
Concept explainers
Concept Introduction:
Accounting equation represents the mathematical relationship between assets, liabilities and equity. According to this equation, assets are equal to the sum of liabilities and equity. The formal for basic accounting equation is as follows:
Requirement 1a.
The amount of Equity on December 31, 2018 for Company V
Answer to Problem 2BPSB
The amount of Equity on December 31, 2018 for Company V is $29,000
Explanation of Solution
The amount of Equity can be calculated by subtracting Assets and liabilities =54000-25000 = $29,000.
Concept Introduction:
Accounting equation represents the mathematical relationship between assets, liabilities and equity. According to this equation, assets are equal to the sum of liabilities and equity. The formal for basic accounting equation is as follows:
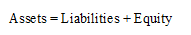
Requirement 1b.
The amount of Equity on December 31, 2019 for Company V
Answer to Problem 2BPSB
The amount of Equity on December 31, 2019 for Company V is $23,000
Explanation of Solution
The amount of Equity can be calculated by subtracting Assets and liabilities =59000-36000 = $23,000.
Concept Introduction:
Accounting Equation:
Accounting equation represents the mathematical relationship between assets, liabilities and equity. According to this equation, assets are equal to the sum of liabilities and equity. The formal for basic accounting equation is as follows:
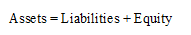
Requirement 1c.
The amount of Net income or loss for the year 2019 for Company V
Answer to Problem 2BPSB
The amount of Net loss for the year 2019 for Company V is $5,500
Explanation of Solution
The amount of Net income for the year 2019 for Company V is as follows:
Ending Equity = Beginning Equity + Owner's investment + Net income −Owner's withdrawals
23,000 = 29000+5000+Net Income -5500
23000 =Net Income +28500
Hence Net income = -5500 or Net Loss =$5500
Concept Introduction:
Accounting Equation:
Accounting equation represents the mathematical relationship between assets, liabilities and equity. According to this equation, assets are equal to the sum of liabilities and equity. The formal for basic accounting equation is as follows:
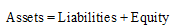
Requirement 2a.
The amount of Equity on December 31, 2018 for Company W
Answer to Problem 2BPSB
The amount of Equity on December 31, 2018 for Company W is $20,000
Explanation of Solution
The amount of Equity can be calculated by subtracting Assets and liabilities =80,000-60,000 = 20,000
Concept Introduction:
Accounting Equation:
Accounting equation represents the mathematical relationship between assets, liabilities and equity. According to this equation, assets are equal to the sum of liabilities and equity. The formal for basic accounting equation is as follows:
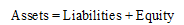
Requirement 2b.
The amount of Equity on December 31, 2019 for Company W
Answer to Problem 2BPSB
The amount of Equity on December 31, 2019 for Company W is $78,000
Explanation of Solution
The amount of Equity on December 31, 2019 for Company W is calculated as follows:
Ending Equity = Beginning Equity + Owner's investment + Net income −Owner's withdrawals
=20000+20000+40000-2000
= $78,000
Concept Introduction:
Accounting Equation:
Accounting equation represents the mathematical relationship between assets, liabilities and equity. According to this equation, assets are equal to the sum of liabilities and equity. The formal for basic accounting equation is as follows:
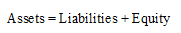
Requirement 2c.
The amount of Liabilities on December 31, 2019 for Company W
Answer to Problem 2BPSB
The amount of Liabilities on December 31, 2019 for Company W is $22,000
Explanation of Solution
The amount of Liabilities on December 31, 2019 for Company W is calculated as follows:
Liabilities = Assets − Equity = 100000-78,000 = $22,000
Concept Introduction:
Accounting Equation:
Accounting equation represents the mathematical relationship between assets, liabilities and equity. According to this equation, assets are equal to the sum of liabilities and equity. The formal for basic accounting equation is as follows:
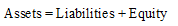
Requirement 3.
The amount of Owner's Investment for Company X during the year 2019
Answer to Problem 2BPSB
The amount of Owner's Investment for Company X during the year 2019 is $29,200
Explanation of Solution
The amount of Owner's Investment for Company X during the year 2019 is calculated as follows:
Equity as on Dec. 31, 2018 =Assets − Liabilities = 141500-68500 =$73,000
Equity as on Dec. 31, 2019 =Assets − Liabilities = 186500-65800 = $120,700
Ending Equity = Beginning Equity + Owner's investment + Net income −Owner's withdrawals
120700 = 73000 + Owner's investment +18500-0
120700 = 91500+ Owner's investment
Owner's investment = 120700-91500 =$29,200
Concept Introduction:
Accounting Equation:
Accounting equation represents the mathematical relationship between assets, liabilities and equity. According to this equation, assets are equal to the sum of liabilities and equity. The formal for basic accounting equation is as follows:
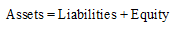
Requirement 4.
The amount of Assets for Company Y as on Dec. 31, 2019
Answer to Problem 2BPSB
The amount of Assets for Company Y as on Dec. 31, 2019 is $135,100
Explanation of Solution
The amount of Assets for Company Y as on Dec. 31, 2019 is calculated as follows:
Equity as on Dec. 31, 2018 =Assets − Liabilities = 92500-51500 =$41,000
Equity as on Dec. 31, 2019 = Beginning Equity + Owner's investment + Net income −Owner's withdrawals =41000+48100+24000-20000 =$93,100
Assets as on Dec. 31, 2019 = Equity + Liabilities = 93100+42000 =$135,100
Concept Introduction:
Accounting Equation:
Accounting equation represents the mathematical relationship between assets, liabilities and equity. According to this equation, assets are equal to the sum of liabilities and equity. The formal for basic accounting equation is as follows:
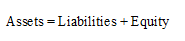
Requirement 5.
The amount of Liabilities for Company Z as on Dec. 31, 2018
Answer to Problem 2BPSB
The amount of Liabilities for Company Z as on Dec. 31, 2018 is $100,000
Explanation of Solution
The amount of Liabilities for Company Z as on Dec. 31, 2018 is calculated as follows:
Equity as on Dec. 31, 2019 =Assets − Liabilities = 170,000-42000 =$128,000
Ending Equity = Beginning Equity + Owner's investment + Net income −Owner's withdrawals
128000 = Beginning Equity+60000+32000-8000
128000 = Beginning Equity+ 84,000
Beginning Equity = 128000-84000 = $44,000
Liabilities as on Dec. 31, 2018 = Assets- Equity =144000-44000 =$100,000
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
FUNDAMENTAL ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLES
- I am looking for the correct answer to this general accounting problem using valid accounting standards.arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting problem with appropriate steps and explanations?arrow_forward(1) prepare the december 31 entry for bramble corporation to record amortization of intangibles. the trademark has an estimated useful life of 4 years with a residual value of $3,520 [it is not $3,460]arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





