Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the organic compounds that are obtained in foods and living matters in the shape of sugars, cellulose, and starch. The general formula of carbohydrates is Cn(H2O)2. The ratio of H and O present in carbohydrates is identical to water.
Starch
Starch is a polysaccharide carbohydrate that belongs to the category of polysaccharide carbohydrates.
Mutarotation
The rotation of a particular structure of the chiral compound because of the epimerization is called mutarotation. It is the repercussion of the ring chain tautomerism. In terms of glucose, this can be defined as the modification in the equilibrium of the α- and β- glucose anomers upon its dissolution in the solvent water. This process is usually seen in the chemistry of carbohydrates.
L Sugar
A chemical compound that is represented with a molecular formula C6H12O6 is called L-(-) sugar. At the carbon’s 5th position, the hydroxyl group is placed to the compound’s left and therefore the sugar is represented as L(-)-sugar. It is capable of rotating the polarized light’s plane in the direction anticlockwise. L isomers are one of the 2 isomers formed by the configurational stereochemistry of the carbohydrates.
![The image contains a handwritten chemical reaction and some proposed products. Here’s the transcription:
**Chemical Reaction:**
\[ \text{H}_3\text{C}-\text{CH}_2-\text{CH}=\text{CH}_2 + \text{H}_2\text{O} \xrightarrow{\text{H}^+} \]
**Proposed Products:**
A. \[ \text{H}_3\text{C}-\text{CH}_2-\text{CH}_2-\text{CH}_2\text{OH} \]
B. \[ \text{H}_3\text{C}-\text{CH}_2-\text{CH}(\text{OH})-\text{CH}_3 \]
C. \[ \text{H}_3\text{C}-\text{CH}(\text{OH})-\text{CH}_2-\text{CH}_2\text{OH} \]
D. \[ \text{H}_3\text{C}-\text{CH}(\text{OH})-\text{CH}-\text{CH}_3 \]
**Explanation of Reaction:**
This reaction depicts the hydration of an alkene (\(\text{H}_3\text{C}-\text{CH}_2-\text{CH}=\text{CH}_2\)) in the presence of an acid (indicated by \(\text{H}^+\)) to form various alcohol products. The starting material, 1-butene, reacts with water (\(\text{H}_2\text{O}\)) to form an alcohol. Different products are proposed based on the Markovnikov or anti-Markovnikov addition of water across the double bond.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fd5dead9f-e821-4d1f-b49e-a22938bc1d4f%2F5b69abaa-ed0d-4e5c-81df-3746d053e325%2F435mqp_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
The product for the given reaction is to be identified.
The given reaction is,
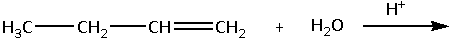
The alkenes on acidic hydrolysis undergoes addition of H2O across the C=C bond. The reaction proceeds the through formation of carbocation due to abstraction of H+. Thus, the hydroges goes to less substituted carbon of C=C bond and results in formation of most substituted carbocation.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









