
a.
Prepare horizontal analysis to show the affect of each event in the
a.
Explanation of Solution
Accounting event:
An accounting event is a cost-effective event that affects assets, liabilities, or
Horizontal statement model: In this model the analysts will analyse the effect of the transactions on balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows.
Prepare horizontal analysis:
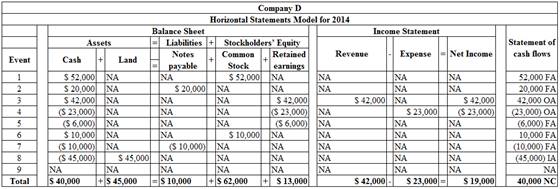
Table (1)
Note: FA represents financing activity, OA represents operating activity, IA represents investing activity NA represents no affect and NC represents no change.
b.
Report the amount of total assets that is reported on the December 31, 2014, balance sheet.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Balance sheet:
Balance is the financial statement that reports a company’s resources (assets) and claims of creditors (liabilities) and stockholders (stockholders’ equity) over those resources. The resources of the company are assets which include money contributed by stockholders and creditors. Hence, the main elements of the balance sheet are assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity.
Calculate the total amount of assets:
Therefore, the total amount of cash reported on the balance sheet is $85,000.
c.
Identify the asset source transactions and related amounts for 2014.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Assets source transaction:
Transaction that acquires the assets from primary sources of the business is called as assets source transaction. Assets source transactions increase the value of assets account, and increase the corresponding liabilities or stockholder’s equity account. The increased assets account is recorded with the debit entry, and increased liabilities or stockholder’s equity account is recorded with credit entry
The asset source transaction are identifed as follows along with the related amounts:
| Sources of Assets | Amount ($) |
| 1. Issue of stock | 52,000 |
| 2. Cash from loan | 20,000 |
| 3. Cash from revenue | 42,000 |
| 6. Issue of stock | 10,000 |
| Total Sources of Assets | 124,000 |
Table (2)
d.
Calculate the net income that is reported on the income statement for the 2014 and explain the reason for the non appearance of dividends in the income statement.
d.
Explanation of Solution
The amount of net income reported is $19,000 (refer figure (1)). But dividend does not appear in the income statement because it is not considered as an expense.
e.
Calculate the net cash flows from operating activities, financing activities, and investing activities.
e.
Explanation of Solution
Statement of cash flows:
Statement of cash flows is one among the financial statement of a company statement that shows aggregate data of all
Operating activities:
Operating activities refer to the normal activities of a company to carry out the business. The examples for operating activities are purchase of inventory, payment of salary, sales, and others.
Investing activities:
Investing activities refer to the activities carried out by a company for acquisition of long term assets. The examples for investing activities are purchase of equipment, long term investment, sale of land, and others.
Financing activities:
Financing activities refer to the activities carried out by a company to mobilize funds to carry out the business activities. The examples for financing activities are purchase of bonds, issuance of common shares, and others.
The net cash flows from operating activities, financing activities, and investing activities are calculated as follows:
| Operating Activities | |
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Cash from revenue | 42,000 |
| Cash paid for expenses | (23,000) |
| Net Cash Flow from Operating Activities | 19,000 |
Table (3)
| Investing Activities | |
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Cash paid to purchase land | (45,000) |
| Net Cash Flow from Investing Activities | (45,000) |
Table (4)
| Financing Activities | |
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Cash from stock issue ($52,000 + $10,000) | 62,000 |
| Cash from loan | 20,000 |
| Paid cash dividend | (6,000) |
| Cash paid on loan principal | (10,000) |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing Activities | 66,000 |
Table (5)
f.
Calculate the percentage of assets that were provided by investors, creditors and earnings.
f.
Explanation of Solution
Stockholders’ equity to asset ratio:
Stockholders ‘equity to asset ratio is the ratio that measures the difference between total asset and stockholders ‘equity of the company. Stockholders’ equity ratio reflects the amount of assets that can be claimed by the stockholders in proportion to the value of shares owned by them.
Percentage of total assets acquired from investors is calculated as follows:
Note:
Debt to Asset Ratio:
Debt to asset ratio is the ratio that measures the difference between total asset and total liability of the company. Debt ratio reflects the finance strategy of the company. It is used to evaluate company’s ability to pay its debts. Higher debt ratio implies the higher financial risk.
Percentage of assets acquired from creditors is calculated as follows:
Note:
Return on assets:
Return on assets is the financial ratio which determines the amount of net income earned by the business with the use of total assets owned by it. It indicates the magnitude of the company’s earnings with relative to its total assets.
Percentage of total assets acquired from
Note:
Therefore the percentage of total assets acquired from investors is 72.94%, the percentage of total assets acquired from creditors is 11.76% and the percentage of total assets from retained earnings is 15.29%.
g.
Calculate the balance in the retained accounts
g.
Explanation of Solution
Retained earnings:
Retained earnings are the portion of earnings kept by the business for the purpose of reinvestments, payment of debts, or for future growth.
Balance in the retained earnings account is as follows:
The balance in the account of retained earnings is zero. The revenue earned is recorded in the revenue accounts and not recorded in the retained earnings account.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
SURVEY OF ACCOUNTING-ACCESS
- I need guidance with this general accounting problem using the right accounting principles.arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this general accounting question using the correct accounting procedures?arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this general accounting question using valid accounting techniques?arrow_forward
- Can you solve this general accounting problem using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forwardI am looking for the correct answer to this general accounting problem using valid accounting standards.arrow_forwardPlease help me solve this general accounting problem with the correct financial process.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





