Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
Which of the following forces does methanol (CH3-OH) exhibit? Select all that apply.
hydrogen bonding
London forces
dipole-dipole attractions
Expert Solution
Introduction
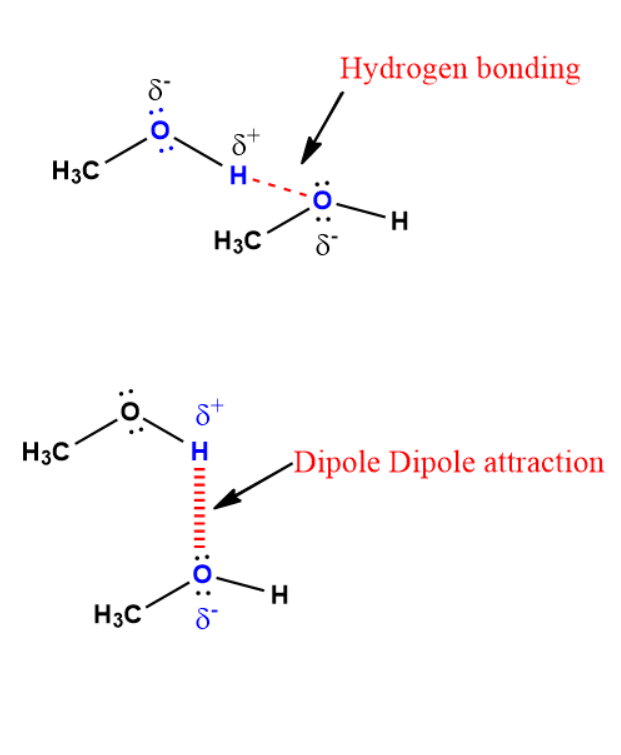
Hydrogen bonding -
- Electrostatic force of attraction.
- It exists between hydrogen atom that is bonded to more electronegative atom and another electronegative atom.
- Strong IMF.
Types-
- Intramolecular H-bonding (within molecule)
- Intermolecular H-bonding (between molecules)
London forces -
- Also known as London dispersion forces or Van der Waals forces.
- These are the temporary attractive forces that occur due to motion of electrons.
- Exists between polar, non-polar, ions , noble gases.
- Bond strength is high.
- Molecule with instantaneous dipole moment show dipole-dipole attractions.
Dipole-dipole attractions
- Electrostatic interaction and attractive forces between polar molecule.
- Partial positive end of polar molecule is attracted tp partial negative end of another polar molecule.
- Occur due to unequal sharing of electrons
- Bond strength is weak.
- Molecule with permanent dipole moment show dipole-dipole attractions.
Step 2
- London forces exists between all types of molecules.
- It has hydrogen boding between H attached to electronegative O atom and oxygen of another methanol molecule.
- This is intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
- Methanol is a polar molecule.
- It is permanent dipole moment.
- Dipole -dipole attraction is between partial positive H atom and partial negative oxygen atom.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY