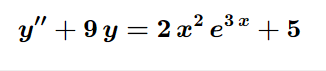1 Functions And Models 2 Limits And Derivatives 3 Differentiation Rules 4 Applications Of Differentiation 5 Integrals 6 Applications Of Integration 7 Techniques Of Integration 8 Further Applications Of Integration 9 Differential Equations 10 Parametric Equations And Polar Coordinates 11 Infinite Sequences And Series 12 Vectors And The Geometry Of Space 13 Vector Functions 14 Partial Derivatives 15 Multiple Integrals 16 Vector Calculus 17 Second-order Differential Equations Chapter1: Functions And Models
1.1 Four Ways To Represent A Function 1.2 Mathematical Models: A Catalog Of Essential Functions 1.3 New Functions From Old Functions 1.4 Exponential Functions 1.5 Inverse Functions And Logarithms Chapter Questions Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RCC: (a) What is a function? What are its domain and range? (b) What is the graph of a function? (c) How... Problem 2RCC: Discuss four ways of representing a function. Illustrate your discussion with examples. Problem 3RCC: (a) What is an even function? How can you tell if a function is even by looking at its graph? Give... Problem 4RCC: What is an increasing function? Problem 5RCC: What is a mathematical model? Problem 6RCC: Give an example of each type of function. (a) Linear function (b) Power function (c) Exponential... Problem 7RCC: Sketch by hand, on the same axes, the graphs of the following functions. (a) f(x) = x (b) g(x) = x2... Problem 8RCC: Draw, by hand, a rough sketch of the graph of each function. (a) y = sin x (b) y = tan x (c) y = ex... Problem 9RCC: Suppose that f has domain A and g has domain B. (a) What is the domain of f + g? (b) What is the... Problem 10RCC: How is the composite function f g defined? What is its domain? Problem 11RCC: Suppose the graph of f is given. Write an equation for each of the graphs that are obtained from the... Problem 12RCC: (a) What is a one-to-one function? How can you tell if a function is one-to-one by looking at its... Problem 13RCC: (a) How is the inverse sine function f(x) = sin1 x defined? What are its domain and range? (b) How... Problem 1RQ: Determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is true, explain why. If it is false,... Problem 2RQ: Determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is true, explain why. If it is false,... Problem 3RQ: Determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is true, explain why. If it is false,... Problem 4RQ: Determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is true, explain why. If it is false,... Problem 5RQ: Determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is true, explain why. If it is false,... Problem 6RQ: Determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is true, explain why. If it is false,... Problem 7RQ: Determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is true, explain why. If it is false,... Problem 8RQ: Determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is true, explain why. If it is false,... Problem 9RQ: Determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is true, explain why. If it is false,... Problem 10RQ: Determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is true, explain why. If it is false,... Problem 11RQ: Determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is true, explain why. If it is false,... Problem 12RQ: Determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is true, explain why. If it is false,... Problem 13RQ: Determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is true, explain why. If it is false,... Problem 14RQ: Determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is true, explain why. If it is false,... Problem 1RE: Let f be the function whose graph is given. (a) Estimate the value of f(2). (b) Estimate the values... Problem 2RE: The graph of g is given. (a) State the value of g(2). (b) Why is g one-to-one? (c) Estimate the... Problem 3RE: lf f(x) = x2 2x + 3, evaluate the difference quotient f(a+h)f(a)h Problem 4RE: Sketch a rough graph or the yield of a crop as a function of the amount of fertilizer used. Problem 5RE: Find the domain and range of the function. Write your answer in interval notation. 5. f(x) = 2/(3x ... Problem 6RE: Find the domain and range of the function. Write your answer in interval notation. 6. g(x)=16x4 Problem 7RE Problem 8RE: Find the domain and range of the function. Write your answer in interval notation. 8. F(t) = 3 + cos... Problem 9RE Problem 10RE: The graph of .f is given. Draw the graphs of the following functions. (a) y = f(x 8) (b) y = f(x)... Problem 11RE Problem 12RE: Use transformations to sketch the graph of the function. y=2x Problem 13RE Problem 14RE: Use transformations to sketch the graph of the function. y = In(x + 1) Problem 15RE: Use transformations to sketch the graph of the function. f(x) = cos 2x Problem 16RE: Use transformations to sketch the graph of the function. f(x)={xifx0ex1ifx0 Problem 17RE: Determine whether f is even, odd, or neither even nor odd. (a) f(x)=2x53x2+2. (h) f(x) = x3 x7 (c)... Problem 18RE: Find an expression for the function whose graph consists of the line segment from point (2, 2) to... Problem 19RE: If f(x) = In x and g(x) = x2 9. find the functions (a) fg (b) gf (c) ff (d) gg, and their domains. Problem 20RE: Express the function F(x)=1/x+x as a composition of three functions. Problem 22RE: A small-appliance manufacturer finds that it costs 9000 to produce 1000 toaster ovens a week and... Problem 23RE: If f(x) = 2x + In x, find f1(2). Problem 24RE: Find the inverse function of f(x)=x+12x+1. Problem 25RE: Find the exact value of each expression. 64. (a) tan13 (b) arctan (1) 25. Find the exact value of... Problem 26RE Problem 27RE: The half-life of palladium-100, 100Pd, is four days. (So half of any given quantity of 100Pd will... Problem 28RE: The population of a certain species in a limited environment with initial population 100 and... Problem 1P: One of the legs of a right triangle has length 4 cm. Express the length of the altitude... Problem 2P: The altitude perpendicular to the hypotenuse of a right triangle is 12 cm. Express the length of the... Problem 3P: Solve the equation |2x 1| |x + 5| = 3. Problem 4P: Solve the inequality |x 1| |x 3| 5. Problem 5P Problem 6P: Sketch the graph of the function g(x) = |x2 1 | |x2 4|. Problem 7P Problem 8P Problem 9P: The notation max{a, b, } means the largest of the numbers a, b. Sketch the graph of each function.... Problem 10P: Sketch the region in the plane defined by each of the following equations or inequalities. (a)... Problem 11P: Evaluate (log2 3)(log3 4)(log4 5)(log31 32). Problem 12P: (a) Show that the function f(x)=ln(x+x2+1) is an odd function. (b) Find the inverse function of f. Problem 13P: Solve the inequality ln(x2 2x 2) 0. Problem 14P: Use indirect reasoning to prove that log2 5 is an irrational number. Problem 15P: A driver sets out on a journey. For the first half of the distance she drives at the leisurely pace... Problem 16P: Is it true that f(g+h)=fg+fh? Problem 17P: Prove that if n is a positive integer, then 7n 1 is divisible by 6. Problem 18P: Prove that 1 + 3 + 5 + + (2n l ) = n2. Problem 19P: If fo(x) = x2 and fn+1(x) = fo(fn(x)) for n = 0, 1, 2,, find a formula for fn(x). Problem 20P: (a) If fo(x)=12x and fn+1=fofnforn=0,1,2,, find an expression for fn(x) and use mathematical... Problem 1RCC: (a) What is a function? What are its domain and range? (b) What is the graph of a function? (c) How...
Related questions
Solve the following differential equation.
Transcribed Image Text: **Differential Equation Analysis**
The equation displayed is:
\[ y'' + 9y = 2x^2 e^{3x} + 5 \]
### Explanation:
This is a second-order non-homogeneous linear differential equation, where:
- \( y'' \) represents the second derivative of \( y \) with respect to \( x \).
- \( 9y \) is a term where the function \( y \) is multiplied by 9.
- The right-hand side, \( 2x^2 e^{3x} + 5 \), is the non-homogeneous part of the equation.
- \( 2x^2 e^{3x} \) represents a term with a polynomial of degree 2 in \( x \) multiplied by an exponential function.
- The constant 5 is an external forcing term.
This equation might be analyzed or solved to find \( y(x) \), the function describing a particular physical or theoretical system influenced by the given non-homogeneity. Solutions typically involve finding both the complementary solution (related to the homogeneous equation) and a particular solution for the non-homogeneous part.
With integration, one of the major concepts of calculus. Differentiation is the derivative or rate of change of a function with respect to the independent variable.
Expert Solution
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 7 images
![**Differential Equation Analysis**
The equation displayed is:
\[ y'' + 9y = 2x^2 e^{3x} + 5 \]
### Explanation:
This is a second-order non-homogeneous linear differential equation, where:
- \( y'' \) represents the second derivative of \( y \) with respect to \( x \).
- \( 9y \) is a term where the function \( y \) is multiplied by 9.
- The right-hand side, \( 2x^2 e^{3x} + 5 \), is the non-homogeneous part of the equation.
- \( 2x^2 e^{3x} \) represents a term with a polynomial of degree 2 in \( x \) multiplied by an exponential function.
- The constant 5 is an external forcing term.
This equation might be analyzed or solved to find \( y(x) \), the function describing a particular physical or theoretical system influenced by the given non-homogeneity. Solutions typically involve finding both the complementary solution (related to the homogeneous equation) and a particular solution for the non-homogeneous part.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fa9d4f1dd-159d-4044-a522-696d25a3cc6c%2F7dda9d9c-7e1a-4127-aa78-d56168a1a551%2Fotv5g4q_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)