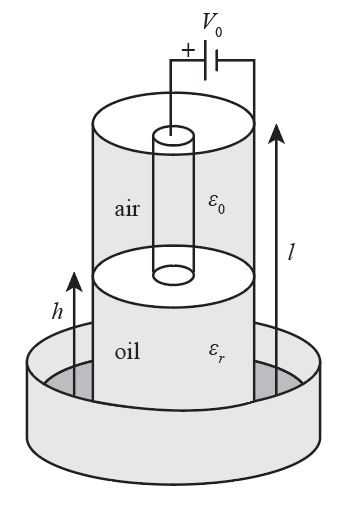
Two coaxial tubes are inserted into a tray containing an insulating liquid (oil) with a dielectric constant of , and a mass density of Pm [kg/m³]. A voltage Vo is applied between the tubes as shown, and this causes the level of the oil to rise to a level h in the space between the tubes due to electrostatic forces. Recall that the capacitance per unit length of a coaxial structure is given by [F/m] C= 2πε In(b/a) h air Eo oil Er where a and b are the inner and outer radii of the coaxial structure, respectively. (a) First find the capacitance of the structure as shown. (b) Next find the force acting on the dielectric (oil) (c) Find the height h to which the oil rises in the tube as a function of V.
Two coaxial tubes are inserted into a tray containing an insulating liquid (oil) with a dielectric constant of , and a mass density of Pm [kg/m³]. A voltage Vo is applied between the tubes as shown, and this causes the level of the oil to rise to a level h in the space between the tubes due to electrostatic forces. Recall that the capacitance per unit length of a coaxial structure is given by [F/m] C= 2πε In(b/a) h air Eo oil Er where a and b are the inner and outer radii of the coaxial structure, respectively. (a) First find the capacitance of the structure as shown. (b) Next find the force acting on the dielectric (oil) (c) Find the height h to which the oil rises in the tube as a function of V.
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:Robert L. Boylestad
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P: Visit your local library (at school or home) and describe the extent to which it provides literature...
Related questions
Question
Handwrite and step by step solution
![Two coaxial tubes are inserted into a tray containing an insulating liquid (oil) with a dielectric constant of \( \varepsilon_r \), and a mass density of \( \rho_m \) [kg/m\(^3\)]. A voltage \( V_0 \) is applied between the tubes as shown, and this causes the level of the oil to rise to a level \( h \) in the space between the tubes due to electrostatic forces. Recall that the capacitance **per unit length** of a coaxial structure is given by
\[
C = \frac{2 \pi \varepsilon}{\ln(b/a)} \quad [\text{F/m}]
\]
where \( a \) and \( b \) are the inner and outer radii of the coaxial structure, respectively.
(a) First find the capacitance of the structure as shown.
(b) Next find the force acting on the dielectric (oil).
(c) Find the height \( h \) to which the oil rises in the tube as a function of \( V_0 \).
**Diagram Explanation:**
The diagram shows two concentric cylinders (coaxial tubes) with an insulating liquid (oil) between them. The inner cylinder is surrounded by air with permittivity \( \varepsilon_0 \) and the space between the cylinders is filled with oil with permittivity \( \varepsilon_r \). The voltage applied is \( V_0 \), and this setup causes the liquid to rise to height \( h \). The length of the tubes is \( \ell \).](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F584ffa08-94ad-4eb4-a87d-fd258db9f802%2Fe894ee82-d787-4a23-b009-4f82765ea2d5%2Ffkcdyp_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:Two coaxial tubes are inserted into a tray containing an insulating liquid (oil) with a dielectric constant of \( \varepsilon_r \), and a mass density of \( \rho_m \) [kg/m\(^3\)]. A voltage \( V_0 \) is applied between the tubes as shown, and this causes the level of the oil to rise to a level \( h \) in the space between the tubes due to electrostatic forces. Recall that the capacitance **per unit length** of a coaxial structure is given by
\[
C = \frac{2 \pi \varepsilon}{\ln(b/a)} \quad [\text{F/m}]
\]
where \( a \) and \( b \) are the inner and outer radii of the coaxial structure, respectively.
(a) First find the capacitance of the structure as shown.
(b) Next find the force acting on the dielectric (oil).
(c) Find the height \( h \) to which the oil rises in the tube as a function of \( V_0 \).
**Diagram Explanation:**
The diagram shows two concentric cylinders (coaxial tubes) with an insulating liquid (oil) between them. The inner cylinder is surrounded by air with permittivity \( \varepsilon_0 \) and the space between the cylinders is filled with oil with permittivity \( \varepsilon_r \). The voltage applied is \( V_0 \), and this setup causes the liquid to rise to height \( h \). The length of the tubes is \( \ell \).
Expert Solution
Step 1
Given data:
The capacitance,
The given diagram is shown below,
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028229
Author:
Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134746968
Author:
James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028151
Author:
Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:
Mcgraw-hill Education,