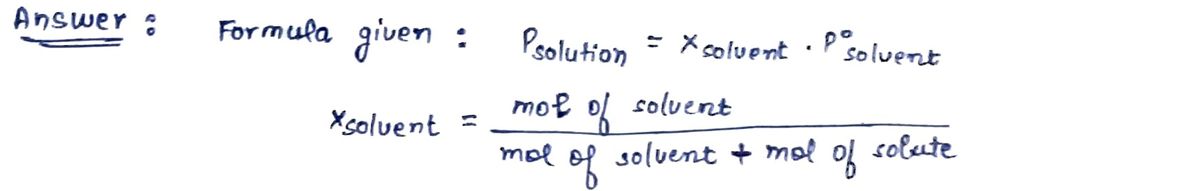
Vapor Pressure Lowering The vapor pressure of a pure solvent is REDUCED when a nonvolatile solute is added. This is summarized by Raoult's Law: Psolution = Xsolvent Posolvent Where: Psolution is the vapor pressure of the solution Xsolvent is the mole fraction of the solvent in the solution = (mol solvent)/(mol solvent + mol solute) Pºsolvent is the vapor pressure of the pure solvent As more solute particles are added, the mole fraction of the solvent goes down, and the vapor pressure is reduced.
Vapor Pressure Lowering The vapor pressure of a pure solvent is REDUCED when a nonvolatile solute is added. This is summarized by Raoult's Law: Psolution = Xsolvent Posolvent Where: Psolution is the vapor pressure of the solution Xsolvent is the mole fraction of the solvent in the solution = (mol solvent)/(mol solvent + mol solute) Pºsolvent is the vapor pressure of the pure solvent As more solute particles are added, the mole fraction of the solvent goes down, and the vapor pressure is reduced.
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter11: Properties Of Solutions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7RQ: Vapor-pressure lowering is a colligative property, as are freezing-point depression and...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Vapor Pressure Lowering
The vapor pressure of a pure solvent is REDUCED when a nonvolatile solute is added.
This is summarized by Raoult's Law:
Psolution = Xsolvent Posolvent
Where:
Psolution is the vapor pressure of the solution
Xsolvent is the mole fraction of the solvent in the solution = (mol solvent)/(mol solvent + mol solute)
Pº solvent is the vapor pressure of the pure solvent
As more solute particles are added, the mole fraction of the solvent goes down, and the vapor pressure is reduced.

Transcribed Image Text:The vapor pressure of chloroform is 173.11 mm Hg at 25 °C. A nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte that dissolves in
chloroform is aspirin.
Calculate the vapor pressure of the solution at 25 °C when 12.85 grams of aspirin, C9Hg04 (180.1 g/mol), are
dissolved in 186.9 grams of chloroform.
chloroform =
VP(solution)
=
CHCl3 = 119.40 g/mol.
mm Hg
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning