Two blocks , each of mass m = 4.0 kg, are hung from the ceiling of an elevator as shown below. The elevator moves with an upward acceleration a, and the tension of the rope supporting the upper mass is T1 = 80N. Find: Provide free body diagrams and summation of the forces. 1. The magnitude of the acceleration. 2. The value of Tension T2
Two blocks , each of mass m = 4.0 kg, are hung from the ceiling of an elevator as shown below. The elevator moves with an upward acceleration a, and the tension of the rope supporting the upper mass is T1 = 80N. Find: Provide free body diagrams and summation of the forces. 1. The magnitude of the acceleration. 2. The value of Tension T2
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter1: Units, Trigonometry. And Vectors
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1CQ: Estimate the order of magnitude of the length, in meters, of each of the following; (a) a mouse, (b)...
Related questions
Question
100%
Two blocks , each of mass m = 4.0 kg, are hung from the ceiling of an elevator as shown below. The elevator moves with an upward acceleration a, and the tension of the rope supporting the upper mass is T1 = 80N. Find:
Provide free body diagrams and summation of the forces.
1. The magnitude of the acceleration.
2. The value of Tension T2

Transcribed Image Text:### Diagram Explanation
This diagram illustrates a mechanical system involving two masses inside a vertically accelerating frame, which is suspended by a rope. Here's a detailed breakdown of the components in the diagram:
1. **Masses**: There are two masses labeled as \( m \). They are connected in a vertical orientation.
2. **Tensions**:
- \( T_1 \) is the tension in the rope above the first mass.
- \( T_2 \) is the tension in the rope between the two masses.
3. **Acceleration**:
- The entire system is experiencing an upward acceleration, indicated by the vector \( \vec{a} \) pointing upwards.
### Educational Context
This setup is typically used to study the effects of forces and acceleration in a non-inertial reference frame. Key concepts include:
- Understanding how tension varies in a system with multiple masses.
- The effect of an accelerating frame of reference, which adds a fictitious force in the opposite direction of acceleration.
- Application of Newton’s Second Law (\( F = ma \)) to each mass, accounting for gravitational and tension forces, as well as the effect of the frame's acceleration.
Expert Solution
Step 1
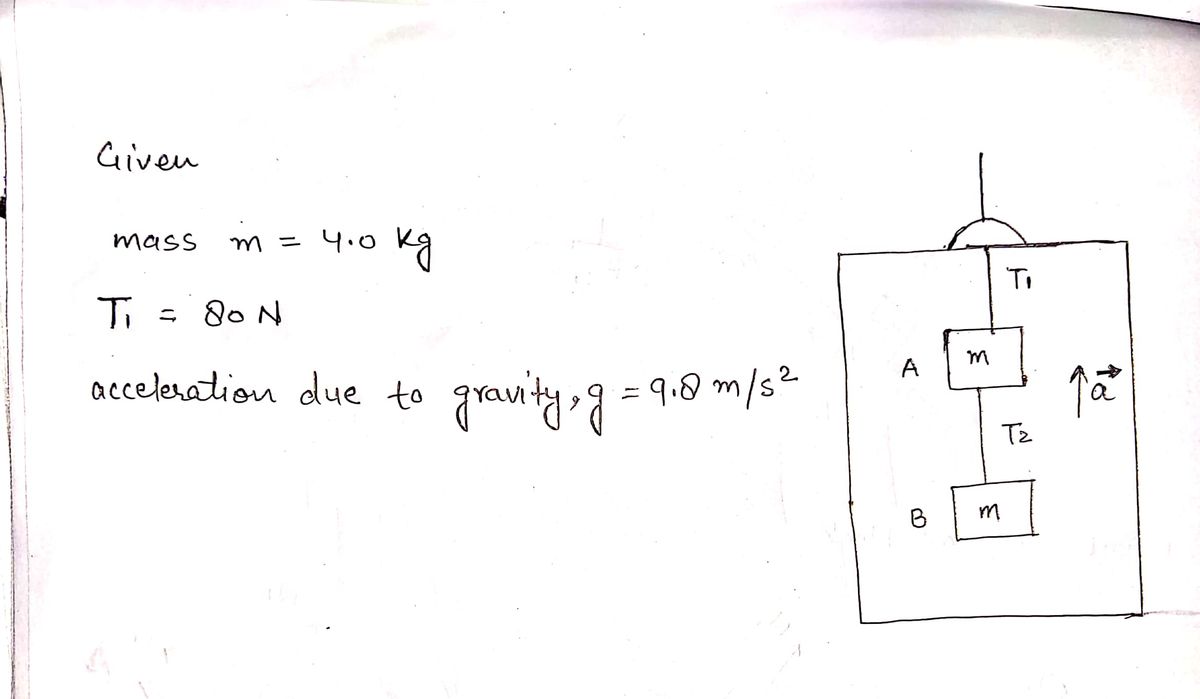
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:
9780321820464
Author:
Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:
Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio…
Physics
ISBN:
9780134609034
Author:
Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:
PEARSON