
Concept explainers
(a)
Concept introduction: The space filling molecular models represent the atoms and compounds. The same structures indicate the same atoms or compounds. Each sphere indicates an atom and the attached spheres indicate the compound.
(a)
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution: Figure (i)
Explanation of Solution
The figure (i) represents the space filling molecular models of two spheres attached to each other with the same color.
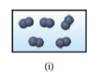
Therefore, figure (i) indicate the diatomic molecule of the same atoms in it. Thus, it corresponds to a pure element.
Figure (i) represent the structure corresponding to pure element.
(b)
Concept introduction: The space filling molecular models represent the atoms and compounds. The same structures indicate the same atoms or compounds. Each sphere indicates an atom and the attached spheres indicate the compound.
(b)
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution: The figures that represent a mixture of two elements are (v) and (vi).
Explanation of Solution
The figures (v) and (vi) represent the space filling molecular models of two differently colored spheres apart from each other.
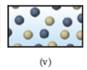
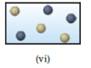
Therefore, it does not indicate any compound. Instead, it indicates the mixture of two different elements.
Figure (v) and (vi) represent the structures corresponding to a mixture of two elements.
(c)
Concept introduction: The space filling molecular models represent the atoms and compounds. The same structures indicate the same atoms or compounds. Each sphere indicates an atom and the attached spheres indicate the compound.
(c)
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution: The figure that represents a pure compound is (iv).
Explanation of Solution
The figure (iv) represents the space filling molecular models of two spheres attached to each other with the different colors.
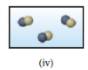
Therefore, figure (iv) indicates the diatomic molecule of the different atoms in it. Thus, it corresponds to a pure compound.
Figure (iv) represents the structure corresponding to pure compound.
(d)
Concept introduction: The space filling molecular models represent the atoms and compounds. The same structures indicate the same atoms or compounds. Each sphere indicates an atom and the attached spheres indicate the compound.
(d)
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution: The figures that represent a mixture of an element and a compound are (ii) and (iii).
Explanation of Solution
The figure (ii) represents a space filling molecular model of a diatomic molecule with two spheres of same color attached to each other and a compound with two spheres of different color attached to each other.
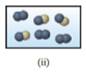
Therefore, figure (ii) represents a mixture of diatomic molecule of pure element and a compound.
The figure (iii) represents a space filling molecular model of a monatomic sphere with single spheres of same color apart from each other and a compound with two spheres of different color attached to each other.
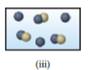
Therefore, figure (iii) represents atoms of pure element and a compound.
Figure (ii) and (iii) represent the structures corresponding to a mixture of an element and a compound.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
CHEMISTRY THE CENTRAL SCIENCE >EBOOK<
- . Draw the products for addition reactions (label as major or minor) of the reaction between 2-methyl-2-butene and with following reactants : Steps to follow : A. These are addition reactions you need to break a double bond and make two products if possible. B. As of Markovnikov rule the hydrogen should go to that double bond carbon which has more hydrogen to make stable products or major product. Here is the link for additional help : https://study.com/academy/answer/predict-the-major-and-minor-products-of-2-methyl- 2-butene-with-hbr-as-an-electrophilic-addition-reaction-include-the-intermediate- reactions.html H₂C CH3 H H3C CH3 2-methyl-2-butene CH3 Same structure CH3 IENCESarrow_forwardDraw everything on a piece of paper including every single step and each name provided using carbons less than 3 please.arrow_forwardTopics] [References] Write an acceptable IUPAC name for the compound below. (Only systematic names, not common names are accepted by this question.) Keep the information page open for feedback reference. H The IUPAC name isarrow_forward
- [Review Topics] [References] Write an acceptable IUPAC name for the compound below. (Only systematic names, not common names are accepted by this question.) Keep the information page open for feedback reference. The IUPAC name is Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remainingarrow_forwardPlease draw.arrow_forwardA chromatogram with ideal Gaussian bands has tR = 9.0 minutes and w1/2 = 2.0 minutes. Find the number of theoretical plates that are present, and calculate the height of each theoretical plate if the column is 10 centimeters long.arrow_forward
- An open tubular column has an inner diameter of 207 micrometers, and the thickness of the stationary phase on the inner wall is 0.50 micrometers. Unretained solute passes through in 63 seconds and a particular solute emerges at 433 seconds. Find the distribution constant for this solute and find the fraction of time spent in the stationary phase.arrow_forwardConsider a chromatography column in which Vs= Vm/5. Find the retention factor if Kd= 3 and Kd= 30.arrow_forwardTo improve chromatographic separation, you must: Increase the number of theoretical plates on the column. Increase the height of theoretical plates on the column. Increase both the number and height of theoretical plates on the column. Increasing the flow rate of the mobile phase would Increase longitudinal diffusion Increase broadening due to mass transfer Increase broadening due to multiple paths You can improve the separation of components in gas chromatography by: Rasing the temperature of the injection port Rasing the temperature of the column isothermally Rasing the temperature of the column using temperature programming In GC, separation between two different solutes occurs because the solutes have different solubilities in the mobile phase the solutes volatilize at different rates in the injector the solutes spend different amounts of time in the stationary phasearrow_forward
- please draw and example of the following: Show the base pair connection(hydrogen bond) in DNA and RNAarrow_forwardNaming and drawing secondary Write the systematic (IUPAC) name for each of the following organic molecules: CH3 Z structure CH3 CH2 CH2 N-CH3 CH3-CH2-CH2-CH-CH3 NH CH3-CH-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3 Explanation Check ☐ name ☐ 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy C Garrow_forwardC This question shows how molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to understand the chemical properties of elemental oxygen O₂ and its anionic derivative superoxide Oz. a) Draw the MO energy diagram for both O2 and O2. Clearly label your diagram with atomic orbital names and molecular orbital symmetry labels and include electrons. Draw the Lewis structure of O2. How does the MO description of O2 differ from the Lewis structure, and how does this difference relate to the high reactivity and magnetic properties of oxygen? ) Use the MO diagram in (a) to explain the difference in bond length and bond energy between superoxide ion (Oz, 135 pm, 360 kJ/mol) and oxygen (O2, 120.8 pm, 494 kJ/mol).arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





