
Concept explainers
1.
Find the
1.
Answer to Problem 16CAP
The mean difference for the difference scoresis –0.8.
The standard deviationfor the difference scores is 2.8.
The standard errorfor the difference scores is 1.3.
Explanation of Solution
Calculations:
From the Question 15, the calculated difference scores are –4, 1, –2, –2, and 3.
The formula for sample mean difference score is,
The formula for sample standard deviation difference score is,
The formula for sample standard errorof difference score is,
Where D is difference in scores, and
Mean for the difference:
Substitute, the values for difference scores, –4, 1, –2, –2, 3 and
Thus, the mean for the difference scores is –0.8.
Standard deviation for the difference scores:
Substitute, the values for difference scores, –4, 1, –2, –2, 3 ,
Thus, the standard deviation for the difference scores is 2.8.
Standard error for the difference scores:
Substitute,
Thus, the standard error for the difference scores is 1.3.
2.
Sketch the shape of the distribution of mean difference scores
2.
Answer to Problem 16CAP
The shape of the distribution of mean difference scores
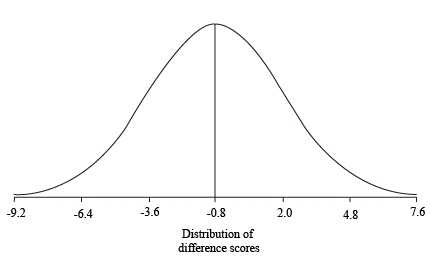
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The value of
For 1 standard deviation:
For two standard deviations:
For three standard deviations:
Thus, the standard deviation limits for the distribution are
Sketch of Graph:
Step by step procedure for sketching the graph:
- The mean of the distribution is taken in the centre of the graph.
- The one standard deviation limits are taken on either side of the mean.
- The two standard deviations limits are taken on either side of one standard deviation limits.
- The three standard deviations limits are taken on either side of two standard deviations limits.
- Draw the graph.
3.
Sketch the shape of the distribution of mean difference scores
3.
Answer to Problem 16CAP
The shape of the distribution of mean difference scores
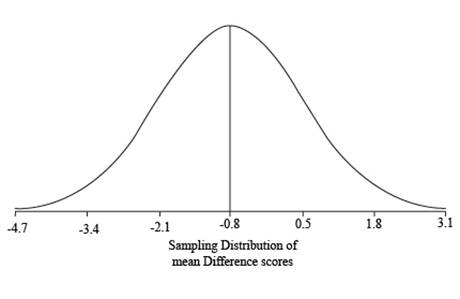
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The value of
For 1 standard deviation:
For two standard deviations:
For three standard deviations:
Thus, the standard deviation limits for the distribution are
Sketch of Graph:
Step by step procedure for sketching the graph:
- The mean of the distribution is taken in the centre of the graph.
- The one standard deviation limits are taken on either side of the mean.
- The two standard deviations limits are taken on either side of one standard deviation limits.
- The three standard deviations limits are taken on either side of two standard deviations limits.
- Draw the graph.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
STAT. FOR BEHAVIORAL SCIENCES WEBASSIGN
- Students - Term 1 - Def X W QUAT6221wA1.docx X C Chat - Learn with Chegg | Cheg X | + w:/r/sites/TertiaryStudents/_layouts/15/Doc.aspx?sourcedoc=%7B2759DFAB-EA5E-4526-9991-9087A973B894% QUAT6221wA1 Accessibility Mode பg Immer The following table indicates the unit prices (in Rands) and quantities of three consumer products to be held in a supermarket warehouse in Lenasia over the time period from April to July 2025. APRIL 2025 JULY 2025 PRODUCT Unit Price (po) Quantity (q0)) Unit Price (p₁) Quantity (q1) Mineral Water R23.70 403 R25.70 423 H&S Shampoo R77.00 922 R79.40 899 Toilet Paper R106.50 725 R104.70 730 The Independent Institute of Education (Pty) Ltd 2025 Q Search L W f Page 7 of 9arrow_forwardCOM WIth Chegg Cheg x + w:/r/sites/TertiaryStudents/_layouts/15/Doc.aspx?sourcedoc=%7B2759DFAB-EA5E-4526-9991-9087A973B894%. QUAT6221wA1 Accessibility Mode Immersi The following table indicates the unit prices (in Rands) and quantities of three meals sold every year by a small restaurant over the years 2023 and 2025. 2023 2025 MEAL Unit Price (po) Quantity (q0)) Unit Price (P₁) Quantity (q₁) Lasagne R125 1055 R145 1125 Pizza R110 2115 R130 2195 Pasta R95 1950 R120 2250 Q.2.1 Using 2023 as the base year, compute the individual price relatives in 2025 for (10) lasagne and pasta. Interpret each of your answers. 0.2.2 Using 2023 as the base year, compute the Laspeyres price index for all of the meals (8) for 2025. Interpret your answer. Q.2.3 Using 2023 as the base year, compute the Paasche price index for all of the meals (7) for 2025. Interpret your answer. Q Search L O W Larrow_forwardQUAI6221wA1.docx X + int.com/:w:/r/sites/TertiaryStudents/_layouts/15/Doc.aspx?sourcedoc=%7B2759DFAB-EA5E-4526-9991-9087A973B894%7 26 QUAT6221wA1 Q.1.1.8 One advantage of primary data is that: (1) It is low quality (2) It is irrelevant to the purpose at hand (3) It is time-consuming to collect (4) None of the other options Accessibility Mode Immersive R Q.1.1.9 A sample of fifteen apples is selected from an orchard. We would refer to one of these apples as: (2) ھا (1) A parameter (2) A descriptive statistic (3) A statistical model A sampling unit Q.1.1.10 Categorical data, where the categories do not have implied ranking, is referred to as: (2) Search D (2) 1+ PrtSc Insert Delete F8 F10 F11 F12 Backspace 10 ENG USarrow_forward
- epoint.com/:w:/r/sites/TertiaryStudents/_layouts/15/Doc.aspx?sourcedoc=%7B2759DFAB-EA5E-4526-9991-9087A 23;24; 25 R QUAT6221WA1 Accessibility Mode DE 2025 Q.1.1.4 Data obtained from outside an organisation is referred to as: (2) 45 (1) Outside data (2) External data (3) Primary data (4) Secondary data Q.1.1.5 Amongst other disadvantages, which type of data may not be problem-specific and/or may be out of date? W (2) E (1) Ordinal scaled data (2) Ratio scaled data (3) Quantitative, continuous data (4) None of the other options Search F8 F10 PrtSc Insert F11 F12 0 + /1 Backspaarrow_forward/r/sites/TertiaryStudents/_layouts/15/Doc.aspx?sourcedoc=%7B2759DFAB-EA5E-4526-9991-9087A973B894%7D&file=Qu Q.1.1.14 QUAT6221wA1 Accessibility Mode Immersive Reader You are the CFO of a company listed on the Johannesburg Stock Exchange. The annual financial statements published by your company would be viewed by yourself as: (1) External data (2) Internal data (3) Nominal data (4) Secondary data Q.1.1.15 Data relevancy refers to the fact that data selected for analysis must be: (2) Q Search (1) Checked for errors and outliers (2) Obtained online (3) Problem specific (4) Obtained using algorithms U E (2) 100% 高 W ENG A US F10 点 F11 社 F12 PrtSc 11 + Insert Delete Backspacearrow_forwardA client of a commercial rose grower has been keeping records on the shelf-life of a rose. The client sent the following frequency distribution to the grower. Rose Shelf-Life Days of Shelf-Life Frequency fi 1-5 2 6-10 4 11-15 7 16-20 6 21-25 26-30 5 2 Step 2 of 2: Calculate the population standard deviation for the shelf-life. Round your answer to two decimal places, if necessary.arrow_forward
- A market research firm used a sample of individuals to rate the purchase potential of a particular product before and after the individuals saw a new television commercial about the product. The purchase potential ratings were based on a 0 to 10 scale, with higher values indicating a higher purchase potential. The null hypothesis stated that the mean rating "after" would be less than or equal to the mean rating "before." Rejection of this hypothesis would show that the commercial improved the mean purchase potential rating. Use = .05 and the following data to test the hypothesis and comment on the value of the commercial. Purchase Rating Purchase Rating Individual After Before Individual After Before 1 6 5 5 3 5 2 6 4 6 9 8 3 7 7 7 7 5 4 4 3 8 6 6 What are the hypotheses?H0: d Ha: d Compute (to 3 decimals).Compute sd (to 1 decimal). What is the p-value?The p-value is What is your decision?arrow_forwardWhy would you use a histograph or bar graph? Which would be better and why for the data shown.arrow_forwardPlease help me with this question on statisticsarrow_forward
- Please help me with this statistics questionarrow_forwardPlease help me with the following statistics questionFor question (e), the options are:Assuming that the null hypothesis is (false/true), the probability of (other populations of 150/other samples of 150/equal to/more data/greater than) will result in (stronger evidence against the null hypothesis than the current data/stronger evidence in support of the null hypothesis than the current data/rejecting the null hypothesis/failing to reject the null hypothesis) is __.arrow_forwardPlease help me with the following question on statisticsFor question (e), the drop down options are: (From this data/The census/From this population of data), one can infer that the mean/average octane rating is (less than/equal to/greater than) __. (use one decimal in your answer).arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

