
Concept explainers
Exercise 14-9 Preparing financial statements for a manufacturer C4 P2
Refer to the data in Exercise 14-8. For each company, prepare (1) an income statement, and (2) the current assets section of the
Income Statement:
Income statement gives a detail representation of the revenues generated and the expenses incurred by the company in a fiscal year thereby concluding the company’s financial status. It is a financial statement which deals with operating and non-operating activities of the company.
Net Income:
Net income is the net revenue earned by the company after taking into account various charges, costs, expenses and deductions. The net income is crucial for the shareholders and gives an idea of profitability level of the company.
Balance Sheet:
The balance sheet concludes the assets invested in by the company as well as reports the liabilities and equity taken up thus showing the economic or financial status of the company.
Current Assets:
It comprises of all the assets which gets converted into cash in less than a year. Example: inventory, other current assets, etcetera.
Operating Expenses:
The costs incurred in the day to day operations to continue with the business though not related directly with the production of goods are termed as operating expenses.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS):
Cost of goods sold is the total expense or the cost incurred by the business during the process of manufacturing of goods and is directly related to the production. It generally includes the cost of material, labor and other manufacturing support costs.
(1)
To prepare: an income statement for each of the company.
Explanation of Solution
Given info,
G Company:
Sales amounts to $195,030
Selling expenses are of $50,000
Administrative and general expenses are $21,000.
For cost of goods sold of G Company refer to the question 91,030.
P Company:
Sales amount to $290,000.
Selling expenses are $46,000.
Administrative and general expenses are $43,000.
For cost of goods sold of $143,010 refer to question 8E.
Formula to calculate income before tax is,
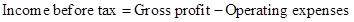
Income statement for G Company
Income before tax:
| G Company | |
| Income Statement | |
| For the Year Ended 31 December, 2017 | |
| Particulars | Amount($) |
| Sales | 195,030 |
| Less: Cost of goods sold | (91,030) |
| Gross profit | 104,000 |
| Add: | |
| Selling expenses | 50,000 |
| Administrative and general expenses | 21,000 |
| Income before tax | 33,000 |
Table (1)
The income before tax for G Company amounts to $33,000.
Note: Selling expenses and administrative and general expenses are operating expenses thus taken up to compute income before tax.
Income statement for P Company
Income before tax:
| P Company | |
| Income Statement | |
| For the Year Ended 31 December, 2017 | |
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Sales | 290,010 |
| Less: Cost of goods sold | (143,010) |
| Gross profit | 147,000 |
| Add: | |
| Selling expenses | 46,000 |
| Administrative and general expenses | 43,000 |
| Income before tax | 58,000 |
Table (2)
The income before tax for the P Company is $58,000.
Note: Selling expenses and administrative and general expenses are operating expenses thus taken up to compute income before tax.
(2)
To compute: Current assets for both the company.
Explanation of Solution
Given info,
G Company:
Cash amounts to $20,000.
Receivable accounts to $13,200.
Raw material inventory is $5,300.
Work in progress inventory is $22,000.
Finished goods amount to $17,650.
P Company:
Cash amounts to $15,700.
Receivable accounts to $19,450.
Raw material inventory $7,200.
Work in progress inventory is $16,000.
Finished goods amount to $13,300.
G Company’s current assets
| Particulars | Amount($) |
| Cash | 20,000 |
| Receivable accounts | 13,200 |
| Raw material inventory | 5,300 |
| Work in progress inventory | 22,000 |
| Finished inventory | 17,650 |
| Net current assets | 78,150 |
Table (3)
Current assets account to $79,150 for G Company.
P Company’s current assets
| Particulars | Amount($) |
| Cash | 15,700 |
| Receivables accounts | 19,450 |
| Raw material inventory | 7,200 |
| Work in progress inventory | 16,000 |
| Finished inventory | 13,300 |
| Net current assets | 71,650 |
Table (4)
P Company’s current assets amount to $71,650.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Managerial Accounting (Looseleaf)
- Can you solve this general accounting question with accurate accounting calculations?arrow_forwardUsing the above information provided for caspian manufacturing,what is the total standard unit cost?arrow_forwardI need guidance with this financial accounting problem using the right financial principles.arrow_forward
- Can you help me solve this financial accounting question using the correct financial procedures?arrow_forwardI am looking for help with this financial accounting question using proper accounting standards.arrow_forwardPlease explain the correct approach for solving this general accounting question.arrow_forward
 Accounting Information SystemsFinanceISBN:9781337552127Author:Ulric J. Gelinas, Richard B. Dull, Patrick Wheeler, Mary Callahan HillPublisher:Cengage Learning
Accounting Information SystemsFinanceISBN:9781337552127Author:Ulric J. Gelinas, Richard B. Dull, Patrick Wheeler, Mary Callahan HillPublisher:Cengage Learning Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning





