The next 9 questions are related to the titration of 20.00 mL of a 0.0750 M acetic acid solution with 0.0700 M KOH. How many mmol of the salt are present at the equivalence point? (ANALYTICAL AMOUNT, NOT EQUILIBRIUM AMOUNT)
The next 9 questions are related to the titration of 20.00 mL of a 0.0750 M acetic acid solution with 0.0700 M KOH.
How many mmol of the salt are present at the equivalence point? (ANALYTICAL AMOUNT, NOT EQUILIBRIUM AMOUNT)
When an acid and a base reacts, they undergo neutralisation reaction to form salt and water. In the given problem, acetic acid reacts with potassium hydroxide. The reaction proceeds as:
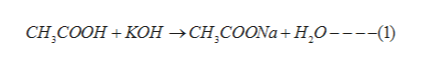
Number of millimoles of a species = Volume of solution (mL) × Molarity of solution ( moles/L)
Thus, millimoles of the acid and base may be determined as;

At the equivalence point, the millimoles of acid and base are equal and thus neutralise each other completely. Thus, the volume of base solution (V) may be determined as;
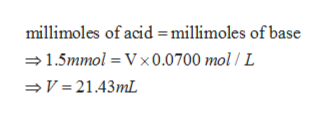
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 3 images









