
Concept explainers
Citric acid is responsible for the tartness of citrus fruits, especially lemons and limes.
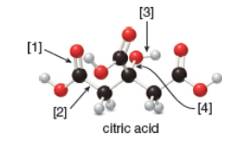
a. What is the molecular formula of citric acid?
b. How many lone pairs are present?
c. Draw a skeletal structure.
d. How many
e. What orbitals are used to form each indicated bond
(a)
Interpretation: The molecular formula of citric acid is to be stated.
Concept introduction: In ball-and-stick model, each colored ball represents a specific atom and each stick represents a bond. In this model, each black ball represents
Answer to Problem 40P
The molecular formula of citric acid is
Explanation of Solution
The given ball-and-stick model of citric acid is,
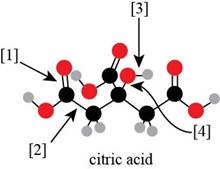
Figure 1
In ball-and-stick model, each colored ball represents a specific atom and each stick represents a bond. In this model, each black ball represents
In the above model,
• There are seven red balls. Thus, there are seven
• There are six black balls. Thus, there are six
• There are eight grey balls. Thus, there are eight
Hence, the molecular formula of citric acid is
The molecular formula of citric acid is
(b)
Interpretation: The number of lone pairs present in citric acid is to be stated.
Concept introduction: In a compound or molecule, the lone pairs represent number of unshared electrons on atom. An atom may or may not have unshared electrons. For example, carbon and hydrogen atoms have no lone pair but each oxygen atom has two lone pairs.
Answer to Problem 40P
There are total
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula of citric acid is
There are total
(c)
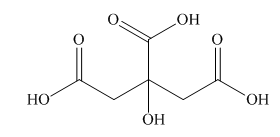
Interpretation: A skeletal structure of citric acid is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: A ball-and-stick model is converted into skeletal structure by replacing black ball with
Answer to Problem 40P
A skeletal structure of citric acid is,
Explanation of Solution
In ball-and-stick model each colored ball represents a specific atom and each stick represents a bond. A ball-and-stick model is converted into skeletal structure by replacing black ball with
A skeletal structure of citric acid is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2
In ball-and-stick model each colored ball represents a specific atom and each stick represents a bond.
(d)
Interpretation: The number of
Concept introduction: According to the rule of hybridization, an atom that is surrounded with two groups is
Answer to Problem 40P
There are three
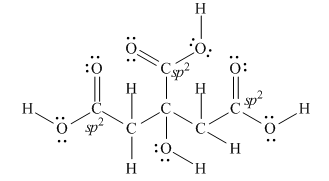
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis structure of citric acid is,
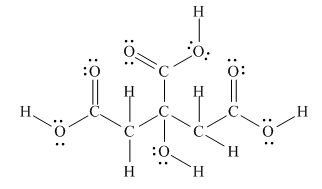
Figure 3
According to the rules of hybridization, an atom that is surrounded with two groups is
The

Figure 4
Thus, there are three
There are three
(e)
Interpretation: The orbitals that are used to form each indicated bond is to be stated.
Concept introduction: According to the rule of hybridization, an atom that is surrounded with two groups is
Answer to Problem 40P
Bond
Explanation of Solution
Bond [1] represents
Bond
Thus,
Bond
Thus,
Bond
The number of surrounded group around any atom predicts the hybridization of that atom, which is further helpful to predict the orbitals involve in bond formation.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY W/ALEKS
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- State the formula to find the electromotive force of a battery as a function of the potential of the anode and the cathode.arrow_forwardWhy are normal electrode potentials also called relative electrode potentials?arrow_forwardEasily differentiate between electrochemical potential and Galvani potential.arrow_forward
- Construct a molecular orbital diagram for carbon monoxide. Identify the relevant point group,include all of the appropriate symmetry labels and pictures, and fill in the electrons. Make sure toaccount for the difference in electronegativity between C and O. Hint: CO is substantiallyisoelectronic to N2. (PLEASE DRAW THE ENTIRE MO DIAGRAM!!!)arrow_forwardplease help with hwarrow_forwardhelp me solve this hwarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning



