Use source trans tor motion to find lo in the circuit showwn. io 3A O 12V
Use source trans tor motion to find lo in the circuit showwn. io 3A O 12V
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
7th Edition
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Stephen L. Herman
Chapter7: Parallel Circuits
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3PP: Using the rules for parallel circuits and Ohmslaw, solve for the missing values....
Related questions
Question

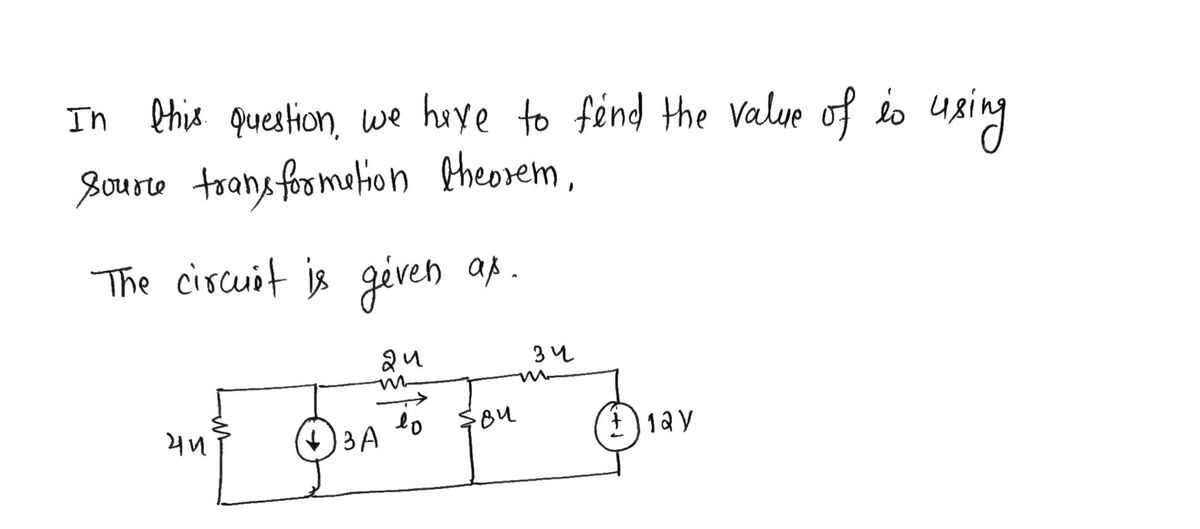
Transcribed Image Text:**Circuit Analysis Using Source Transformation**
**Objective:** Use source transformation to find \( i_o \) in the circuit shown.
**Circuit Description:**
- The circuit contains the following elements in series and parallel arrangements:
- A 4-ohm resistor connected in series with a current source of 3 A, pointing downward.
- A 2-ohm resistor, labeled to carry current \( i_o \), in parallel with an 8-ohm resistor.
- A 3-ohm resistor connected in series after the parallel combination.
- A voltage source of 12 V connected at the end of the series.
**Analysis Approach:**
1. **Identify Source Transformations:**
- Consider replacing the current source (3 A) and the series 4-ohm resistor with an equivalent voltage source. The equivalent voltage source value is found by multiplying the current by the resistance (V = I × R).
2. **Re-draw the Circuit:**
- After applying the source transformation, re-draw the circuit to reflect the changes and make further analysis easier.
3. **Calculate the Output Current \( i_o \):**
- Use Ohm’s Law and any other necessary circuit theorems (such as nodal or mesh analysis) to find the value of the current \( i_o \) flowing through the 2-ohm resistor.
In the educational context, illustrating the step-by-step process of source transformations and circuit simplifications allows for a clearer understanding of the methods used in electrical engineering analysis.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning