when an opinion poll calls landline telephone numbers at random, approximately 35% of the numbers are working residential phone numbers. The remainder are either non-residential, non-working, or computer/fax numbers. You watch the random dialing machine make 20 calls. (a) What is the mean number of calls that reach working residential numbers? (Enter your answer to one decimal place.) calls (b) What is the standard deviation ? of the count of calls that reach working residential numbers? (Round your answer to four decimal places.) calls (c) Suppose that the probability of reaching a working residential number was only p = 0.25. How does this new p affect the standard deviation? (Round your answer to four decimal places.) calls (d) What would be the standard deviation if p = 0.10? (Round your answer to four decimal places.) calls (e) What does your work show about the behavior of the standard deviation of a binomial distribution as the probability of a success gets closer to zero? As p approaches 0, the standard deviation increases. As p approaches 0, the standard deviation rises then falls. As p approaches 0, the standard deviation falls then rises. As p approaches 0, the standard deviation decreases. As p approaches 0, the standard deviation remains constant.
when an opinion poll calls landline telephone numbers at random, approximately 35% of the numbers are working residential phone numbers. The remainder are either non-residential, non-working, or computer/fax numbers. You watch the random dialing machine make 20 calls. (a) What is the mean number of calls that reach working residential numbers? (Enter your answer to one decimal place.) calls (b) What is the standard deviation ? of the count of calls that reach working residential numbers? (Round your answer to four decimal places.) calls (c) Suppose that the probability of reaching a working residential number was only p = 0.25. How does this new p affect the standard deviation? (Round your answer to four decimal places.) calls (d) What would be the standard deviation if p = 0.10? (Round your answer to four decimal places.) calls (e) What does your work show about the behavior of the standard deviation of a binomial distribution as the probability of a success gets closer to zero? As p approaches 0, the standard deviation increases. As p approaches 0, the standard deviation rises then falls. As p approaches 0, the standard deviation falls then rises. As p approaches 0, the standard deviation decreases. As p approaches 0, the standard deviation remains constant.
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
when an opinion poll calls landline telephone numbers at random, approximately 35% of the numbers are working residential phone numbers. The remainder are either non-residential, non-working, or computer/fax numbers. You watch the random dialing machine make 20 calls.
(a) What is the mean number of calls that reach working residential numbers? (Enter your answer to one decimal place.)
calls
(b) What is the standard deviation ? of the count of calls that reach working residential numbers? (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
calls
(c) Suppose that theprobability of reaching a working residential number was only
calls
(d) What would be the standard deviation if
calls
(e) What does your work show about the behavior of the standard deviation of a binomial distribution as the probability of a success gets closer to zero?
calls
(b) What is the standard deviation ? of the count of calls that reach working residential numbers? (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
calls
(c) Suppose that the
p = 0.25.
How does this new p affect the standard deviation? (Round your answer to four decimal places.)calls
(d) What would be the standard deviation if
p = 0.10?
(Round your answer to four decimal places.)calls
(e) What does your work show about the behavior of the standard deviation of a binomial distribution as the probability of a success gets closer to zero?
As p approaches 0, the standard deviation increases.
As p approaches 0, the standard deviation rises then falls.
As p approaches 0, the standard deviation falls then rises.
As p approaches 0, the standard deviation decreases.
As p approaches 0, the standard deviation remains constant.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Binomial distribution: A discrete r.v. X taking values 0,1,2,3, …., n is said to follow a binomial distribution with parameters n and p if it's p.m.f is given by,
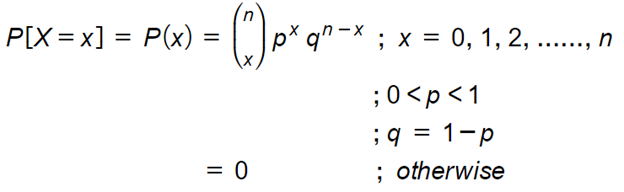
Given,
Sample size = n = 20
Probability of success = p = 35% = 0.35
q = 1-p = 1-0.35 = 0.65
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman