
(a)
Interpretation: The compound that is likely to be more soluble in 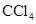 among the given pair is to be predicted.
among the given pair is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: The polarity of solute and solvent determines the solubility solution. Solute and solvent of same polarity are soluble with each other and insoluble if polarity is different.
To determine: The compound that is likely to be more soluble in 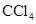 among the given pair.
among the given pair.
(a)
Answer to Problem 10.42QP
Solution
The solubility of 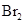 in
in 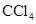 is more than that of
is more than that of 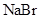 .
.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The dipole moment of the given compound is important for its solubility in 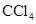 . The dipole moment of
. The dipole moment of 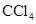 is zero and it solubilizes only non-polar compounds.
is zero and it solubilizes only non-polar compounds.
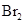 is a non-polar compound whereas
is a non-polar compound whereas 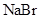 is a polar compound. Therefore,
is a polar compound. Therefore, 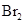 is more soluble in
is more soluble in 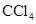 than
than 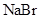 .
.
(b)
To determine: The compound that is likely to be more soluble in 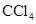 among the given pair.
among the given pair.
(b)
Answer to Problem 10.42QP
Solution
The solubility of 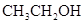 in
in 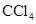 is more than that of
is more than that of 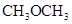 .
.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The polarity of ethanol in comparison to acetone is more because in ethanol, oxygen is attached to one carbon atom, whereas in acetone it lies between two carbon atoms and they cancel out each other.
Therefore, acetone being less polar solubilizes more in 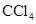 than ethanol.
than ethanol.
(c)
To determine: The compound that is likely to be more soluble in 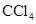 among the given pair.
among the given pair.
(c)
Answer to Problem 10.42QP
Solution
The solubility of 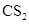 in
in 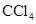 is more than that of
is more than that of 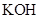 .
.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The given compound 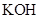 is ionic compound and
is ionic compound and 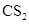 is a non-ionic compound.
is a non-ionic compound.
Ionic compounds are polar in nature and solubilize in polar solvent.
Therefore, 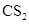 being non-polar compound solubilizes more in
being non-polar compound solubilizes more in 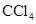 than
than 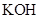 .
.
(d)
To determine: The compound that is likely to be more soluble in 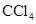 among the given pair.
among the given pair.
(d)
Answer to Problem 10.42QP
Solution
The solubility of 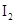 in
in 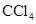 is more than that of
is more than that of 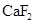 .
.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The given compounds are 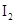 and
and 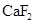 . Iodine is non-polar compound as its dipole moment is zero whereas
. Iodine is non-polar compound as its dipole moment is zero whereas 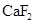 is ionic molecule and polar in nature. Therefore,
is ionic molecule and polar in nature. Therefore, 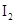 being non-polar compound solubilizes more in
being non-polar compound solubilizes more in 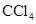 than
than 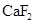 .
.
Conclusion
- a. The solubility of
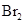 in
in 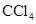 is more than that of
is more than that of 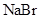 .
. - b. The solubility of
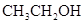 in
in 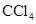 is more than that of
is more than that of 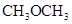 .
. - c. The solubility of
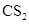 in
in 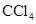 is more than that of
is more than that of 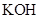 .
. - d. The solubility of
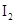 in
in 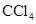 is more than that of
is more than that of 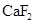 .
.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
CHEMISTRY:SCI.IN CONTEXT (CL)-PACKAGE
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





