The total number P of prey taken by a predator depends on the availability of prey. C. S. Holling proposed a function of the form P cn/(1 + dn) to model the number of prey taken in certain situations. Here n is the density of prey available, and e and d are constants that depend on the organisms involved as vell as on other environmental features. Holling took data gathered earlier by T. Burnett on the number of sawfly cocoons found by a small wasp parasite at given host density. In one such experiment conducted, Holling found the relationship P21.96n 1+ 2.410 where Pis the number of cocoons parasitized and n is the density of cocoons available (measured as number per square inch). (a) Draw a graph of P versus n. Include values of n up to 2 cocoons per square inch. 15 15 10 10 0.5 1.0 1.5 0.5 2.0" 1.0 1.5 15 1아 10 0.5 1.0 1.5 20" 05 1.0 1.5 2.0 (b) what density of cocoons will ensure that the vasp will find and parasitize 4 of them? (Round your answer to one decimal place.) cocoon(s) per square inch (c) There is a limit to the number of cocoons that the wasp is able to parasitize no matter how readily available the prey may be. What is this upper limit? (Round your answer to the nearest whole number.) cocoons
The total number P of prey taken by a predator depends on the availability of prey. C. S. Holling proposed a function of the form P cn/(1 + dn) to model the number of prey taken in certain situations. Here n is the density of prey available, and e and d are constants that depend on the organisms involved as vell as on other environmental features. Holling took data gathered earlier by T. Burnett on the number of sawfly cocoons found by a small wasp parasite at given host density. In one such experiment conducted, Holling found the relationship P21.96n 1+ 2.410 where Pis the number of cocoons parasitized and n is the density of cocoons available (measured as number per square inch). (a) Draw a graph of P versus n. Include values of n up to 2 cocoons per square inch. 15 15 10 10 0.5 1.0 1.5 0.5 2.0" 1.0 1.5 15 1아 10 0.5 1.0 1.5 20" 05 1.0 1.5 2.0 (b) what density of cocoons will ensure that the vasp will find and parasitize 4 of them? (Round your answer to one decimal place.) cocoon(s) per square inch (c) There is a limit to the number of cocoons that the wasp is able to parasitize no matter how readily available the prey may be. What is this upper limit? (Round your answer to the nearest whole number.) cocoons
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Erwin Kreyszig
Chapter2: Second-order Linear Odes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:The total number P of prey taken by a predator depends on the availability of prey. C. S. Holling proposed a function of the form P = cn/(1 + dn) to model the number of prey taken in certain situations. Here n is the density of prey available, and c and d are constants that depend on the
organisms involved as well as on other environmental features. Holling took data gathered earlier by T. Burnett on the number of sawfly cocoons found by a small wasp parasite at given host density. In one such experiment conducted, Holling found the relationship
21.96n
1 + 2.412
where Pis the number of cocoons parasitized and a is the density of cocoons available (measured as number per square inch).
(a) Draw a graph of P versus n. Include values of n up to 2 cocoons per square inch.
P
15
15
10
10
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
15
15
10
10-
5
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
(b) What density of cocoons will ensure that the wasp will find and parasitize 4 of them? (Round your ansswer to one decimal place.)
cocoon(s) per square inch
(c) There is a limit to the number of cocoons that the wasp is able to parasitize no matter how readily available the prey may be. What is this upper limit? (Round your answer to the nearest whole number.)
cocoons
Expert Solution
Step 1
Given relationship is
(i)
Where is the number of cocoons parasitized and is the density of cocoons available measured in per square inch.
The graph of the given relation is shown below.
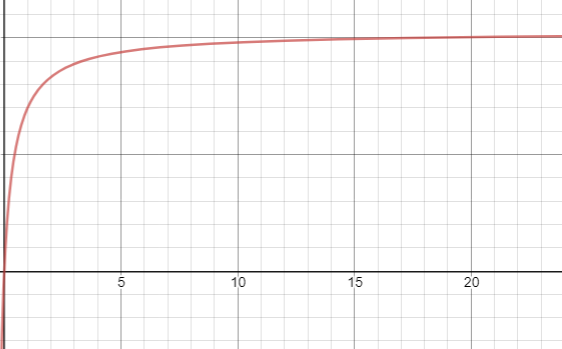
So, correct answer is C
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

