THERMODYNAMIC TABLES AG Values AH: Values Substance kJ/mole Substance kJ/mole co (g) -137 -110 co(s) co2 (g) -395 -394 Co2 (g) Fez03 (s) -742 238
THERMODYNAMIC TABLES AG Values AH: Values Substance kJ/mole Substance kJ/mole co (g) -137 -110 co(s) co2 (g) -395 -394 Co2 (g) Fez03 (s) -742 238
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P
Related questions
Question
Please answer and show all work, thank you!! Thermodynamics table is shown below :)

Transcribed Image Text:**Thermodynamic Tables**
### ΔH<sub>f</sub>° Values
| Substance | kJ/mole |
|----------------|---------|
| CO(g) | -110 |
| CO₂(g) | -394 |
| CH₃OH(l) | -238 |
| CH₄(g) | -75 |
| C₂H₄(g) | +52 |
| Fe₂O₃(s) | -824 |
| H₂O(l) | -286 |
| H₂O(g) | -242 |
| NaCl(s) | -413 |
| NaOH(aq) | -470 |
| NH₃(g) | -46 |
| NO(g) | +90 |
| C₂H₅OH(l) | -485 |
| HC₂H₃O₂(l) | -278 |
### ΔG<sub>f</sub>° Values
| Substance | kJ/mole |
|----------------|---------|
| CO(g) | -137 |
| CO₂(g) | -395 |
| Fe₂O₃(s) | -742 |
| H₂O(l) | -237 |
| H₂O(g) | -228 |
| NH₃(g) | -17 |
| NO(g) | +87 |
| NO₂(g) | +51 |
| N₂O₄(g) | +98 |
| C₂H₅OH(l) | -390 |
| HC₂H₃O₂(l) | -175 |
### Atomization Energies
| Atom | kJ/mole atom |
|------|--------------|
| C(g) | 715 |
| Cl(g)| 121 |
| H(g) | 218 |
| I(g) | 107 |
| Na(g)| 108 |
| O(g) | 249 |
| N(g) | 473 |
### Bond Energies
| Bond | kJ/mole bond |
|---------|--------------|
| C-C(g) | 348 |
| C-Cl(g) | 326 |
| C=O(g)
![**Problem Statement:**
Calculate the absolute entropy of steam, in J/mole-K, if \( H_2O(l) \) has an absolute entropy of 70 J/mole-K.
(Hint: write the chemical equation for boiling water and use the Thermodynamic Tables.)
---
**Explanation:**
To calculate the absolute entropy of steam, we start by considering the phase change of water from liquid to gas:
- **Chemical Equation for Boiling Water:**
\[
H_2O(l) \rightarrow H_2O(g)
\]
- **Thermodynamic Tables:**
Typically, these tables provide the standard molar entropy values for various substances in different phases.
- **Approach:**
Use the thermodynamic tables to find the entropy change for the phase transition and then add it to the given entropy of liquid water to find the absolute entropy of steam.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F17525826-644e-4b54-80a2-4cc5c7d853ae%2F22ca0f99-f91a-48d9-8afd-661a40747bb2%2F149dhek_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem Statement:**
Calculate the absolute entropy of steam, in J/mole-K, if \( H_2O(l) \) has an absolute entropy of 70 J/mole-K.
(Hint: write the chemical equation for boiling water and use the Thermodynamic Tables.)
---
**Explanation:**
To calculate the absolute entropy of steam, we start by considering the phase change of water from liquid to gas:
- **Chemical Equation for Boiling Water:**
\[
H_2O(l) \rightarrow H_2O(g)
\]
- **Thermodynamic Tables:**
Typically, these tables provide the standard molar entropy values for various substances in different phases.
- **Approach:**
Use the thermodynamic tables to find the entropy change for the phase transition and then add it to the given entropy of liquid water to find the absolute entropy of steam.
Expert Solution
Entropy change

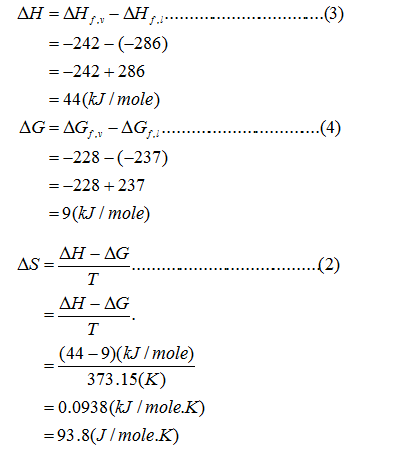
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285061238
Author:
Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:
Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780072848236
Author:
Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Companies, The