Use a 0.05 to test for any significant differences. State the null and alternative hypotheses. O Ho: Not all the population means are equal. На: М1 = М2 = из =H4 о но: H1 + H2 + H3 + H4 На: М1 = M2 = M3 = H4 O Ho: At least two of the population means are equal. Ha: At least two of the population means are different. о но н1 = H2= H3 = 14 на: M1 #H2 + H3 + H4 о но: H1 = H2= из = H4 Ha: Not all the population means are equal. Find the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) Find the p-value. (Round p-value = answer to three decimal places.) State your conclusion. O Reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the four treatments are not all equal. O Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the four treatments are not all equal. O Do not reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the four treatments are not all equal. O Do not reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the four treatments are not all equal.
Use a 0.05 to test for any significant differences. State the null and alternative hypotheses. O Ho: Not all the population means are equal. На: М1 = М2 = из =H4 о но: H1 + H2 + H3 + H4 На: М1 = M2 = M3 = H4 O Ho: At least two of the population means are equal. Ha: At least two of the population means are different. о но н1 = H2= H3 = 14 на: M1 #H2 + H3 + H4 о но: H1 = H2= из = H4 Ha: Not all the population means are equal. Find the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) Find the p-value. (Round p-value = answer to three decimal places.) State your conclusion. O Reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the four treatments are not all equal. O Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the four treatments are not all equal. O Do not reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the four treatments are not all equal. O Do not reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the four treatments are not all equal.
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
State the null hypthosis and after please. Don't worry filling out the table.

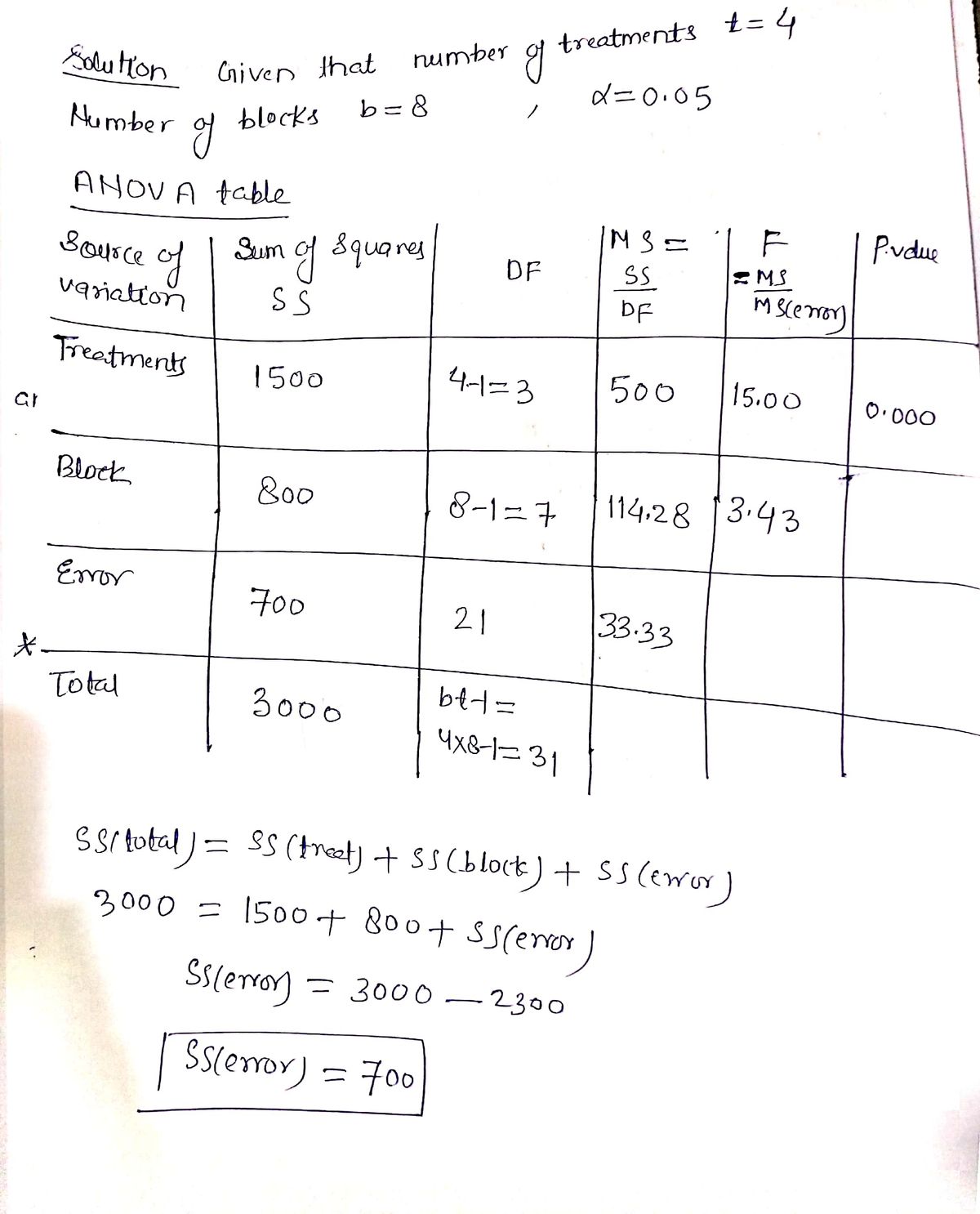
Transcribed Image Text:An experiment has been conducted for four treatments with eight blocks. Complete the following analysis of variance table. (Round your values for mean squares and F to two decimal places, and your p-value to three decimal places.)
| Source of Variation | Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom | Mean Square | F | p-value |
|---------------------|----------------|--------------------|-------------|---|---------|
| Treatments | 1,500 | | | | |
| Blocks | 800 | | | | |
| Error | | | | | |
| Total | 3,000 | | | | |
Use α = 0.05 to test for any significant differences.
![Use \(\alpha = 0.05\) to test for any significant differences.
State the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}\): Not all the population means are equal.
\(H_{a}\): \(\mu_{1} = \mu_{2} = \mu_{3} = \mu_{4}\)
- \(H_{0}\): \(\mu_{1} = \mu_{2} \ne \mu_{3} \ne \mu_{4}\)
\(H_{a}\): \(\mu_{1} = \mu_{2} = \mu_{3} = \mu_{4}\)
- \(H_{0}\): At least two of the population means are equal.
\(H_{a}\): At least two of the population means are different.
- \(H_{0}\): \(\mu_{1} = \mu_{2} = \mu_{3} = \mu_{4}\)
\(H_{a}\): \(\mu_{1} \ne \mu_{2} + \mu_{3} \ne \mu_{4}\)
- \(H_{0}\): \(\mu_{1} = \mu_{2} = \mu_{3} = \mu_{4}\)
\(H_{a}\): Not all the population means are equal.
Find the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
\[ \_\_\_\_\_\_ \]
Find the \(p\)-value. (Round your answer to three decimal places.)
\[ p\text{-value} = \_\_\_\_\_\_ \]
State your conclusion.
- \(\circ\) Reject \(H_{0}\). There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the four treatments are not all equal.
- \(\circ\) Reject \(H_{0}\). There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the four treatments are not all equal.
- \(\circ\) Do not reject \(H_{0}\). There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the four treatments are not all equal.
- \(\circ\) Do not reject \(H_{0}\). There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the four treatments are not all equal.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F8ad87420-52d2-4e34-815e-eb9bcb5c95c0%2F420d1e1e-8714-4a6b-be88-ea3892e305cb%2Fer6xyw_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:Use \(\alpha = 0.05\) to test for any significant differences.
State the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}\): Not all the population means are equal.
\(H_{a}\): \(\mu_{1} = \mu_{2} = \mu_{3} = \mu_{4}\)
- \(H_{0}\): \(\mu_{1} = \mu_{2} \ne \mu_{3} \ne \mu_{4}\)
\(H_{a}\): \(\mu_{1} = \mu_{2} = \mu_{3} = \mu_{4}\)
- \(H_{0}\): At least two of the population means are equal.
\(H_{a}\): At least two of the population means are different.
- \(H_{0}\): \(\mu_{1} = \mu_{2} = \mu_{3} = \mu_{4}\)
\(H_{a}\): \(\mu_{1} \ne \mu_{2} + \mu_{3} \ne \mu_{4}\)
- \(H_{0}\): \(\mu_{1} = \mu_{2} = \mu_{3} = \mu_{4}\)
\(H_{a}\): Not all the population means are equal.
Find the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
\[ \_\_\_\_\_\_ \]
Find the \(p\)-value. (Round your answer to three decimal places.)
\[ p\text{-value} = \_\_\_\_\_\_ \]
State your conclusion.
- \(\circ\) Reject \(H_{0}\). There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the four treatments are not all equal.
- \(\circ\) Reject \(H_{0}\). There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the four treatments are not all equal.
- \(\circ\) Do not reject \(H_{0}\). There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the four treatments are not all equal.
- \(\circ\) Do not reject \(H_{0}\). There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the four treatments are not all equal.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman