The prior probabilities for events Aj and Az are P(A1) = 0.40 and P(A2) = 0.60. It is also known that P(A, n A2) = 0. Suppose P(B|A,) =0.20 and P(B|A2) = 0.05. a. Are events A1 and A2 mutually exclusive? No Explain. (i) P(A1 N A2) = 0 (ii) P(A1) + P(A2) = 1 (iii) P(A2) + P (A2 | A1) (iv) P(A2) + P(A2 | A1) Select your answer Compute P(A1B) (to 2 decimals). Compute P(A2N B) (to 2 decimals). c. Compute P(B) (to 2 decimals).
The prior probabilities for events Aj and Az are P(A1) = 0.40 and P(A2) = 0.60. It is also known that P(A, n A2) = 0. Suppose P(B|A,) =0.20 and P(B|A2) = 0.05. a. Are events A1 and A2 mutually exclusive? No Explain. (i) P(A1 N A2) = 0 (ii) P(A1) + P(A2) = 1 (iii) P(A2) + P (A2 | A1) (iv) P(A2) + P(A2 | A1) Select your answer Compute P(A1B) (to 2 decimals). Compute P(A2N B) (to 2 decimals). c. Compute P(B) (to 2 decimals).
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN:9780134753119
Author:Sheldon Ross
Publisher:Sheldon Ross
Chapter1: Combinatorial Analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P: a. How many different 7-place license plates are possible if the first 2 places are for letters and...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:The prior probabilities for events A1 and Az are P(A1) = 0.40 and P(A2) = 0.60. It is also known that P(A, n A2) =0. Suppose P(B|A,) =0.20 and P(B|A2) = 0.05.
%3D
a. Are events A1 and A2 mutually exclusive?
No
Explain.
(i) P(A1 N A2) = 0
%3D
(ii) P(A1) + P(A2) = 1
(iii) P(A2) P (A2 | A1)
(iv) P(A2) = P(A2 | A1)
Select your answer - ▼
Compute P(A1NB) (to 2 decimals).
Compute P(A2N B) (to 2 decimals).
c. Compute P(B) (to 2 decimals).
Apply Bayes' theorem to compute P(A1|B) (to 4 decimals).
Also apply Bayes' theorem to compute P(A2 B) (to 4 decimals).
Expert Solution
Step 1
As per our guidelines, we are allowed to answer first three sub-parts only. Thanks
Mutually Exclusive events are those events which can not happen at the same time
For Ex : Tossing a coin will result in Head or Tail , If we get tail , we can not get head.

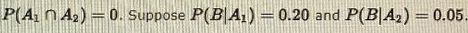
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 6 images

Recommended textbooks for you

A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:
9780134753119
Author:
Sheldon Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON


A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:
9780134753119
Author:
Sheldon Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON
