
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether the following change is physical or chemical is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The change that takes place only in state or appearance and not in the composition is known as physical change. The atoms or the molecules of a substance do not change their identity when a substance undergoes a physical change. The change accompanied by the change in the physical properties only is classified as physical change. The substance remains the same before and after the change. For example, the melting of ice is a physical change.
The change that takes place in the composition is known as chemical change. The atoms or the molecules of the substance rearrange and transformed into a new substance. For example, the burning of paper is a chemical change.
(a)
Answer to Problem 1.1P
The mixing of substances in A and B to give substance in C is a chemical change.
Explanation of Solution
The change is depicted as follows:
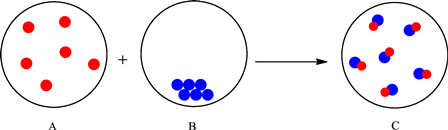
Each sphere represents one particle or atom. Atoms from A react with the atoms in B to form a new substance with one red and one blue atom depicted in the C. Formation of a new substance in a change is classified as a chemical change. Thus, the mixing of substances in A and B to give substance in C is a chemical change.
The particles in the A interact with the particles in B and result in the formation of new substance (change in composition). Therefore, it can be classified as a chemical change.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether the following change is physical or chemical is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The change that takes place only in state or appearance and not in the composition is known as physical change. The atoms or the molecules of a substance do not change their identity when a substance undergoes a physical change. The change accompanied by the change in the physical properties only is classified as physical change. The substance remains the same before and after the change. For example, the melting of ice is a physical change.
The change that takes place in the composition is known as chemical change. The atoms or the molecules of the substance rearrange and transformed into a new substance. For example, the burning of paper is a chemical change.
(b)
Answer to Problem 1.1P
The mixing of substances in A and B to give substance in D is a chemical change.
Explanation of Solution
The change is depicted as follows:
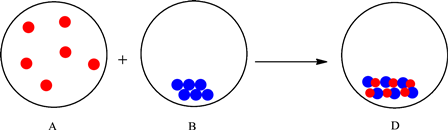
Each sphere represents one particle or atom. Atoms from A react with the atoms in B to form a new substance with one red and one blue atom depicted in the D. Formation of a new substance in a change is classified as a chemical change. Thus, the change is classified as a physical change. Therefore, the mixing of substances in A and B to give substance in D is a chemical change.
The particles in A interact with the particles in B and result in the formation of new substance (change in composition). Therefore, it can be classified as a chemical change.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether the following change is physical or chemical is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The change that takes place only in state or appearance and not in the composition is known as physical change. The atoms or the molecules of a substance do not change their identity when a substance undergoes a physical change. The change accompanied by the change in the physical properties only is classified as physical change. The substance remains the same before and after the change. For example, the melting of ice is a physical change.
The change that takes place in the composition is known as chemical change. The atoms or the molecules of the substance rearrange and transformed into a new substance. For example, the burning of paper is a chemical change.
(c)
Answer to Problem 1.1P
The conversion of substance C into D is a physical change.
Explanation of Solution
The change is depicted as follows:
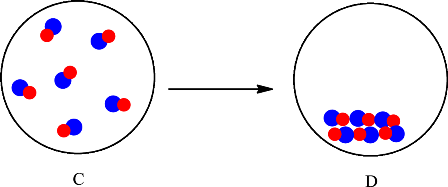
Each sphere represents one particle or atom. C consists of molecules made up of one red sphere and one blue sphere. D also consists of molecules made up of one red sphere and one blue sphere. The only difference is in the arrangement of the particles in C and D. In C the particles are far apart from each other and are in the gaseous state whereas in D the particles are arranged in a regular pattern and in the solid state. Since no new substance is formed, therefore conversion of substance C into D is considered as a physical change.
The particles in C rearranged to give substance D. Since no new substance is formed the change is classified as a physical change.
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether the following change is accompanied by the change in physical properties or chemical properties is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The change that takes place only in state or appearance and not in the composition is known as physical change. The atoms or the molecules of a substance do not change their identity when a substance undergoes a physical change. The change accompanied by the change in the physical properties only is classified as physical change. The substance remains the same before and after the change. For example, the melting of ice is a physical change.
The change that takes place in the composition is known as chemical change. The atoms or the molecules of the substance rearrange and transformed into a new substance. For example, the burning of paper is a chemical change.
(d)
Answer to Problem 1.1P
After the change in part (c) has occurred the sample have different physical properties.
Explanation of Solution
The change is depicted as follows:
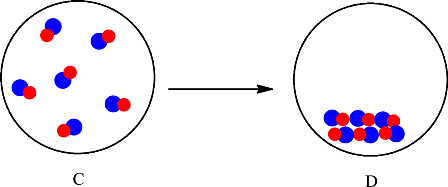
Each sphere represents one particle or atom. C consists of molecules made up of one red sphere and one blue sphere. D also consists of molecules made up of one red sphere and one blue sphere. The only difference is in the arrangement of the particles in C and D. In C the particles are far apart from each other and are in the gaseous state whereas in D the particles are arranged in a regular pattern and in the solid state. Since no new substance is formed, therefore conversion of substance C into D is considered as a physical change.
The change is physical change, therefore, substance C and D will have the same chemical properties but different physical properties.
The particles in C rearranged to give substance D. Since no new substance is formed the substance C and D are the same therefore they will have the same chemical properties but different physical properties.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
LL CHEM: MOL NAT CHNG W/CNCT AC
- Please help me solve this homework problemarrow_forwardPlease help me answer this homework questionarrow_forwardCalculating standard reaction free energy from standard reduction... Using standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy AG° for the following redox reaction. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 3+ H2(g)+2OH¯ (aq) + 2Fe³+ (aq) → 2H₂O (1)+2Fe²+ (aq) 0 kJ x10 Х ? olo 18 Ararrow_forward
- Calculating the pH of a weak base titrated with a strong acid An analytical chemist is titrating 184.2 mL of a 0.7800M solution of dimethylamine ((CH3) NH with a 0.3000M solution of HClO4. The pK₁ of dimethylamine is 3.27. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 424.1 mL of the HClO solution to it. 2 4 Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HClO 4 solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pH = ☐ ☑ ? 000 18 Ar 1 Barrow_forwardUsing the Nernst equation to calculate nonstandard cell voltage A galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction: MnO2 (s)+4H* (aq)+2Cr²+ (aq) → Mn²+ (aq)+2H₂O (1)+2Cr³+ (aq) + 2+ 2+ 3+ Suppose the cell is prepared with 7.44 M H* and 0.485 M Cr²+ in one half-cell and 7.92 M Mn² and 3.73 M Cr³+ in the other. Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. ☐ x10 μ Х 5 ? 000 日。arrow_forwardCalculating standard reaction free energy from standard reduction... Using standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy AG° for the following redox reaction. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. NO (g) +H₂O (1) + Cu²+ (aq) → HNO₂ (aq) +H* (aq)+Cu* (aq) kJ - ☐ x10 x10 olo 18 Ararrow_forward
- Calculating the pH of a weak base titrated with a strong acid b An analytical chemist is titrating 116.9 mL of a 0.7700M solution of aniline (C6H5NH2) with a 0.5300M solution of HNO3. The pK of aniline is 9.37. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 184.2 mL of the HNO 3 solution to it. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HNO3 solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pH = ☐ ☑ 5arrow_forwardQUESTION: Find the standard deviation for the 4 different groups 5.298 3.977 223.4 148.7 5.38 4.24 353.7 278.2 5.033 4.044 334.6 268.7 4.706 3.621 305.6 234.4 4.816 3.728 340.0 262.7 4.828 4.496 304.3 283.2 4.993 3.865 244.7 143.6 STDEV = STDEV = STDEV = STDEV =arrow_forwardQUESTION: Fill in the answers in the empty green boxes regarding 'Question 5: Calculating standard error of regression' *The images of the data showing 'coefficients for the standard curve' have been providedarrow_forward
- Using the Nernst equation to calculate nonstandard cell voltage Try Again Your answer is wrong. In addition to checking your math, check that you used the right data and DID NOT round any intermediate calculations. A galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction: 2+ 2+ Sn²+ Ba(s) (aq) + Ba (s) Sn (s) + Ba²+ (aq) →>> Suppose the cell is prepared with 6.10 M Sn 2+ 2+ in one half-cell and 6.62 M Ba in the other. Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. 1.71 V ☐ x10 ☑ 5 0/5 ? 00. 18 Ararrow_forwardQuestion: Find both the b (gradient) and a (y-intercept) value from the list of data below: (x1 -x̄) 370.5 (y1 - ȳ) 5.240 (x2 - x̄) 142.5 (y2 - ȳ) 2.004 (x3 - x̄) 28.5 (y3 - ȳ) 0.390 (x4 - x̄) -85.5 (y4 - ȳ) -1.231 (x5 - x̄) -199.5 (y5 - ȳ) -2.829 (x6 - x̄) -256.5 (y6 - ȳ) -3.575arrow_forwardCalculating standard reaction free energy from standard reduction... Using standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy AG° for the following redox reaction. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 3Cu+ (aq) + Cro²¯ (aq) +4H₂O (1) → 3Cu²+ (aq) +Cr(OH)3 (s)+5OH˜¯ (aq) 0 kJ ☐ x10 00. 18 Ararrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





