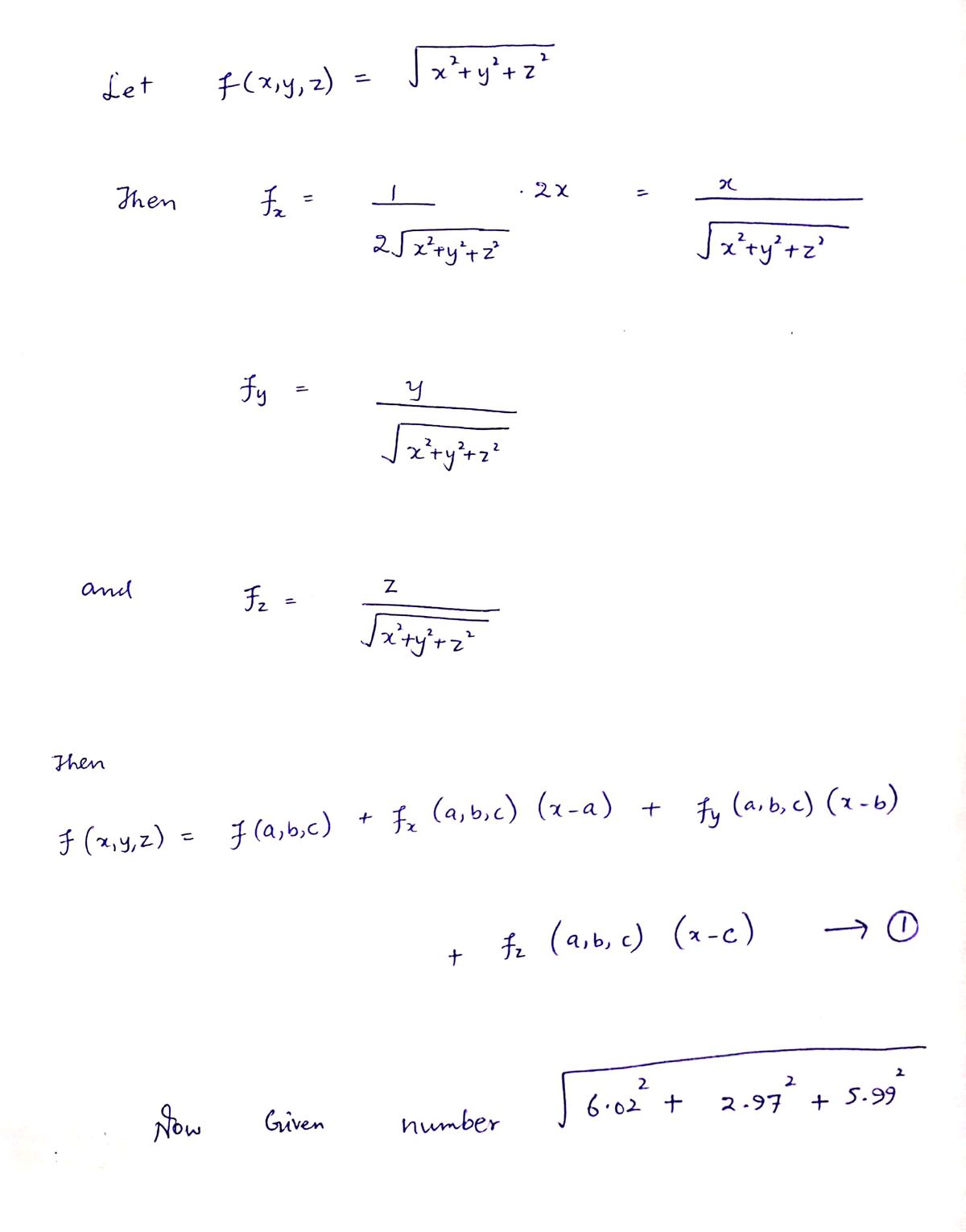
Use differentials to approximate the number V6.022 + 2.972 + 5.99². (Round your answer to five decimal place 8.9967
Use differentials to approximate the number V6.022 + 2.972 + 5.99². (Round your answer to five decimal place 8.9967
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Erwin Kreyszig
Chapter2: Second-order Linear Odes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:**Problem Statement:**
Use differentials to approximate the number \(\sqrt{6.02^2 + 2.97^2 + 5.99^2}\). (Round your answer to five decimal places.)
**User Input:**
8.9967 (This answer is marked as incorrect with an "X")
---
**Explanation:**
In this exercise, you are asked to use differentials to approximate a numerical expression. Differentials are a way to estimate small changes in functions based on their derivatives. In this context, they can be applied to approximate the square root expression provided.
When applying differentials to approximate \(\sqrt{x^2 + y^2 + z^2}\), you consider the small changes in \(x\), \(y\), and \(z\) as they slightly deviate from whole numbers (e.g., from 6.02 to 6, from 2.97 to 3, etc.).
The expression implies calculating the distance in three-dimensional space from the origin using the modified coordinates, and the use of differentials involves approximating this result efficiently, particularly when the modifications to each coordinate are small. The emphasis on approximation suggests utililzing linear approximations or first-order Taylor expansions around a point (x = 6, y = 3, z = 6).
After determining the appropriate calculations, results are rounded to five decimal places for precision.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

