Electronic Effects
The effect of electrons that are located in the chemical bonds within the atoms of the molecule is termed an electronic effect. The electronic effect is also explained as the effect through which the reactivity of the compound in one portion is controlled by the electron repulsion or attraction producing in another portion of the molecule.
Drawing Resonance Forms
In organic chemistry, resonance may be a mental exercise that illustrates the delocalization of electrons inside molecules within the valence bond theory of octet bonding. It entails creating several Lewis structures that, when combined, reflect the molecule's entire electronic structure. One Lewis diagram cannot explain the bonding (lone pair, double bond, octet) elaborately. A hybrid describes a combination of possible resonance structures that represents the entire delocalization of electrons within the molecule.
Using Molecular Structure To Predict Equilibrium
Equilibrium does not always imply an equal presence of reactants and products. This signifies that the reaction reaches a point when reactant and product quantities remain constant as the rate of forward and backward reaction is the same. Molecular structures of various compounds can help in predicting equilibrium.
Which hydrogen in this photo will be the most acidic and why?
![Consider the compound below. It is not a strong drug on its own, but when combined with antibiotics like amoxicillin or ticarcillin, it helps kill antibiotic-resistant bacteria. It does this by inhibiting an enzyme called β-lactamase, which resistant bacteria secrete to break down antibiotics to stop them from working.
[Chemical structure diagram]
- **Diagram Explanation:**
- The chemical structure in the center is a molecule with specific atoms labeled as Carbon and Oxygen.
- Each labeled atom has an associated box to indicate hybridization and geometry.
**Questions:**
a. What are the respective **hybridizations** and **geometries** of the indicated atoms in the compound? Fill the answers in the boxes provided above.
b. Identify all unique functional groups in the molecule.
c. Provide the molecular formula for this compound in the space below. Use the elements H, N, O.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fe51527b3-59d8-42fd-95cc-02eb00bd4c1c%2F9b7b8d99-2598-4e84-bb4b-f49382c3ad3a%2Fiej50ec.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Given:
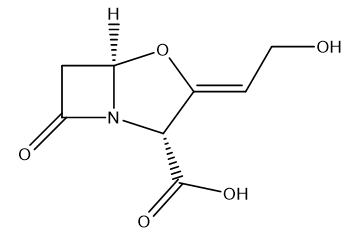
Generally the protons bonded to electronegative atom are more acidic and easily donated.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









