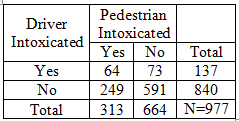
The table summarizes results from pedestrian deaths that were caused by automobile accidents. Pedestrian Deaths Pedestrian Intoxicated? Driver Intoxicated? Yes No Yes 64 73 No 249 591 If two different pedestrian deaths are randomly selected, find the probability that they both involved drivers that were not intoxicated. Report the answer rounded to four decimal place accuracy.
Contingency Table
A contingency table can be defined as the visual representation of the relationship between two or more categorical variables that can be evaluated and registered. It is a categorical version of the scatterplot, which is used to investigate the linear relationship between two variables. A contingency table is indeed a type of frequency distribution table that displays two variables at the same time.
Binomial Distribution
Binomial is an algebraic expression of the sum or the difference of two terms. Before knowing about binomial distribution, we must know about the binomial theorem.
![The table summarizes results from pedestrian deaths that were caused by automobile accidents.
**Pedestrian Deaths**
| Driver Intoxicated? | Pedestrian Intoxicated? Yes | Pedestrian Intoxicated? No |
|---------------------|----------------------------|---------------------------|
| Yes | 64 | 73 |
| No | 249 | 591 |
If two different pedestrian deaths are randomly selected, find the probability that they both involved drivers that were not intoxicated. Report the answer rounded to four decimal place accuracy.
**[Input Box]**
**[Submit Question Button]**
### Explanation:
The table provides data on pedestrian deaths due to automobile accidents, classified by whether the driver and pedestrian were intoxicated. The possible outcomes are divided into four categories:
1. Both driver and pedestrian intoxicated: 64 cases
2. Intoxicated driver and non-intoxicated pedestrian: 73 cases
3. Non-intoxicated driver and intoxicated pedestrian: 249 cases
4. Neither driver nor pedestrian intoxicated: 591 cases
To calculate the required probability, you need to use the number of deaths involving non-intoxicated drivers.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fce002935-0cb2-4ae4-99f4-aff8adef33c2%2F81870ca9-a836-4149-9d57-1ff6e00ce86c%2F5j0w6qe_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Obtain the probability that they both involved drivers that were not intoxicated.
The probability that they both involved drivers that were not intoxicated is obtained below as follows:
From the information, given that
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









