
1.
Prepare
1.
Explanation of Solution
Bonds: Bonds are long-term promissory notes that are issued by a company while borrowing money from investors to raise fund for financing the operations.
Journal:
Journal is the method of recording monetary business transactions in chronological order. It records the debit and credit aspects of each transaction to abide by the double-entry system.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
| Date | Accounts and Explanations | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2017 | ||||
| January | 1 | Cash (A+) | 493,608 | |
| Premium on Bonds Payable (L+) (1) | 43,608 | |||
| Bonds Payable (L+) | 450,000 | |||
| (To record sale of bonds on states issue date) | ||||
Table (1)
- Cash is an asset account. The amount has increased because bonds are issued at a premium; therefore, debit Cash account with $493,608.
- Premium on Bonds Payable is an adjunct account to Bonds Payable account and it has a normal credit balance; therefore, credit Premium on Bonds Payable account with $43,608.
- Bonds Payable is a liability account and it is increased therefore; credit Bonds Payable account with 450,000.
Working note:
Calculate premium on bonds payable:
2.
Ascertain the total bond interest expense recognized.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Bond interest expense:
Bond interest expense is the interest charged by the bondholders at a certain rate of interest.
Calculate the bond interest expense:
| Particulars | Amount |
| Eight payments of interest | $234,000 |
| Par value at maturity | $450,000 |
| Total repaid | $684,000 |
| Less: amount borrowed | ($493,608) |
| Total bond interest expense | $190,392 |
Table (2)
Note: Eight payments of interest=$234,000
Working note:
Calculate the semi-annual face interest rate:
Calculate amount of interest payable.
Calculate the number of periods for semi-annual interest payment:
3.
Prepare an effective interest amortization table for the first two years of bonds.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Amortization of bond:
The process of allocation and reduction of the discount or premium on bonds to interest expense over the life of bonds is referred to as amortization of bonds.
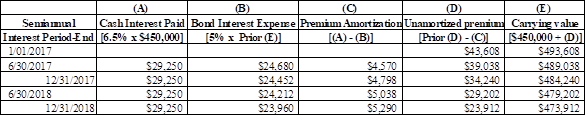
Table (3)
Note: 6.5 % is semi-annual face interest rate and 5 % is semi-annual market interest rate.
4.
Prepare the journal entries to record the first two interest payments
4.
Explanation of Solution
Journal:
Journal is the method of recording monetary business transactions in chronological order. It records the debit and credit aspects of each transaction to abide by the double-entry system.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
Journalize the entry for the issue of bonds:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| 2017 | Bond interest Expense [Refer to table(3) ] | 24,680 | |
| June 30 | Premium on Bonds payable [Refer to table(3) ] | 4,570 | |
| Cash (3) | 29,250 | ||
| (To record six months’ interest and premium amortization.) |
Table (4)
- Bond Interest Expense is a component of
stockholders equity. There is an increase in the expense account which decreased the stockholders’ equity. Therefore, debit interest expense account by $24,680. - Premium on Bonds payable is a contra liability account. The amount is decreased since the premium is amortized therefore; debit Premium on Bonds Payable account by $4,570.
- Cash is an asset and it is decreased. Therefore cash is credited by $29,250.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| 2017 | Bond interest Expense [Refer to table(3) ] | 24,452 | |
| December 30 | Premium on Bonds payable [Refer to table(3) ] | 4,798 | |
| Cash (3) | 29,250 | ||
| (To record six months’ interest and premium amortization.) |
Table (5)
- Bond Interest Expense is a component of stockholders equity. There is an increase in the expense account which decreased the stockholders’ equity. Therefore, debit interest expense account by $24,452.
- Premium on Bonds payable is a contra liability account. The amount is decreased since the premium is amortized therefore; debit Premium on Bonds Payable account by $4,798.
- Cash is an asset and it is decreased. Therefore cash is credited by $29,250.
5.
Prepare the journal entries to record retirement of bonds.
5.
Explanation of Solution
Retirement of Bonds:
The process of repaying the sale amount of bonds to bondholders at the time of maturity or before the maturity period is called as redemption of bonds. It is otherwise called as redemption of bonds.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | Bonds Payable | 450,000 | ||
| January 1 | Premium on bonds payable [Refer to table(3) ] | 23,912 | ||
| Loss on retirement of bonds | 3,088 | |||
| Cash (5) | 477,000 | |||
| (To record the retirement of bonds) | ||||
Table (6)
- Bonds Payable is a liability account and it is decreased. Therefore, debit Bonds Payable account by $450,000.
- Premium on bonds payable is an adjunct-liability and it is decreased by $23,912. Therefore, debit premium on bonds payable account by $23,912.
- Loss on retirement of bonds is a component of stockholders’ equity and the amount is decreased. Therefore debit loss on retirement of bonds by 3,088.
- Cash is an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore credit cash account by $477,000.
Working notes:
Calculate market price paid to retire the bonds.
Calculate loss on retirement of bonds payable.
6.
Describe the effect of change in market rate on the financial statements of Company I.
6.
Explanation of Solution
Financial statements: Financial statements are condensed summary of transactions communicated in the form of reports for the purpose of decision making.
- The bonds would have sold at a discount if the market rate on the issue date has been 14 % instead of 10 % because the contract rate (13%) is lower than the market rate.
- This change affects the
balance sheet as the bond liability would be smaller because the bond liability will increase with amortization of the discount instead of decreasing with amortization of the premium. - The larger amount of interest expense is stated in the income statement over the life of the bonds issued at a discount than it would show if the bonds are issued at a premium.
- The cash received from borrowing is smaller in the statement of
cash flows . But the cash flow prepared over the life of the bonds after its issuance reports the same amount of cash paid for interest.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Financial Accounting Fundamentals
- Acme Corporation purchases machinery for $78,000 with a salvage value of $8,000 and an expected useful life of 7 years. What is the annual depreciation expense using the straight-line method? Helparrow_forwardI need help with this general accounting question using standard accounting techniques.arrow_forwardWhat must the sales be in dollars? In units?arrow_forward
- Jones Co. had $61,500 in sales during 2025. During the year, Jones purchased $18,400 in inventory. The company began the year with $4,100 in inventory and ended the year with $1,300 in inventory. In addition, during 2025, Jones received a prepayment of $2,500, which was correctly classified as unearned revenue. What was Jones's gross profit during 2025? A. $38,000 B. $40,300 C. $39,600 D. $42,100 E. None of the abovearrow_forwardI need the correct answer to this financial accounting problem using the standard accounting approach.arrow_forwardQuine Industries has fixed costs of $600,000 and variable costs are 60% of the selling price. To realize profits of $250,000 from sales of 500,000 units, the selling price per unit: 1. Must be $2.60 2. Must be $3.50 3. Must be $4.25 4. Is indeterminablearrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





