What olume of 17.1 M glacial acetic acid (HC2H3O2) must be added to 100.0 mL of 1.25 M KOH to form a buffer with a pH of 4.20? Ka (HC2H3O2) = 1.8 x 10-5 %3D
Thermochemistry
Thermochemistry can be considered as a branch of thermodynamics that deals with the connections between warmth, work, and various types of energy, formed because of different synthetic and actual cycles. Thermochemistry describes the energy changes that occur as a result of reactions or chemical changes in a substance.
Exergonic Reaction
The term exergonic is derived from the Greek word in which ‘ergon’ means work and exergonic means ‘work outside’. Exergonic reactions releases work energy. Exergonic reactions are different from exothermic reactions, the one that releases only heat energy during the course of the reaction. So, exothermic reaction is one type of exergonic reaction. Exergonic reaction releases work energy in different forms like heat, light or sound. For example, a glow stick releases light making that an exergonic reaction and not an exothermic reaction since no heat is released. Even endothermic reactions at very high temperature are exergonic.
I really don't understand #71

Given,
Molarity of glacial acetic acid=1.71M
Volume of KOH=100mL
Molarity of KOH=1.25M
pH of buffer=4.20
The reaction between acetic acid and potassium hydroxide is given below.
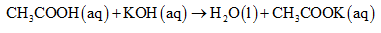
The number of moles of NaOH present in 100mL of 1.25M KOH can be calculated as shown below.
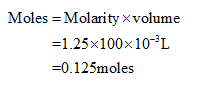
Assume that x moles of acetic acid is added to 0.125moles of KOH and construct the ICE table as follows:
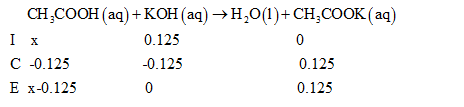
So, the equilibrium concentrations of acid and conjugate base are:
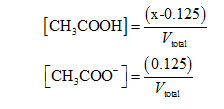
Here, Vtotal is the total volume of the buffer solution.
The value of pKa for acetic acid can be calculated as shown below.
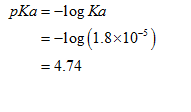
The pH of the buffer is 4.2
Using Henderson-Hasselbach equation, calculate x follows:
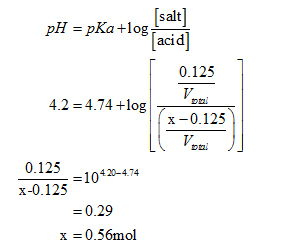
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 9 images









