
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
In a chloroform-filled open end manometer instead of mercury, the level in the arm connected to the gas sample has a pressure of 0.788 atm and the other arm open to the atmosphere has the atmospheric pressure reading of 0.849 atm. Calculate the height difference between the level of chloroform in both arms and which arm has a high level of chloroform.
Concept introduction:
Pressure is force per unit area.
Its unit is Newton per meter square or can say kilogram per meter per Second Square. These two are not the only units of pressure. The International system of unit (S.I unit) of pressure is Pascal, but these are not the only units of pressure. There are more units of pressure like pounds per square inch, atmospheric (atm), mm Hg, torr etc.
Pressure is measured in the U-tube as shown below: The pressure is measured by filling water into this tube so that the difference between the lengths of two sides of the U-tube gives an idea about the pressure. In this tube, one end is kept at the room atmospheric pressure and the other side to that whose pressure has to be measured. This is the reason for using different units of pressure because the length can be measured in different units. In case of water, there would be a requirement of a large U-tube; hence mercury is used instead of water because its density is more than that of water. So, another unit of pressure was invented that is mmHg.
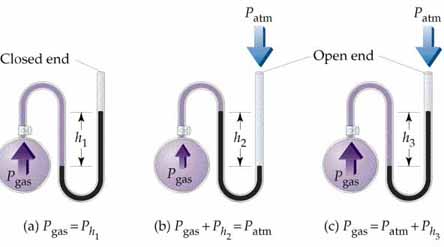
To determine:
The height difference between the two arms of the manometer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Chemistry, Books a la Carte Plus Mastering Chemistry with eText -- Access Card Package (7th Edition)
- Draw an example of the following functional groups: *see imagearrow_forwardAldehydes and Ketones: Show the reaction conditions, and molecules, that connect the reactant to the product. A protecting group will be needed. *see imagearrow_forwardAldehydes and Ketones: Show the reaction conditions, and molecules, that connect the reactant to the product. *see imagearrow_forward
- Provide the missing information for each of the four reactions: *see imagearrow_forward6. Chlorine dioxide (CIO) is used as a disinfectant in municipal water-treatment plants. It decomposes in a first-order reaction with a rate constant of 14 s. How long would it take for an initial concentration of 0.06 M to decrease to 0.02 M? [6 pts]arrow_forwardIf possible, replace an H atom on the a carbon of the molecule in the drawing area with a methyl group substituent, and replace an H atom on the ẞ carbon with a hydroxyl group substituent. If one of the substituents can't be added for any reason, just don't add it. If neither substituent can be added, check the box under the drawing area. en HO OHarrow_forward
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the curved arrows to draw the intermediate and product of this hydrohalogenation reaction. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Br Select to Draw 51°F Sunny esc F1 HBr Select to Draw 1,2-hydride shift Br Select to Draw Q Search F2 F3 F4 1 2 # # 3 DII L F5 F6 F tA $ % Λarrow_forwardplease help i cant find the article to even startarrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forward
- help with the rf values i am so confusedarrow_forwardPredict the organic reactant of X and Y that are involved in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactant. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardPredict the major organic product for this reaction.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





