What is the difference between these 2 signals: a(n) = (3)"-lu(n – 1) b(n) = (3)"-lu(n)
What is the difference between these 2 signals: a(n) = (3)"-lu(n – 1) b(n) = (3)"-lu(n)
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:Robert L. Boylestad
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P: Visit your local library (at school or home) and describe the extent to which it provides literature...
Related questions
Question
100%
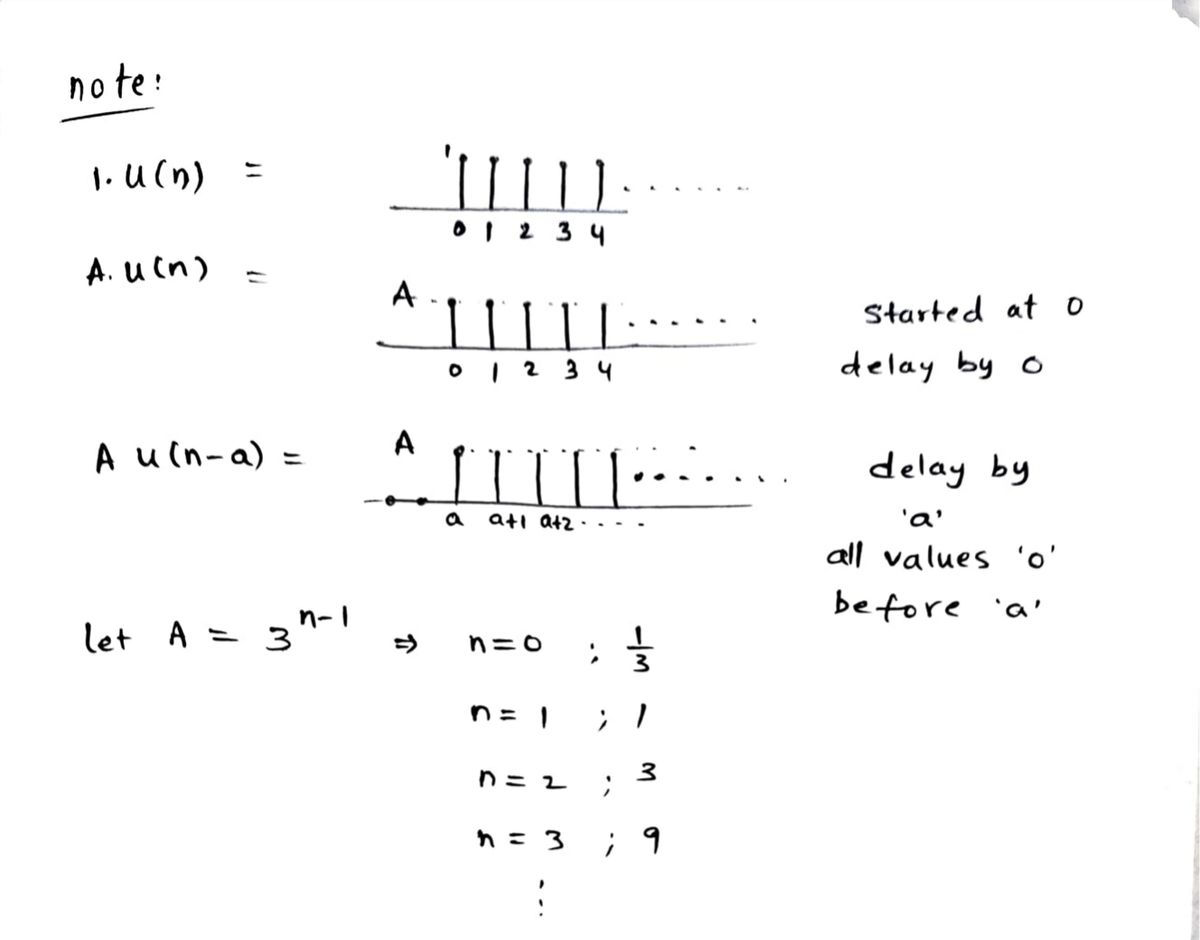
![**Understanding the Difference Between Two Signal Functions**
In this lesson, we are exploring the difference between two discrete-time signals given by the following mathematical expressions:
1. **Signal \(a(n)\):**
\[
a(n) = (3)^{n-1} u(n-1)
\]
2. **Signal \(b(n)\):**
\[
b(n) = (3)^{n-1} u(n)
\]
**Key Components:**
- \( (3)^{n-1} \): This is an exponential term that affects how rapidly the signal changes with \(n\).
- \( u(n) \) and \( u(n-1) \): These represent the unit step functions. The unit step function \( u(n) \) is 0 for \( n < 0 \) and 1 for \( n \geq 0 \). Similarly, \( u(n-1) \) shifts this step to the right by one unit.
**Difference Analysis:**
- **Starting Point:**
- \(a(n)\) starts from \(n = 1\) because the function is \(u(n-1)\), which implies the signal is zero for \(n < 1\).
- \(b(n)\) starts from \(n = 0\) since the function is \(u(n)\), making the signal non-zero starting at \(n = 0\).
- **Effect of the Unit Step Function:**
- The shift in the step function for \(a(n)\) modifies when the signal becomes active, effectively delaying the signal by one unit compared to \(b(n)\).
By understanding the impact of these elements, we can analyze how these signals differ in terms of their behavior and starting points. The presence of the unit step function \(u(n-1)\) in \(a(n)\) causes a delay compared to the signal \(b(n)\), which starts immediately at \(n = 0\).](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F519bfe9f-adbe-447c-99db-12033d74cebc%2Feb5bf714-f78e-48e9-83ec-d5ede9984e05%2Fa7vy5kt_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Understanding the Difference Between Two Signal Functions**
In this lesson, we are exploring the difference between two discrete-time signals given by the following mathematical expressions:
1. **Signal \(a(n)\):**
\[
a(n) = (3)^{n-1} u(n-1)
\]
2. **Signal \(b(n)\):**
\[
b(n) = (3)^{n-1} u(n)
\]
**Key Components:**
- \( (3)^{n-1} \): This is an exponential term that affects how rapidly the signal changes with \(n\).
- \( u(n) \) and \( u(n-1) \): These represent the unit step functions. The unit step function \( u(n) \) is 0 for \( n < 0 \) and 1 for \( n \geq 0 \). Similarly, \( u(n-1) \) shifts this step to the right by one unit.
**Difference Analysis:**
- **Starting Point:**
- \(a(n)\) starts from \(n = 1\) because the function is \(u(n-1)\), which implies the signal is zero for \(n < 1\).
- \(b(n)\) starts from \(n = 0\) since the function is \(u(n)\), making the signal non-zero starting at \(n = 0\).
- **Effect of the Unit Step Function:**
- The shift in the step function for \(a(n)\) modifies when the signal becomes active, effectively delaying the signal by one unit compared to \(b(n)\).
By understanding the impact of these elements, we can analyze how these signals differ in terms of their behavior and starting points. The presence of the unit step function \(u(n-1)\) in \(a(n)\) causes a delay compared to the signal \(b(n)\), which starts immediately at \(n = 0\).
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028229
Author:
Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134746968
Author:
James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028151
Author:
Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:
Mcgraw-hill Education,