electron.
- Iodine, chlorine, bromine and fluorine like halogens can form only one covalent bond like hydrogen but they have three unshared pair of electrons.
To draw Lewis structure for a carbonyl group, following are the steps:
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure formula with all valence electrons should be drawn for a carboxyl group.
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structures can be prepared by following some point for any compound as mentioned below:
- Find out number of valence electrons present in the molecule
- The connectivity o atoms need to be understood like which atoms are linked with each other and connect them with covalnet bonds
- The arrangements of electrons in proper manner to achieve complete outer shell
Answer to Problem 23P
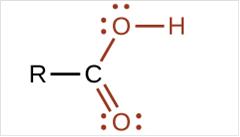
To draw Lewis structure for a carboxyl group:
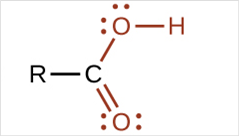
Explanation of Solution
The structure of any atom of prepared with the help of Lewis model which explains guideline for bonding of atom. It guides about the covalent bonds which are formed in various combinations of single, double and triple bonds.
Single covalent bond occurs by sharing one pair of electrons and can be represented by single line in between atoms.
Double and triple bonds are formed when two and three pairs of electrons are shared in between atoms respectively and can be represented by two or three lines in between the atoms.
For several covalent bonds in organic compound containing carbon bonded to hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine and oxygen shows some important points to be noted for structure are as follow:
- Carbon forms four covalent bonds while hydrogen form one covalent bond and both has no unshared pair of electrons.
- Three covalent bonds are formed in nitrogen atom with only one unshared pair of electron left behind.
- Oxygen can form two covalent bonds and have further more two unshared pair of electron.
- Iodine, chlorine, bromine and fluorine like halogens can form only one covalent bond like hydrogen but they have three unshared pair of electrons.
To draw Lewis structure for a carboxyl group, following are the steps:
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure formula with all valence electrons should be drawn for a hydroxyl group.
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structures can be prepared by following some point for any compound as mentioned below:
- Find out number of valence electrons present in the molecule
- The connectivity o atoms need to be understood like which atoms are linked with each other and connect them with covalnet bonds
- The arrangements of electrons in proper manner to achieve complete outer shell
Answer to Problem 23P
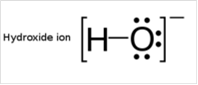
To draw Lewis structure for a hydroxyl group:
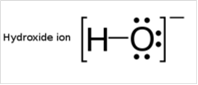
Explanation of Solution
The structure of any atom of prepared with the help of Lewis model which explains guideline for bonding of atom. It guides about the covalent bonds which are formed in various combinations of single, double and triple bonds.
Single covalent bond occurs by sharing one pair of electrons and can be represented by single line in between atoms.
Double and triple bonds are formed when two and three pairs of electrons are shared in between atoms respectively and can be represented by two or three lines in between the atoms.
For several covalent bonds in organic compound containing carbon bonded to hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine and oxygen shows some important points to be noted for structure are as follow:
- Carbon forms four covalent bonds while hydrogen form one covalent bond and both has no unshared pair of electrons.
- Three covalent bonds are formed in nitrogen atom with only one unshared pair of electron left behind.
- Oxygen can form two covalent bonds and have further more two unshared pair of electron.
- Iodine, chlorine, bromine and fluorine like halogens can form only one covalent bond like hydrogen but they have three unshared pair of electrons.
To draw Lewis structure for a hydroxyl group, following are the steps:
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure formula with all valence electrons should be drawn for a primary
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structures can be prepared by following some point for any compound as mentioned below:
- Find out number of valence electrons present in the molecule
- The connectivity o atoms need to be understood like which atoms are linked with each other and connect them with covalnet bonds
- The arrangements of electrons in proper manner to achieve complete outer shell
Answer to Problem 23P
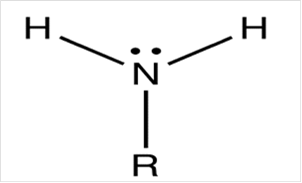
To draw Lewis structure for a primary amino group:
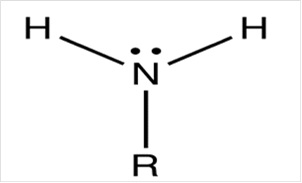
Explanation of Solution
The structure of any atom of prepared with the help of Lewis model which explains guideline for bonding of atom. It guides about the covalent bonds which are formed in various combinations of single, double and triple bonds.
Single covalent bond occurs by sharing one pair of electrons and can be represented by single line in between atoms.
Double and triple bonds are formed when two and three pairs of electrons are shared in between atoms respectively and can be represented by two or three lines in between the atoms.
For several covalent bonds in organic compound containing carbon bonded to hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine and oxygen shows some important points to be noted for structure are as follow:
- Carbon forms four covalent bonds while hydrogen form one covalent bond and both has no unshared pair of electrons.
- Three covalent bonds are formed in nitrogen atom with only one unshared pair of electron left behind.
- Oxygen can form two covalent bonds and have further more two unshared pair of electron.
- Iodine, chlorine, bromine and fluorine like halogens can form only one covalent bond like hydrogen but they have three unshared pair of electrons.
To draw Lewis structure for a carbonyl group, following are the steps:
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure formula with all valence electrons should be drawn for an ester group.
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structures can be prepared by following some point for any compound as mentioned below:
- Find out number of valence electrons present in the molecule
- The connectivity o atoms need to be understood like which atoms are linked with each other and connect them with covalnet bonds
- The arrangements of electrons in proper manner to achieve complete outer shell
Answer to Problem 23P
To draw Lewis structure for an ester group:
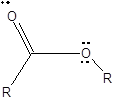
Explanation of Solution
The structure of any atom of prepared with the help of Lewis model which explains guideline for bonding of atom. It guides about the covalent bonds which are formed in various combinations of single, double and triple bonds.
Single covalent bond occurs by sharing one pair of electrons and can be represented by single line in between atoms.
Double and triple bonds are formed when two and three pairs of electrons are shared in between atoms respectively and can be represented by two or three lines in between the atoms.
For several covalent bonds in organic compound containing carbon bonded to hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine and oxygen shows some important points to be noted for structure are as follow:
- Carbon forms four covalent bonds while hydrogen form one covalent bond and both has no unshared pair of electrons.
- Three covalent bonds are formed in nitrogen atom with only one unshared pair of electron left behind.
- Oxygen can form two covalent bonds and have further more two unshared pair of electron.
- Iodine, chlorine, bromine and fluorine like halogens can form only one covalent bond like hydrogen but they have three unshared pair of electrons.
To draw Lewis structure for an ester group, following are the steps:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
EP INTRO.TO GENERAL,ORGANIC...-OWL ACCE
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning




