Write a method in your ArrayUtilities class that meets the following requirements: - It should be named "counts".] - It should declare a parameter for an int array. You may assume that the array will contain only non-negative values. - It should return an int array where the value at each index is the count of how many times the index appears in the original array . For example, if the original array contained the value 10 3 times, then the value at index 10 in the count array should be 3. - Hint: the size of the array is determined by the maximum value in the original array. If the original array is empty, the count array should also be empty. A more detailed example: Given the int array [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 1, 1, 2, 0, 6], your function would return the array [1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 0, 1]. The value at each index indicates how many times the index appears in the original array. The value at index 0 is 1 because 0 appears 1 time in the original array. The value at index 1 is 3 because 1 appears 3 times in the original array. The value at index 5 is 0 because 5 does not appear in the original array. And so on. Modify your main to test your method with at least one unsorted array.
Write a method in your ArrayUtilities class that meets the following requirements: - It should be named "counts".]
- It should declare a parameter for an int array. You may assume that the array will contain only non-negative values.
- It should return an int array where the value at each index is the count of how many times the index appears in the original array
. For example, if the original array contained the value 10 3 times, then the value at index 10 in the count array should be 3.
- Hint: the size of the array is determined by the maximum value in the original array. If the original array is empty, the count array should also be empty.
A more detailed example:
Given the int array [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 1, 1, 2, 0, 6], your function would return the array [1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 0, 1]. The value at each index indicates how many times the index appears in the original array.
The value at index 0 is 1 because 0 appears 1 time in the original array.
The value at index 1 is 3 because 1 appears 3 times in the original array.
The value at index 5 is 0 because 5 does not appear in the original array. And so on. Modify your main to test your method with at least one unsorted array.
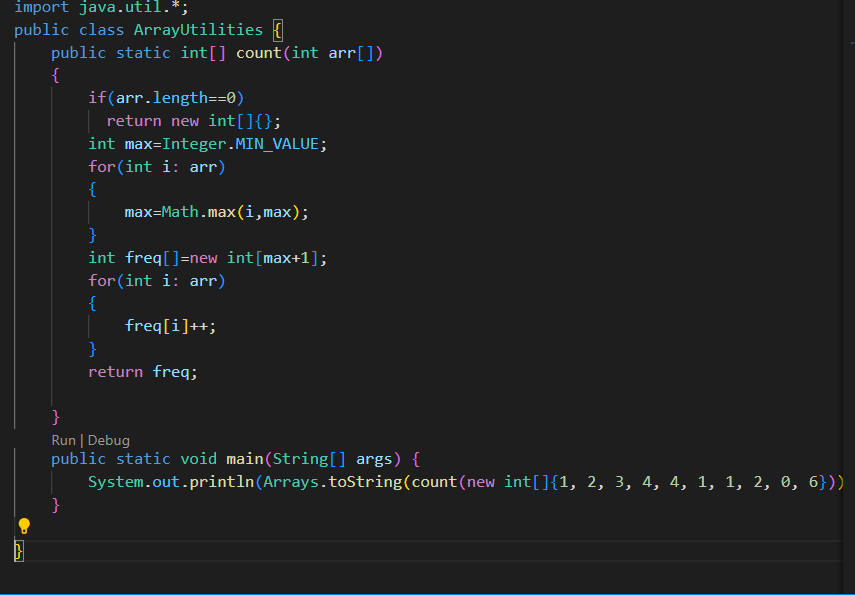
Output Screenshot:
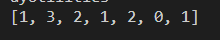
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









