Theory. Fill in the MO diagrams, determine the MO bond order, and indicate which molecules/ions are paramagnetic or diamagnetic 0, 0, diatomic BC" MO diagram MO bond order ...... paramagnetic .....*w..... diamagnetic

According to molecular orbital theory:
Atomic orbitals will combine and form molecular orbitals.
The number of atomic orbitals combined is equal to the number of molecular orbitals.
If two atomic orbitals will combine then, two molecular orbitals will be formed and between them one molecular orbital has lower energy and the other molecular orbital has high energy.
The molecular orbital with lower energy is called bonding molecular orbital and the other with high energy is called anti bonding molecular orbital.
If a molecule has unpaired electrons in its molecular orbitals then it is para magnetic.
If a molecule does not have unpaired electrons then, it is dia magnetic.
The molecular ion diagram for the given molecules:
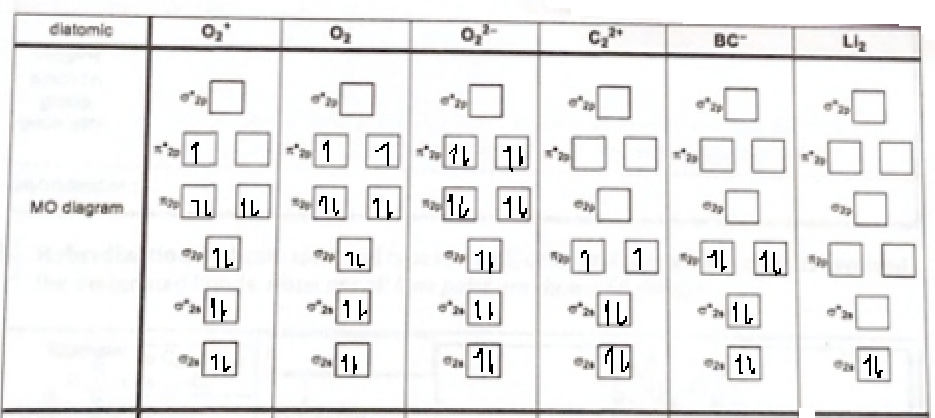
Bond order of O22+:
Bond order O2:
Bond order of O22-:
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 1 images









