
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The equation that shows the reaction of the given acid with water by considering the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory is to be written. All the electron pairs, formal chargers and curved arrows that represent the electron movement in the respective reaction are to be shown.
Concept introduction:
An acid is a chemical substance that readily donates protons and a base is a chemical substance that can easily accept a proton. During an acid-base reaction, the interaction between an acid and a base is taken place because of the transfer of a proton. The stronger the acid, the smaller its
Answer to Problem 63P
Solution:
a)
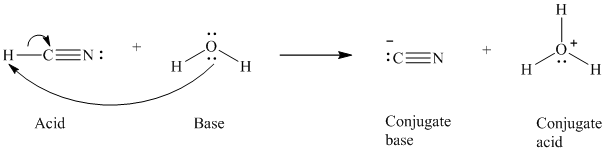
The formal charge on the the oxygen atom is
b)
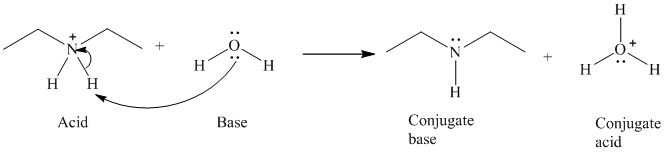
The formal charge on both the the oxygen atom and the nitrogen atom is
c)
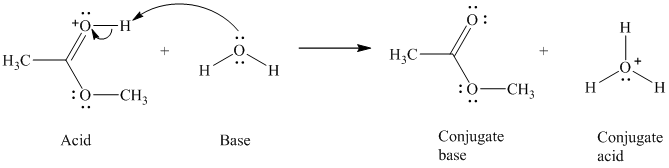 The formal charge on the oxygen atom is
The formal charge on the oxygen atom is
Explanation of Solution
a) The reaction of an acid with water.
In the respective reaction, the water acts as a base. The unshared electron pair of oxygen atom present in water is used to remove the proton from the acid. Water, after accepting the proton, is converted to its conjugate acid, that is, hydronium ion and the acid is converted to its conjugate base.
The curved arrows showing the electron movement is given below:
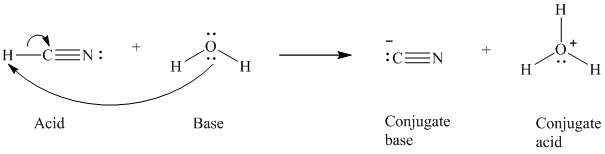
The formula that is used to calculate the electron count on the conjugate base is as follows:
Substitute
The formula that is used to calculate the formal charge on the oxygen atom is as follows:
Substitute
b) The reaction of an acid with water.
The given acid reacts with water. So water acts as a base. The unshared electron pair of the oxygen atom in water is used to remove the proton from the acid. Water, after accepting the proton is converted to its conjugate acid, that is, hydronium ion and the acid is converted to its conjugate base.
The curved arrows showing the electron movement are shown below:
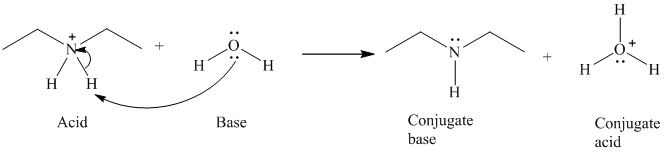
The formula that is used to calculate the electron count on the nitrogen atom is as follows:
Substitute
The formula that is used to calculate the formal charge on the nitrogen atom is as follows:
Substitute
For calculating formal charge on the oxygen atom, recall the electron count formula:
Substitute
Recall the formula for formal charge:
Substitute
c) The given acid reacts with water.
So water acts as a base. The unshared electron pair of the oxygen atom in water is used to remove the proton from the acid. Water, after accepting the proton, is converted to its conjugate acid, that is, hydronium ion and the acid is converted to its conjugate base.
The curved arrows showing the electron movement are shown below:
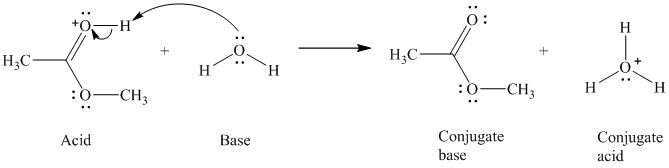
The formula that is used to calculate the electron count on the oxygen is as follows:
Substitute
The formula that is used to calculate the formal charge on the oxygen atom is as follows:
Substitute
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
CAREY: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Determine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forward
- Can I please get help with identifying these?arrow_forward4. Calculate the pH of a 0.10 M acetic acid (CH3COOH) solution if the Ka of acetic acid = 1.8 x 10-5arrow_forwardDraw the Zaitsev product of the dehydration of this alcohol. + I X 5 OH ざ~ TSOH Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning



