
Concept explainers
The post-closing
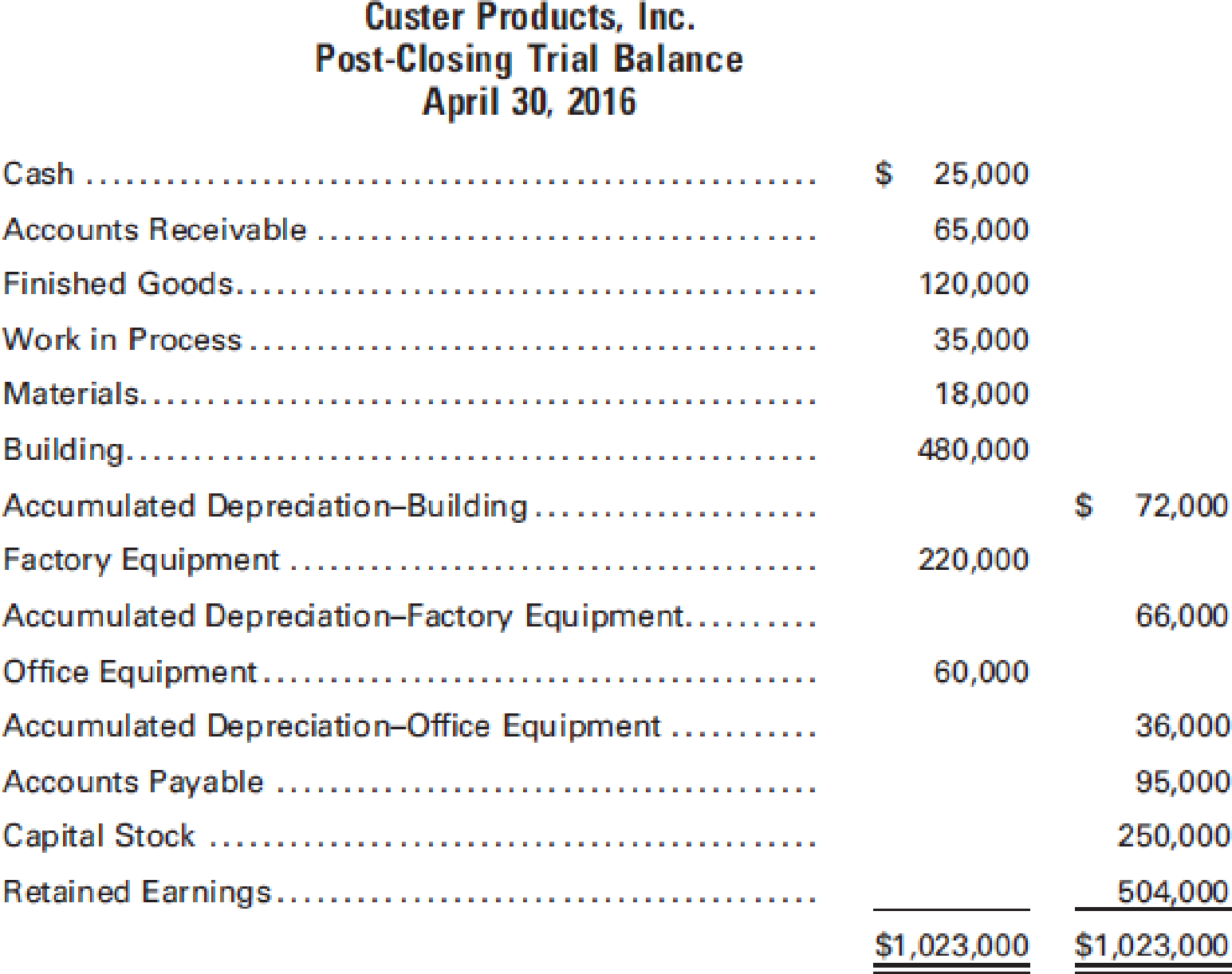
During May, the following transactions took place:
- a. Purchased raw materials at a cost of $45,000 and general factory supplies at a cost of $13,000 on account (recorded materials and supplies in the materials account).
- b. Issued raw materials to be used in production, costing $47,000, and miscellaneous factory supplies costing $15,000.
- c. Recorded the payroll and the payments to employees as follows: factory wages (including $12,000 indirect labor), $41,000; and selling and administrative salaries, $7,000. Additional account titles include Wages Payable and Payroll. (Ignore payroll withholdings and deductions.)
- d. Distributed the payroll in (c).
- e. Recognized
depreciation for the month at an annual rate of 5% on the building, 10% on the factory equipment, and 20% on the office equipment. The sales and administrative staff uses approximately one-fifth of the building for its offices. - f. Incurred other expenses totaling $11,000. One-fourth of this amount is allocable to the office function.
- g. Transferred total
factory overhead costs to Work in Process. - h. Completed and transferred goods with a total cost of $91,000 to the finished goods storeroom.
- i. Sold goods costing $188,000 for $362,000. (Assume that all sales were made on account.)
- j. Collected
accounts receivable in the amount of $345,000. - k. Paid accounts payable totaling $158,000.
Required:
- 1. Prepare
journal entries to record the transactions. - 2. Set up T-accounts. Post the beginning trial balance and the journal entries prepared in (1) to the accounts and determine the balances in the accounts on May 31.
- 3. Prepare a statement of cost of goods manufactured, an income statement, and a balance sheet. (Round amounts to the nearest whole dollar.)
1.
Prepare journal entry to record the given transactions.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry to record the given transactions.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| a | Materials | 58,000 | |
| Accounts payable | 58,000 | ||
| (To record materials purchased on account) | |||
| b | Work in Process | 47,000 | |
| Factory overhead | 15,000 | ||
| Materials | 62,000 | ||
| (To record issue of direct materials and indirect materials) | |||
| c | Payroll | 48,000 | |
| Wages Payable | 48,000 | ||
| (To record factory wages and salaries) | |||
| Wages Payable | |||
| Cash | |||
| (To record the payment of factory wages and salaries) | |||
| d | Work in Process | 29,000 | |
| Factory overhead | 12,000 | ||
| Selling and Administrative Expenses (salaries) | 7,000 | ||
| Payroll | 48,000 | ||
| (To record the distribution of payroll) | |||
| e | Factory overhead (Depreciation of building) (1) | 1,600 | |
| Factory overhead (Depreciation of factory equipment) (3) | 1,833 | ||
| Selling and Administrative Expenses (Depreciation of building) (2) | 400 | ||
| Selling and Administrative Expenses (Depreciation of office equipment) (4) | 1,000 | ||
| Accumulated Depreciation - Building | 2,000 | ||
| Accumulated Depreciation – Factory Equipment | 1,833 | ||
| Accumulated Depreciation – Office Equipment | 1,000 | ||
| (To record depreciation on building, factory equipment, and office equipment) | |||
| f | Factory overhead(miscellaneous) | 8,250 | |
| Selling and Administrative expenses (miscellaneous) | 2,750 | ||
| Accounts payable | 11,000 | ||
| (To record factory overhead costs and selling and administrative expenses on account) | |||
| g. | Work in Process | 38,683 | |
| Factory Overhead | 38,683 | ||
| (To record transfer of factory overhead to Work-in process) | |||
| h. | Finished Goods | 91,000 | |
| Work in Process | 91,000 | ||
| (To record the transfer of cost of completed work to finished goods) | |||
| i | Accounts receivable | 362,000 | |
| Sales | 362,000 | ||
| (To record the sale made on account) | |||
| Cost of goods sold | 188,000 | ||
| Finished goods | 188,000 | ||
| (To record the cost of goods sold) | |||
| j. | Cash | 345,000 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 345,000 | ||
| (To record the receipt on accounts receivable) | |||
| k | Accounts Payable | ||
| Cash | |||
| (To record the payment of accounts payable) |
Table (1)
Working note 1: Calculate depreciation on buildings under factory overhead.
Working note 2: Calculate depreciation on buildings under selling and administrative expenses.
Working note 3: Calculate depreciation on factory equipment under factory overhead.
Working note 4: Calculate depreciation on factory equipment under selling and administrative expenses.
2
Prepare t-account and post the beginning trial balance and journal entries amount to the particular account and determine the ending balance in the account.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare t-account and post the beginning trial balance and journal entries amount to the particular account and determine the ending balance in the account.
| Cash | ||||
|
Beginning balance | 25,000 | (c) | 48,000 | |
| (j) | 345,000 | (k) | 158,000 | |
| Ending Balance | 164,000 | |||
| Accounts Receivable | ||||
|
Beginning balance | 65,000 | (j) | 345,000 | |
| (i) | 362,000 | |||
| Ending Balance | 164,000 | |||
| Finished Goods | ||||
|
Beginning balance | 120,000 | (i) | 188,000 | |
| (h) | 91,000 | |||
| Ending Balance | 23,000 | |||
| Work in Process | ||||
|
Beginning balance | 35,000 | (i) | 188,000 | |
| (h) | 91,000 | |||
| Ending Balance | 23,000 | |||
| Materials | ||||
|
Beginning balance | 18,000 | (b) | 62,000 | |
| (a) | 58,000 | |||
| Ending Balance | 14,000 | |||
| Building | ||||
|
Beginning balance | 480,000 | |||
| Ending Balance | 480,000 | |||
| Accumulated depreciation-Building | |||||||
|
Beginning balance (e) |
72,000 2,000 | ||||||
| Ending Balance | 74,000 | ||||||
|
Factory equipment | |||||||
|
Beginning balance | 220,000 | ||||||
| Ending Balance | 220,000 | ||||||
| Accumulated depreciation- Factory equipment | |||||||
|
Beginning balance (e) |
66,000 1,833 | ||||||
| Ending Balance | 67,833 | ||||||
|
Office equipment | |||||||
|
Beginning balance | 60,000 | ||||||
| Ending Balance | 60,000 | ||||||
| Accumulated depreciation- Office equipment | ||||
|
Beginning balance (e) |
36,000 1,000 | |||
| Ending Balance | 37,000 | |||
| Accounts Payable | ||||
|
(j) | 158,000 |
Beginning balance (a) (f) |
92,000 58,000 11,000 | |
| Ending Balance | 14,000 | |||
| Payroll | ||||
|
Beginning balance | 0 | |||
| (c) | 48,000 | (d) | 48,000 | |
| Ending Balance | 0 | |||
| Wages payable | ||||
|
Beginning balance | 0 | |||
| (c) | 48,000 | (c) | 48,000 | |
| Ending Balance | 0 | |||
| Capital Stock | ||||
|
Beginning balance | 250,000 | |||
| Ending Balance | 250,000 | |||
| Retained Earnings | ||||
|
Beginning balance | 504,000 | |||
| Ending Balance | 504,000 | |||
| Sales | |||||
| (i) | 362,000 | ||||
| Cost of goods sold | |||||
| (i) | 188,000 | ||||
| Factory Overhead | |||||
|
(b) (d) (e) (e) (f) |
15,000 12,000 1,600 1,833 8,250 | (g) | 38,683 | ||
| Selling and administrative expenses | |||||
|
(d) (e) (e) (f) |
7,000 400 1,000 2,750 | ||||
| Ending Balance | 11,150 | ||||
3.
Prepare Incorporation C’s statement of cost of goods manufactured, income statement, and balance sheet.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare Incorporation C’s statement of cost of goods manufactured for the month ended May 31, 2016.
| Incorporation C | ||
| Statement of cost of goods manufactured | ||
| For the month ended May 31, 2016 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Direct materials: | ||
| Inventory, May 1 | 18,000 | |
| Add: Purchases | 58,000 | |
| Total cost of available materials | 76,000 | |
| Less: Inventory, May 31 | 14,000 | |
| Cost of materials used | 62,000 | |
| Less: Indirect materials used | 15,000 | |
| Cost of direct materials used in production | 47,000 | |
| Direct labor | 29,000 | |
| Factory Overhead: | ||
| Indirect materials | 15,000 | |
| Indirect labor | 12,000 | |
| Depreciation of building | 1,600 | |
| Depreciation of factory equipment | 1,833 | |
| Miscellaneous expenses | 8,250 | |
| Total factory overhead | 38,683 | |
| Total manufacturing cost | 114,683 | |
| Add: Work in process inventory, May 1 | 35,000 | |
| 149,683 | ||
| Less: work in process inventory, May 31 | 58,683 | |
| Cost of goods sold manufactured | 91,000 | |
Table (2)
Prepare Incorporation C’s income statement for the month ended May 31, 2016.
| Incorporation C | ||
| Income statement | ||
| For the month ended May 31, 2016 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Sales | 362,000 | |
| Cost of goods sold: | ||
| Finished goods inventory, May 1 | 120,000 | |
| Add: Cost of goods manufactured | 91,000 | |
| Goods available for sale | 211,000 | |
| Less: Finished goods inventory , May 31 | 23,000 | 188,000 |
| Gross profit on sales | 174,000 | |
| Selling and administrative expenses | 11,150 | |
| Net income | 162,850 | |
Table (3)
Prepare Incorporation C’s balance sheet at May 31, 2016.
| Incorporation C | |||
| Balance Sheet | |||
| At May 31, 2016 | |||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) | |
| Current Assets: | |||
| Cash | 164,000 | ||
| Accounts receivable | 82,000 | ||
| Inventories: | |||
| Finished goods | 23,000 | ||
| Work in process | 58,683 | ||
| Materials | 14,000 | 95,683 | |
| Total current assets | 341,683 | ||
| Plant and equipment: | |||
| Building | 480,000 | ||
| Less: Accumulated depreciation | 74,000 | 406,000 | |
| Factory equipment | 220,000 | ||
| Less: Accumulated depreciation | 67,833 | 152,167 | |
| Office equipment | 60,000 | ||
| Less: Accumulated depreciation | 37,000 | 23,000 | |
| Total plant and equipment | 581,167 | ||
| Total assets | 922,850 | ||
| Liabilities and stockholder’s equity | |||
| Current liabilities: | |||
| Accounts payable | 6,000 | ||
| Stockholder’s equity: | |||
| Capital stock | 250,000 | ||
| Retained earnings (5) | 666,850 | ||
| Total Stockholder’s equity | 916,850 | ||
| Total liabilities and stockholder’s equity | 922,850 | ||
Table (4)
Working note 5:
Calculate the amount of retained earnings.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Principles of Cost Accounting
- I am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardHow can I solve this financial accounting problem using the appropriate financial process?arrow_forwardCan you demonstrate the accurate steps for solving this financial accounting problem with valid procedures?arrow_forward
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College


