
Concept explainers
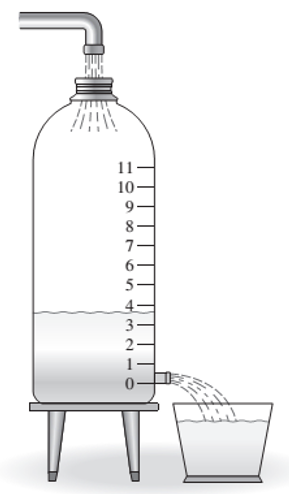
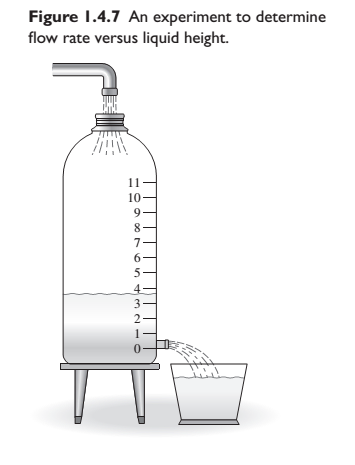
Consider the milk container of Example 1.4.2 (Figure 1.4.7). A straw 9.5 cm long was inserted in the side of the container. While adjusting the tap flow to keep the water height Constant, the time for the outflow to fill a 250-ml cup was measured. This was repeated for several heights. The data are given in the following table.
Obtain a functional description of the volume outflow rate f through the straw as a function of water height h above the hole.

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
System Dynamics
- Auto Controls A union feedback control system has the following open loop transfer function where k>0 is a variable proportional gain i. for K = 1 , derive the exact magnitude and phase expressions of G(jw). ii) for K = 1 , identify the gaincross-over frequency (Wgc) [where IG(jo))| 1] and phase cross-overfrequency [where <G(jw) = - 180]. You can use MATLAB command "margin" to obtain there quantities. iii) Calculate gain margin (in dB) and phase margin (in degrees) ·State whether the closed-loop is stable for K = 1 and briefly justify your answer based on the margin . (Gain marginPhase margin) iv. what happens to the gain margin and Phase margin when you increase the value of K?you You can use for loop in MATLAB to check that.Helpful matlab commands : if, bode, margin, rlocus NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forwardThe 120 kg wheel has a radius of gyration of 0.7 m. A force P with a magnitude of 50 N is applied at the edge of the wheel as seen in the diagram. The coefficient of static friction is 0.3, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.25. Find the acceleration and angular acceleration of the wheel.arrow_forwardAuto Controls Using MATLAB , find the magnitude and phase plot of the compensators NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forward
- 4-81 The corner shown in Figure P4-81 is initially uniform at 300°C and then suddenly exposed to a convection environment at 50°C with h 60 W/m². °C. Assume the = 2 solid has the properties of fireclay brick. Examine nodes 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 and deter- mine the maximum time increment which may be used for a transient numerical calculation. Figure P4-81 1 2 3 4 1 cm 5 6 1 cm 2 cm h, T + 2 cmarrow_forwardAuto Controls A union feedback control system has the following open loop transfer function where k>0 is a variable proportional gain i. for K = 1 , derive the exact magnitude and phase expressions of G(jw). ii) for K = 1 , identify the gaincross-over frequency (Wgc) [where IG(jo))| 1] and phase cross-overfrequency [where <G(jw) = - 180]. You can use MATLAB command "margin" to obtain there quantities. iii) Calculate gain margin (in dB) and phase margin (in degrees) ·State whether the closed-loop is stable for K = 1 and briefly justify your answer based on the margin . (Gain marginPhase margin) iv. what happens to the gain margin and Phase margin when you increase the value of K?you You can use for loop in MATLAB to check that.Helpful matlab commands : if, bode, margin, rlocus NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forwardAuto Controls Hand sketch the root Focus of the following transfer function How many asymptotes are there ?what are the angles of the asymptotes?Does the system remain stable for all values of K NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forward
- Please draw the section view of the following problemsarrow_forward7) Please draw the front, top and side view for the following object. Please cross this line outarrow_forwardA 10-kg box is pulled along P,Na rough surface by a force P, as shown in thefigure. The pulling force linearly increaseswith time, while the particle is motionless att = 0s untilit reaches a maximum force of100 Nattimet = 4s. If the ground has staticand kinetic friction coefficients of u, = 0.6 andHU, = 0.4 respectively, determine the velocityof the A 1 0 - kg box is pulled along P , N a rough surface by a force P , as shown in the figure. The pulling force linearly increases with time, while the particle is motionless at t = 0 s untilit reaches a maximum force of 1 0 0 Nattimet = 4 s . If the ground has static and kinetic friction coefficients of u , = 0 . 6 and HU , = 0 . 4 respectively, determine the velocity of the particle att = 4 s .arrow_forward
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
