it's a Roman numeral. Output the Arabic form. Treat "v" as 5 and "V" as 5000 (aka "v-bar"), etc. You must handle the subtractive rule. Perform basic
Control structures
Control structures are block of statements that analyze the value of variables and determine the flow of execution based on those values. When a program is running, the CPU executes the code line by line. After sometime, the program reaches the point where it has to make a decision on whether it has to go to another part of the code or repeat execution of certain part of the code. These results affect the flow of the program's code and these are called control structures.
Switch Statement
The switch statement is a key feature that is used by the programmers a lot in the world of programming and coding, as well as in information technology in general. The switch statement is a selection control mechanism that allows the variable value to change the order of the individual statements in the software execution via search.
use c
Read a string from command line arg.
Assume it's a Roman numeral.
Output the Arabic form.
Treat "v" as 5 and "V" as 5000 (aka "v-bar"), etc.
You must handle the subtractive rule.
Perform basic error checking.
Desired: do conversion in a function.
ues a Replit URL
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 5 images

why is exit status 1?
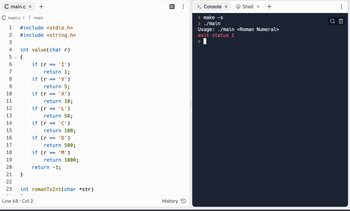
why show me
make -s
./main
Usage: ./main <Roman Numeral>
exit status 1 in replit?
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int value(char r)
{
if (r == 'I')
return 1;
if (r == 'V')
return 5;
if (r == 'X')
return 10;
if (r == 'L')
return 50;
if (r == 'C')
return 100;
if (r == 'D')
return 500;
if (r == 'M')
return 1000;
return -1;
}
int romanToInt(char *str)
{
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(str); i++)
{
int s1 = value(str[i]);
if (i + 1 < strlen(str))
{
int s2 = value(str[i + 1]);
if (s1 >= s2)
{
res=res+s1;
}
else
{
res=res+s2-s1;
i++;
}
}
else
{
res = res + s1;
i++;
}
}
return res;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc < 2)
{
printf("Usage: %s <Roman Numeral>\n", argv[0]);
return 1;
}
char *str = argv[1];
int result = romanToInt(str);
printf("The Arabic numeral equivalent of %s is %d\n", str, result);
return 0;
}
why after run have a lot error?
![C main.c x +
C main.c> f main
123
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
Int value(char r)
{
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23 Int romanToInt(char *str)
24
{
25
26
27
Line 68: Col 2
}
'I').
Return 1;
If (r 'V')
Return 5;
If (r 'X')
Return 10;
(L').
Return 50;
'C')
Return 100;
If (r
If (r
If (r
==
==
If (r 'D')
Return 500;
If (r 'M')
Return 1000;
Return -1;
Int res =
0;
For (int I = 0; I < strlen(str); i++)
|||
History
:
Shell x +
./main.c:10:14: error: non-ASCII characters are not allower
side of literals and identifiers
If (r 'X')
> Console x
./main.c:10:18: error: non-ASCII characters are not allowed out
side of literals and identifiers
If (r
'X')
==
./main.c:10:22: error: expected ';' after expression
If (r
'X')
./main.c:10:17: error: use of undeclared identifier 'X'
If (r 'X')
./main.c:11:9: error: use of undeclared identifier 'Return'
Return 10;
:
./main.c:12:14: error: non-ASCII characters are not allowed out
side of literals and identifiers
If (r = 'L')
==
./main.c:12:18: error: non-ASCII characters are not allowed out
side of literals and identifiers
If (r 'L')
./main.c:12:22: error: expected ';' after expression
If (r
'L')
fatal error: too many errors emitted, stopping now [-ferror-lim
it=]
20 errors generated.
make: *** [Makefile:10: main] Error 1
exit status 2
>](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/5b1907b1-a684-4a7a-a6d2-eae182fd8cd2/d2ea89be-c762-403d-9c80-65055a90ca6f/8b0142j_thumbnail.png)








