With an area of 27.5m^3 used yo concentrate feed of 6453kh/h of apple solution at 11°C and containing sugar content of 10% wt to 25% wt. Saturated stram is at 130°C with the pressure in the evaporator as 20.0kPa. feed enthalpy is 65.5kj/kg and enthalpy of the liquid product is 400kj/kg. Boiling point of the solution in the evaporator is 38.6°C; determine the kg/h of steam used, the steam economy, the overall heat transfer coefficient and new steam flowrate rate if evaporation area is increased by 15%
With an area of 27.5m^3 used yo concentrate feed of 6453kh/h of apple solution at 11°C and containing sugar content of 10% wt to 25% wt. Saturated stram is at 130°C with the pressure in the evaporator as 20.0kPa. feed enthalpy is 65.5kj/kg and enthalpy of the liquid product is 400kj/kg. Boiling point of the solution in the evaporator is 38.6°C; determine the kg/h of steam used, the steam economy, the overall heat transfer coefficient and new steam flowrate rate if evaporation area is increased by 15%
Evaporators are used to concentrate the solution. It is done before the crystallization process.
A single effect evaporator is used to concentrate the feed solution.
Given data:
Area of the evaporator = 27.5 m2
Mass flow rate of feed = 6453 kg/h
Initial composition of sugar content = 10 wt%
Final composition of sugar content = 25 wt%
Temperature of feed = 11 0C
The entering temperature of saturated steam = 130 0C
The pressure in the vapor space = 20 kPa
The enthalpy of the feed (hp) = 65.5 kJ/kg
The enthalpy of liquid product (hl) = 400 kJ/kg
The mass flow rate of the steam used is calculated as follows:
Apply the overall mass balance

Where,
F represents the mass flow rate of feed.
V represents the mass flow rate of water vapor.
L represents the mass flow rate of concentrated liquid.
Apply the solute balance

Where,
xF represents the weight fraction of solute in the feed.
xL represents the weight fraction of solute in the concentrated liquid (product).
F= 6453 kg/h
xF = 0.1
xL = 0.25
Plugin the values on equation (2)
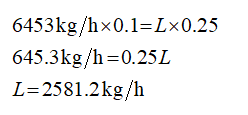
Plugin the values in equation (1)
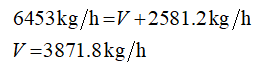
The pressure in the vapor space = 20 kPa
The enthalpy of vaporization of water at 20 kPa (from the property table for water) = 2610 kJ/kg
The temperature of saturated steam = 130 0C
The enthalpy of the saturated steam at 110 0C (from the steam table) = 2721 kJ/kg
Enthalpy of saturated water (at 383 K) = 419.15 kJ/kg
Therefore the enthalpy of condensing steam becomes,
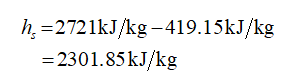
Apply the overall energy balance
Energy in = Energy out

Where,
hs represents the enthalpy of the condensing steam.
Fs represents the mass flow rate of steam.
hf represents the enthalpy of the feed.
hv represents the enthalpy of the water vapor.
hl represents the enthalpy of the liquid.
hs = 2301.85 kJ/kg
hf = 65.5 kJ/kg
hl = 400 kJ/kg
V = 3871.8 kg/h
L = 2581.2 kg/h
F = 6453 kg/j
Plugin the values in equation (3)

Step by step
Solved in 7 steps with 15 images









