You drop a ball of weight 5.00 N from rest from a certain height above the floor into free fall. When the ball is halfway to the floor, its kinetic energy is 5.00 J. How much gravitational potential energy relative to the floor in SI units has the ball lost in falling this much? a. there is not enough information to answer the question b. 5.00 J c. 10.0 J
-
You drop a ball of weight 5.00 N from rest from a certain height above the floor into free fall. When the ball is halfway to the floor, its kinetic energy is 5.00 J. How much gravitational potential energy relative to the floor in SI units has the ball lost in falling this much?
a. there is not enough information to answer the questionb. 5.00 Jc. 10.0 J
The potential energy is a type of energy which depends upon the relative position of the body.
The magnitude of the potential energy is,
P =M×g×h
The other form of energy is kinetic energy, it possesses due to the motion of the body.
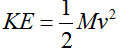
Where,
KE = kinetic energy
P = potential energy
M = mass of the body
v = velocity
According to the work energy theorem, the net work done on the system will equal to the change in the kinetic energy of the body.
Under free fall condition:
If any body is dropped from a fixed height then its potential energy is converted to kinetic energy.
At that height the potential energy is maximum and kinetic energy is zero. And on the ground the kinetic energy is maximum and potential energy is zero.
A ball is falling from certain height. Its the kinetic energy at halfway of journey is equal to 5 J.
The ball is falling from certain height so its potential energy will converted into the kinetic energy and because of that its velocity increases.
Initially, the kinetic energy was zero and potential energy was maximum.
And we know that the energy of a system is conserved .
So, lost in the potential energy will equal to the gain in the kinetic energy of the system.
Lost in potential energy = Gain in Kinetic Energy
Lost in potential energy = 5 J
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images









