
(a) Interpretation:
The structure of Cis-9-Dodecenoic acid should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The cis-9-dodecenoic acid is an isomer of a 9-dodecenoic acid having a cis configuration. The linear chain of this fatty acid consists of 12 carbons, with the terminal ends having a carboxyl group.
Explanation of Solution
The fatty acid Cis-9-Dodecenoic acid having 12 carbon chain and a cis configuration is depicted in the figure given below:
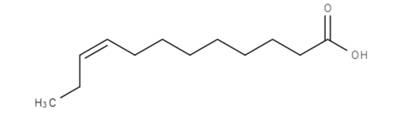
(b) Interpretation:
The structure of 18:1cΔ11 should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The 18:1cΔ11 fatty acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid, in this the number 18 depicts the number of carbon atoms in the linear chain, 1 represents a single unsaturation site, cΔ11 represents the presence of unsaturation at the 11th carbon.
Explanation of Solution
The fatty acid 18:1cΔ11 having 18 carbon chain and with an unsaturation on the 11th carbon is depicted in the figure given below:
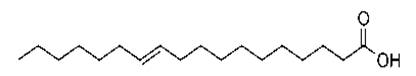
(c) Interpretation:
The structure of a saturated fatty acid that should melt below 300C should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The fatty acids having a lighter chain tends to melt at a lower temperature. Increase in the number of carbons increases the melting point of the fatty acids. The n-octanoic acid is well known to melt at a temperature of 16-170C.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of n-octanoic acid having a melting point 16-170C is depicted in the figure given below:
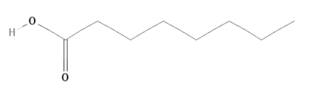
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Pearson eText for Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
- 10. Which one of the following compounds is the major organic product of the series of reactions shown here? Ph A OH Ph B CO₂Et Br -H Ν ΚΑ CO₂Et 1. NaOEt 1. NaOH, H₂O 2. H3O+ 2. PhCH2CH2Br 3. heat NH2 Ph OH NH2 0 OH Ph OH NH2 Ph D NH2 E OHarrow_forward1. What is the isoelectric point of glutamic acid? (Glutamic acid has pKa1 2.10, pKa2 4.07, pKaз 9.47) A) pH 2.1 D) pH 6.8 B) pH 3.1 C) pH 4.1 E) pH 9.5 HO NH2 Glutamic acid (shown without charges) OHarrow_forwardBr Mg, ether 1. HCHO (formaldehyde) 2. H+, H₂O PCC 1. NH3, HCN ? (pyridinium chlorochromate) 2. H2O, HCI 11. Which one of the following compounds is the major organic product of the series of reactions shown above? Ph. Ph. OH NH2₂ A Ph. Ή NH2 B OH Ph Η Ph OH NH2 NH2₂ NH₂ C D Earrow_forward
- B A 6. Which ONE of the labeled bonds in the tripeptide on the right is a peptide bond: H₂N N 'N' OH C H A, B, C, D or E? HN E OHarrow_forwardQuestions 8-9 are 0.4 points each. The next two questions relate to the peptide whose structure is shown here. To answer these questions, you should look at a table of H2N/.. amino acid structures. You don't have to memorize the structures of the amino acids. IZ 8. What is the N-terminal amino acid of this peptide? A) proline B) aspartic acid C) threonine 9. What is the C-terminal amino acid of this peptide? A) proline B) aspartic acid C) threonine N OH D) valine E) leucine D) valine E) leucine NH "OH OHarrow_forward7. What is the correct name of the following tripeptide? A) Ile-Met-Ser B) Leu-Cys-Thr C) Val-Cys-Ser D) Ser-Cys-Leu E) Leu-Cys-Ser H₂N!!!!! N H ΖΙ .SH SF H IN OH OHarrow_forward
- Please draw out the following metabolic pathways: (Metabolic Map) Mitochondrion: TCA Cycle & GNG, Electron Transport, ATP Synthase, Lipolysis, Shuttle Systems Cytoplasm: Glycolysis & GNG, PPP (Pentose Phosphate Pathway), Glycogen, Lipogenesis, Transporters and Amino Acids Control: Cori/ Glc-Ala cycles, Insulin/Glucagon Reg, Local/Long Distance Regulation, Pools Used Correctlyarrow_forwardPlease help provide me an insight of what to draw for the following metabolic pathways: (Metabolic Map) Mitochondrion: TCA Cycle & GNG, Electron Transport, ATP Synthase, Lipolysis, Shuttle Systems Cytoplasm: Glycolysis & GNG, PPP (Pentose Phosphate Pathway), Glycogen, Lipogenesis, Transporters and Amino Acids Control: Cori/ Glc-Ala cycles, Insulin/Glucagon Reg, Local/Long Distance Regulation, Pools Used Correctlyarrow_forwardwrite ionization equilibriumarrow_forward
- write the ionization equilibrium for cysteine and calculate the piarrow_forwardplease answerarrow_forwardf. The genetic code is given below, along with a short strand of template DNA. Write the protein segment that would form from this DNA. 5'-A-T-G-G-C-T-A-G-G-T-A-A-C-C-T-G-C-A-T-T-A-G-3' Table 4.5 The genetic code First Position Second Position (5' end) U C A G Third Position (3' end) Phe Ser Tyr Cys U Phe Ser Tyr Cys Leu Ser Stop Stop Leu Ser Stop Trp UCAG Leu Pro His Arg His Arg C Leu Pro Gln Arg Pro Leu Gin Arg Pro Leu Ser Asn Thr lle Ser Asn Thr lle Arg A Thr Lys UCAG UCAC G lle Arg Thr Lys Met Gly Asp Ala Val Gly Asp Ala Val Gly G Glu Ala UCAC Val Gly Glu Ala Val Note: This table identifies the amino acid encoded by each triplet. For example, the codon 5'-AUG-3' on mRNA specifies methionine, whereas CAU specifies histidine. UAA, UAG, and UGA are termination signals. AUG is part of the initiation signal, in addition to coding for internal methionine residues. Table 4.5 Biochemistry, Seventh Edition 2012 W. H. Freeman and Company B eviation: does it play abbreviation:arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON





